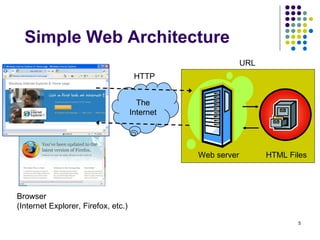
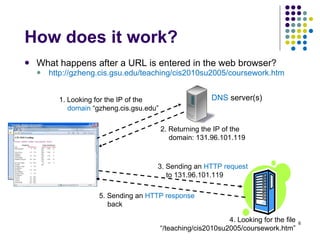
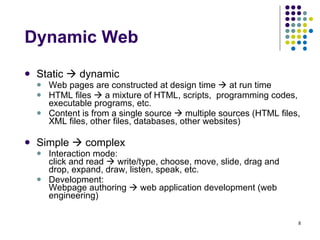
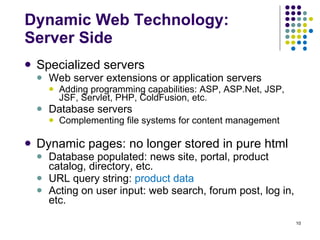
The document provides an overview of the evolution of the web and web applications from early static webpages in the 1990s to today's dynamic web platforms. It discusses the transition from simple document-based websites to complex, database-driven applications and the key technologies that enabled richer user experiences and more integrated systems, including client-side scripting, server-side programming, XML, web services, and AJAX. The rise of Web 2.0 is also summarized, focusing on user-generated content, folksonomies, and new interaction models.