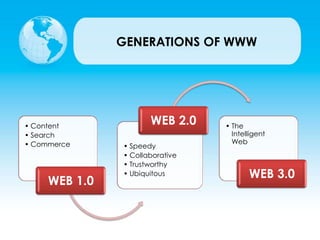
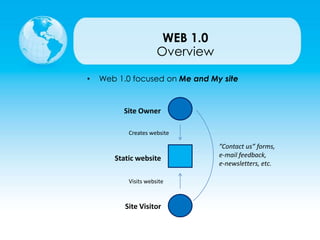
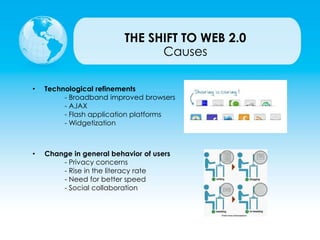
This document provides an overview of web technologies and the evolution of the World Wide Web. It discusses Web 1.0, the first generation focused on static websites, and Web 2.0, the second generation focused on user-generated content and social media. Web 2.0 utilized new technologies like AJAX and introduced characteristics like user participation, tagging, and dynamic content. It also highlights some popular content management systems, web browsers, and software development kits that supported the shift to Web 2.0. Finally, it briefly introduces the concept of Web 3.0 and the Semantic Web.