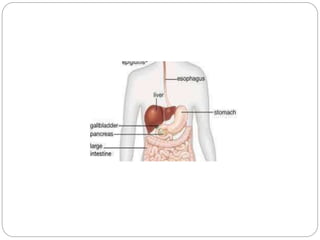
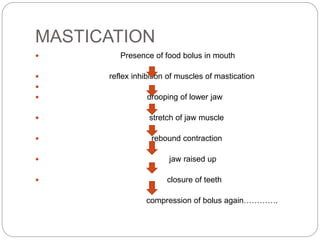
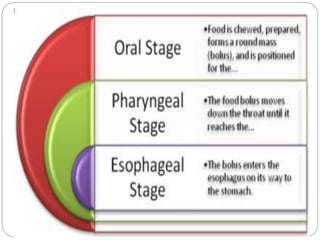
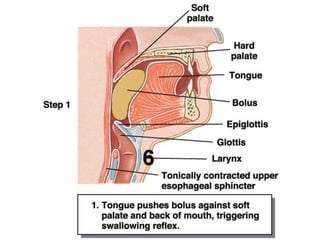
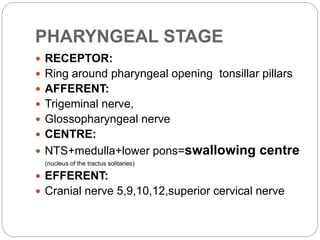
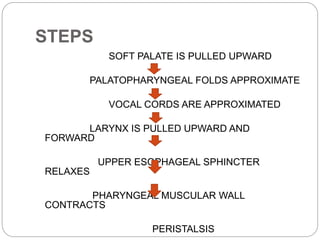
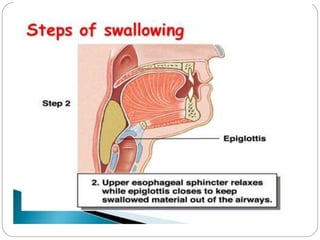
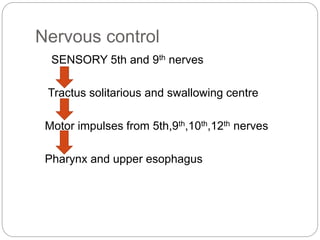
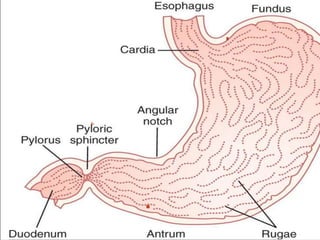
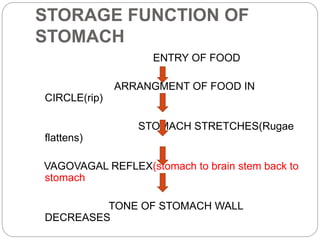
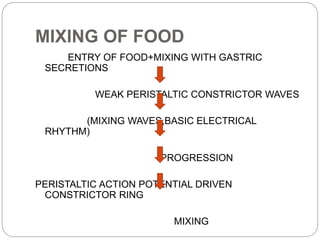
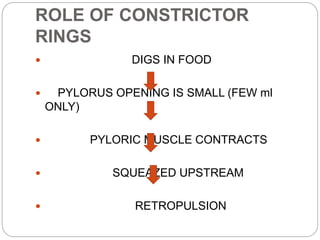
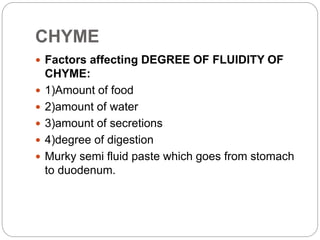
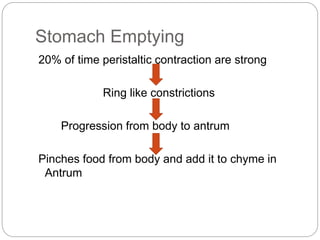
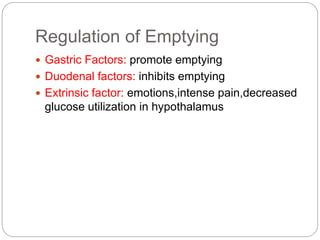
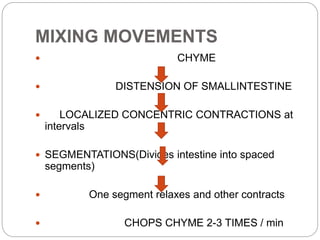
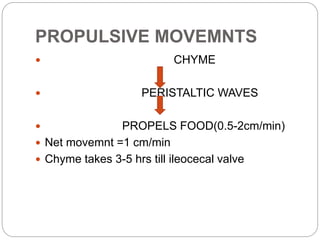
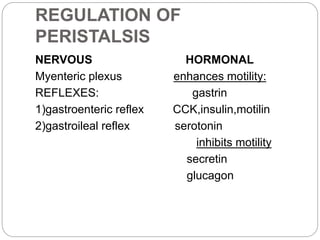
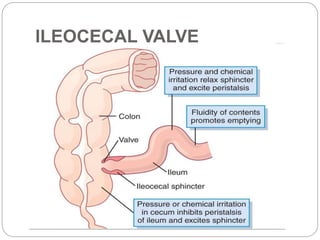
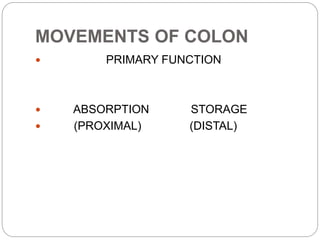
