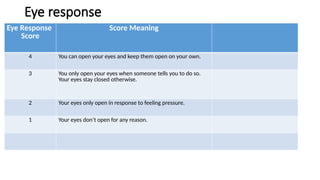
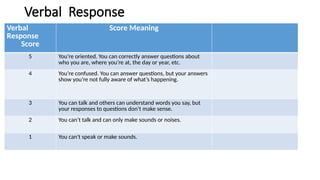
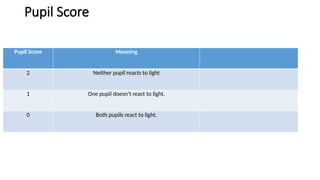
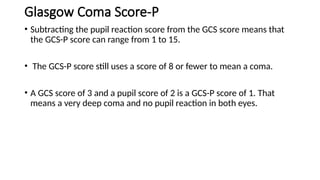
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), developed in 1974 at the University of Glasgow, is a clinical tool for assessing consciousness in brain injury patients based on eye, verbal, and motor responses. It has a scoring system ranging from 3 (unresponsive) to 15 (fully conscious), with lower scores indicating deeper comas and potential need for intubation. An updated version called GCS-P includes an additional pupil reaction score to provide further insight into brain function.