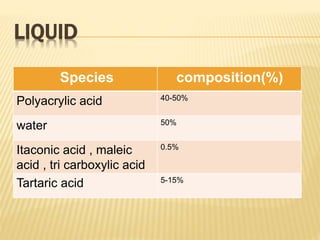
Glass ionomer cement is a tooth-colored dental restorative material that chemically binds to tooth structure. It was invented in 1969 and is based on the reaction between silicate glass powder and polyacrylic acid. Glass ionomer cement has several advantages, such as adhesion to tooth structure, fluoride release, and biocompatibility. However, its disadvantages include low fracture resistance and wear resistance compared to other materials. It is commonly used for restorations, linings, luting, and for its anticariogenic properties with fluoride release.