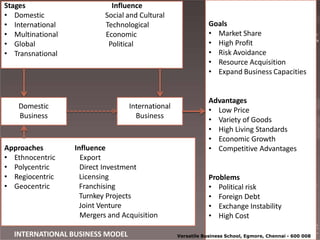
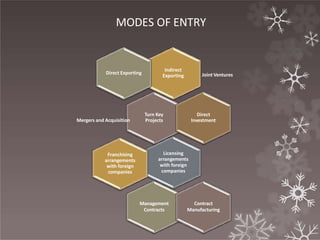
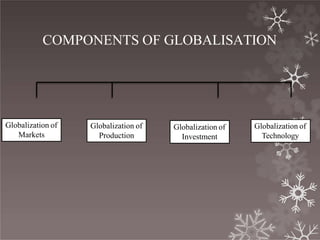
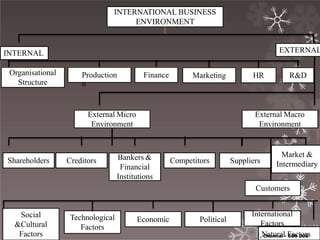
This document provides an overview of international business and globalization. It discusses the evolution of international business from the first phase of globalization in 1870 through the development of organizations like the IMF and IBRD. It also outlines the characteristics of international business including regional integration, declining trade barriers, and the growth of multinational corporations. Additionally, the document examines the components of globalization including the globalization of markets, production, investment, and technology.