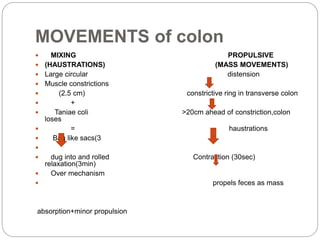
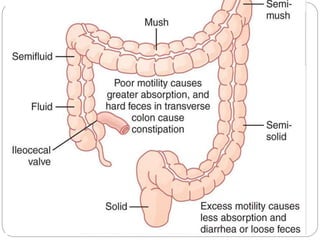
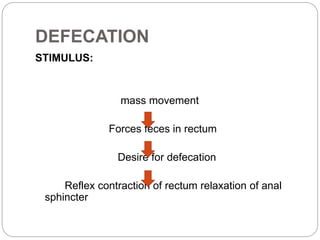
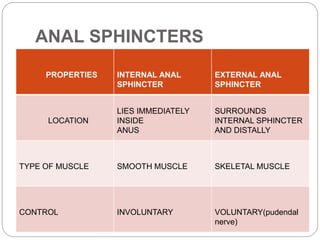
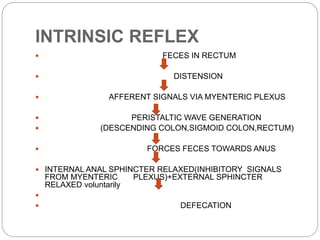
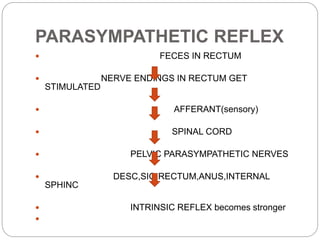
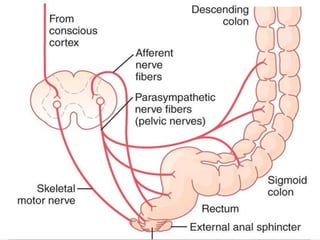
This document describes the structure and function of the gastrointestinal tract. It discusses digestion beginning in the mouth through the stages of swallowing. It describes the movements and regulation of the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine that propel and mix food contents. Key functions and control mechanisms of various structures like the lower esophageal sphincter, ileocecal valve, and anal sphincters are summarized. The reflex pathways involved in defecation are also outlined.