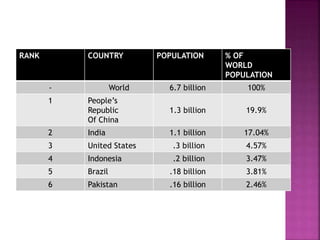
Globalization has increased workforce diversity and cultural sensitivities for organizations globally, leading to the development of global human resource management. HR must now consider the effects of diversity, legal restrictions, and training across cultures on the organization. The five main functions of global HR management are vital to a business's strategic operations. One function is creating local appeal while maintaining a global identity through cultural awareness training and cross-border hiring.