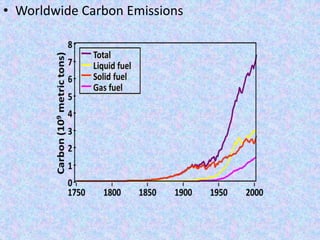
This report summarizes the key causes and effects of global warming. It discusses how global warming was first theorized in 1896 and is caused by both natural phenomena like volcanic eruptions as well as human activities like burning fossil fuels. Main greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming are identified as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons. The report also summarizes evidence of global warming through increases in global temperatures, sea levels, and greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. Potential effects of global warming mentioned include species extinction, water shortages, and increased disease transmission. International efforts to address climate change are also briefly outlined.