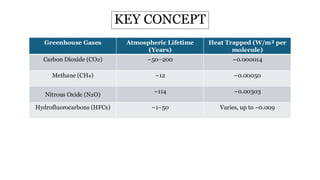
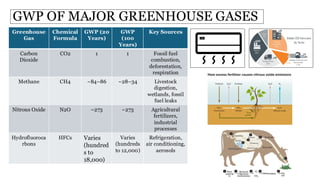
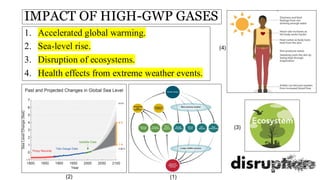
Global Warming Potential (GWP) measures a greenhouse gas's ability to trap heat in the atmosphere over a specific time period, usually 100 years. It compares the warming impact of different gases to carbon dioxide (CO2), which is set as the baseline with a GWP of 1. Gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) have higher GWPs, indicating a stronger warming effect. GWP helps assess the climate impact of various gases and inform strategies to reduce emissions.