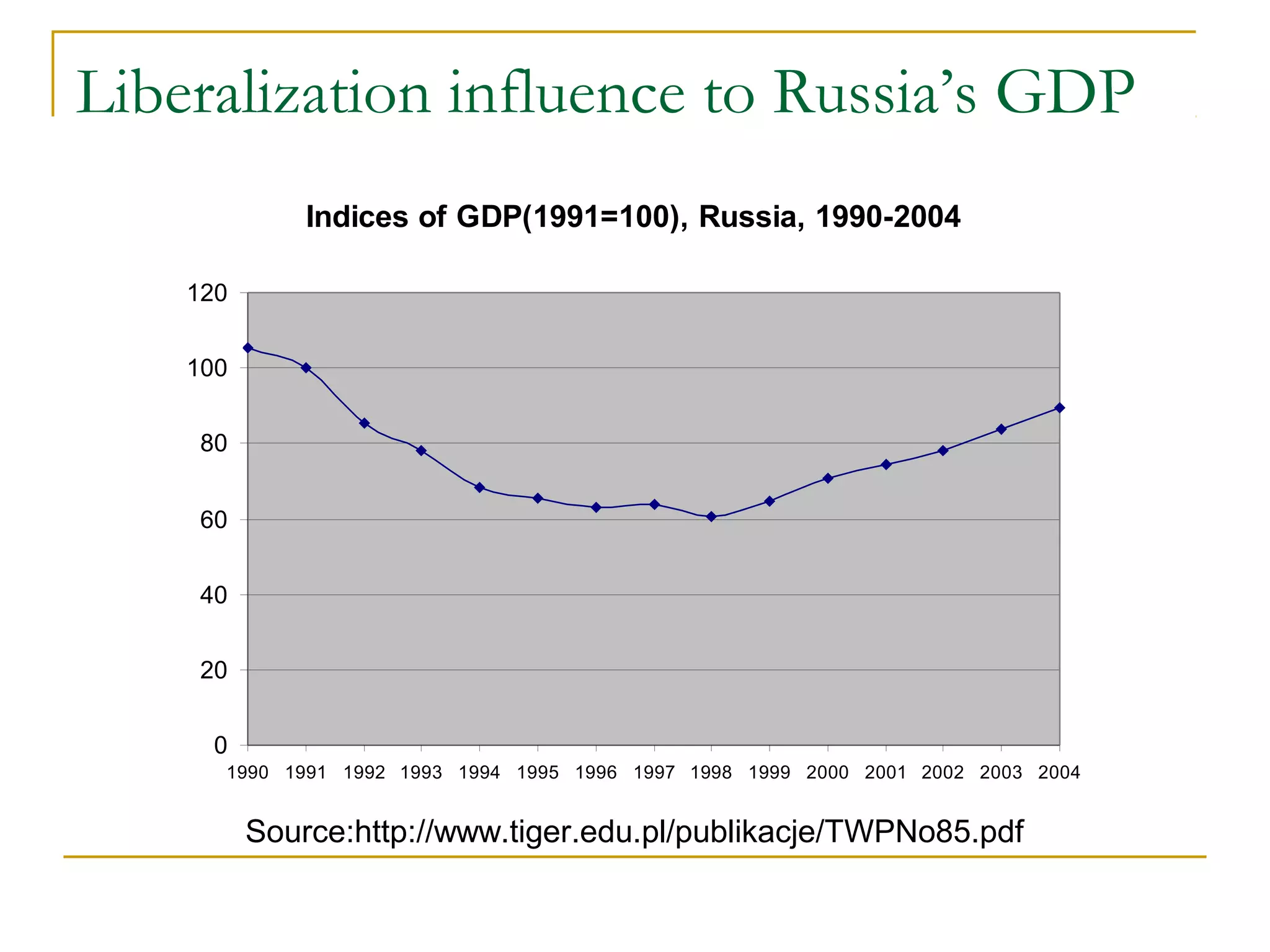
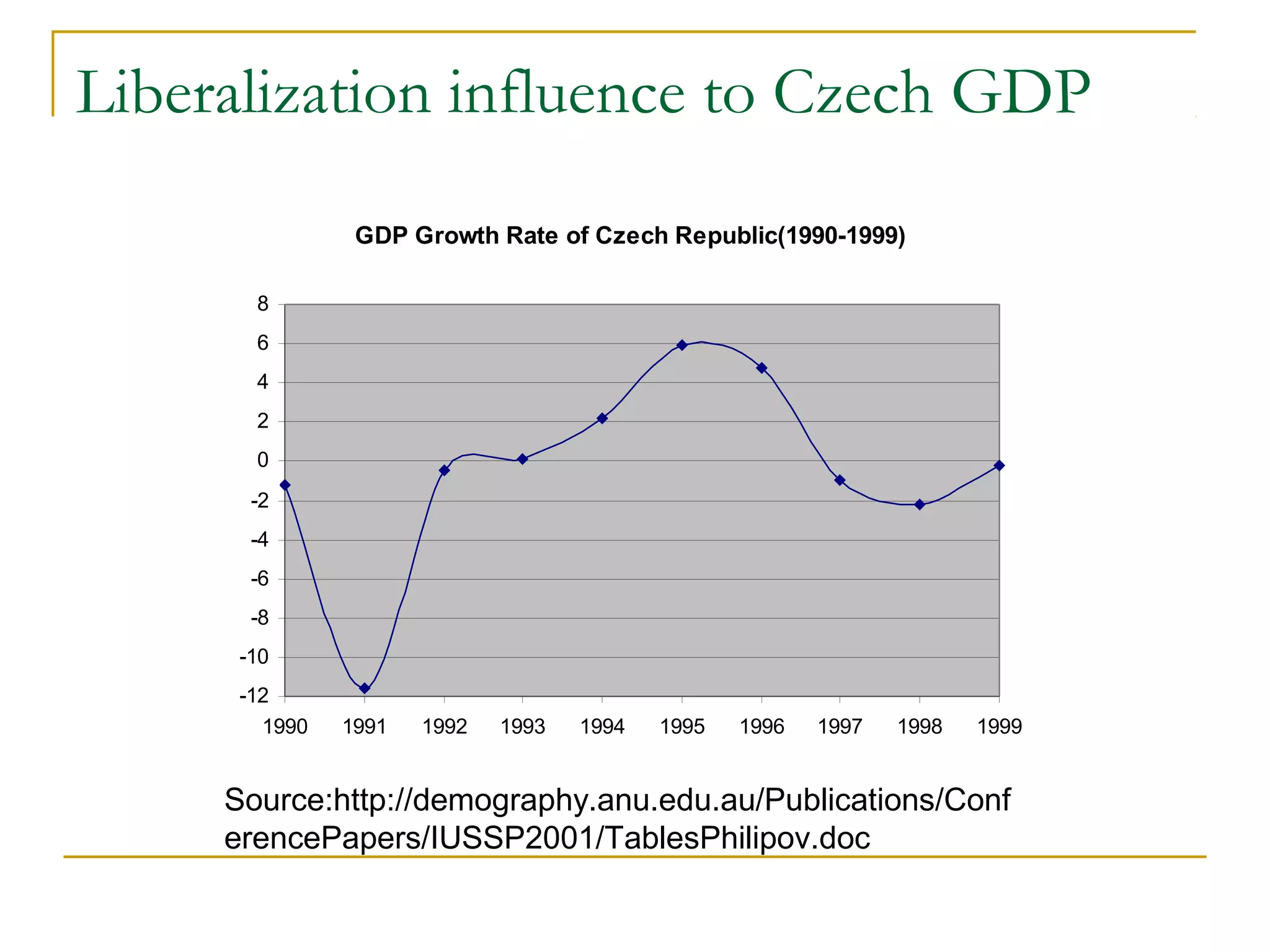
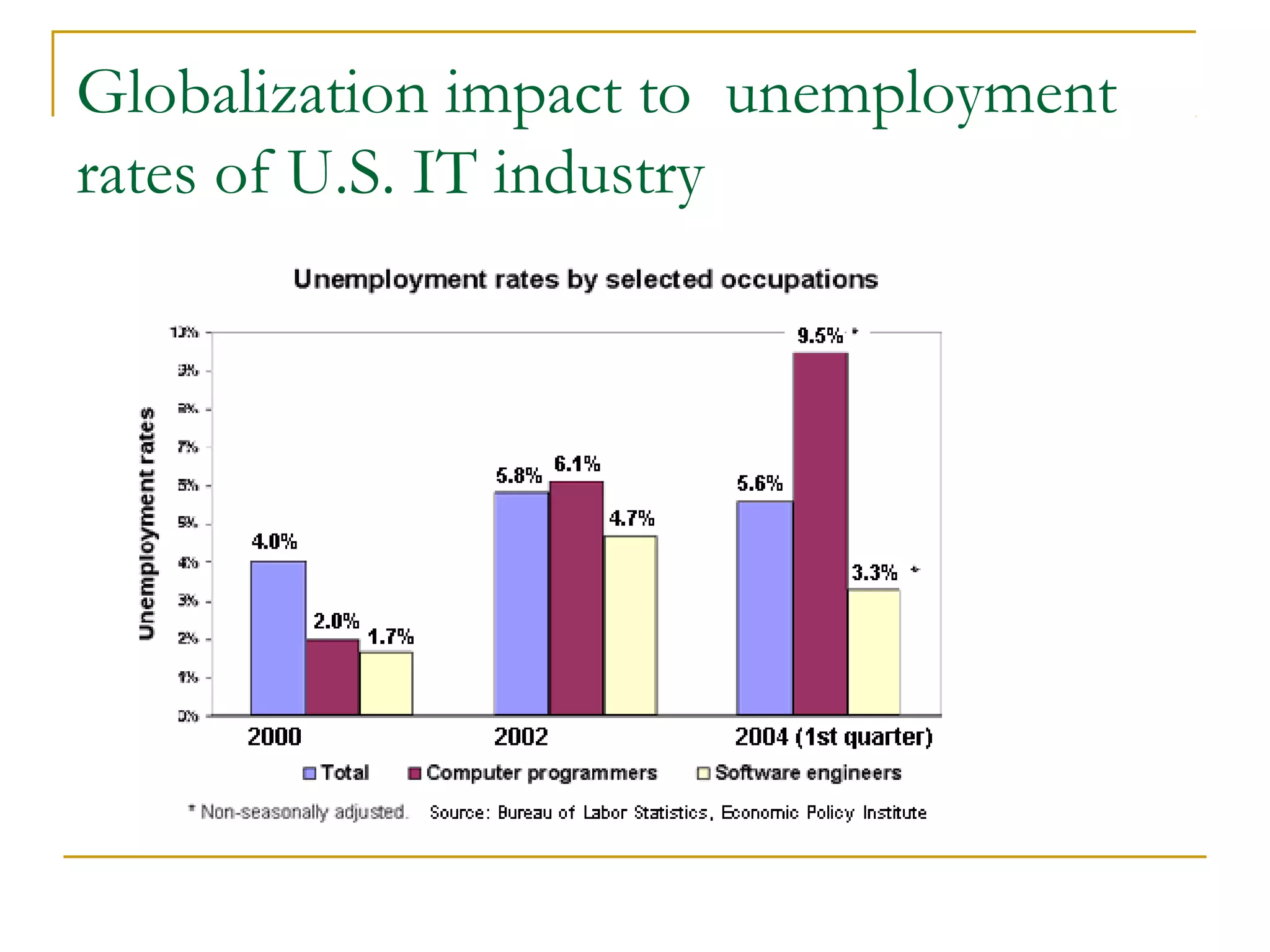
The document discusses globalization, detailing its definitions, influences, advantages, and disadvantages, alongside the emergence of anti-globalization movements as a resistance to globalization's negative impacts. It highlights the economic, social, and environmental repercussions of globalization while presenting examples, such as job losses and cultural homogenization. The document concludes with calls for reforms in global institutions to address inequities and ensure a more balanced approach to globalization.