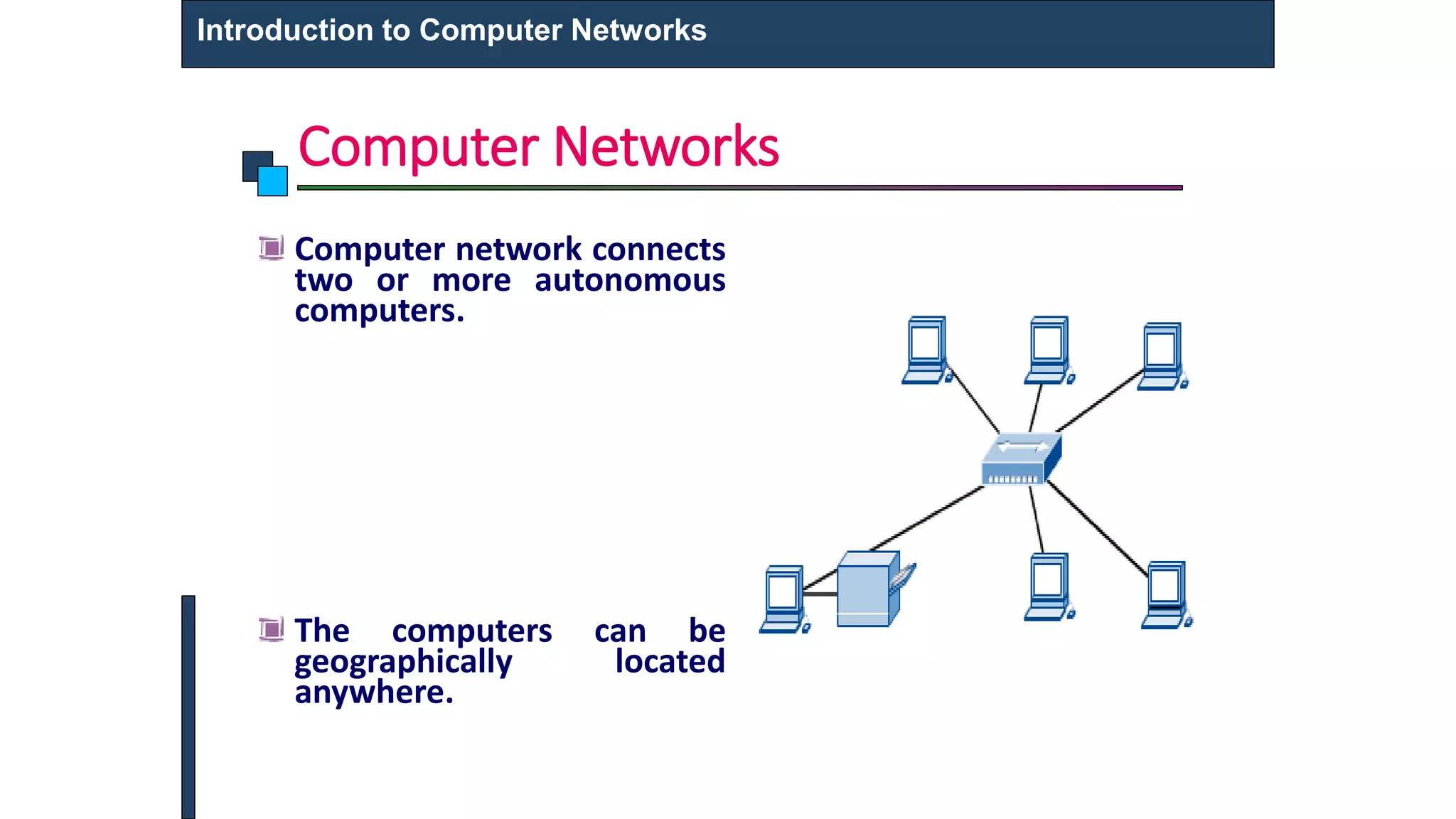
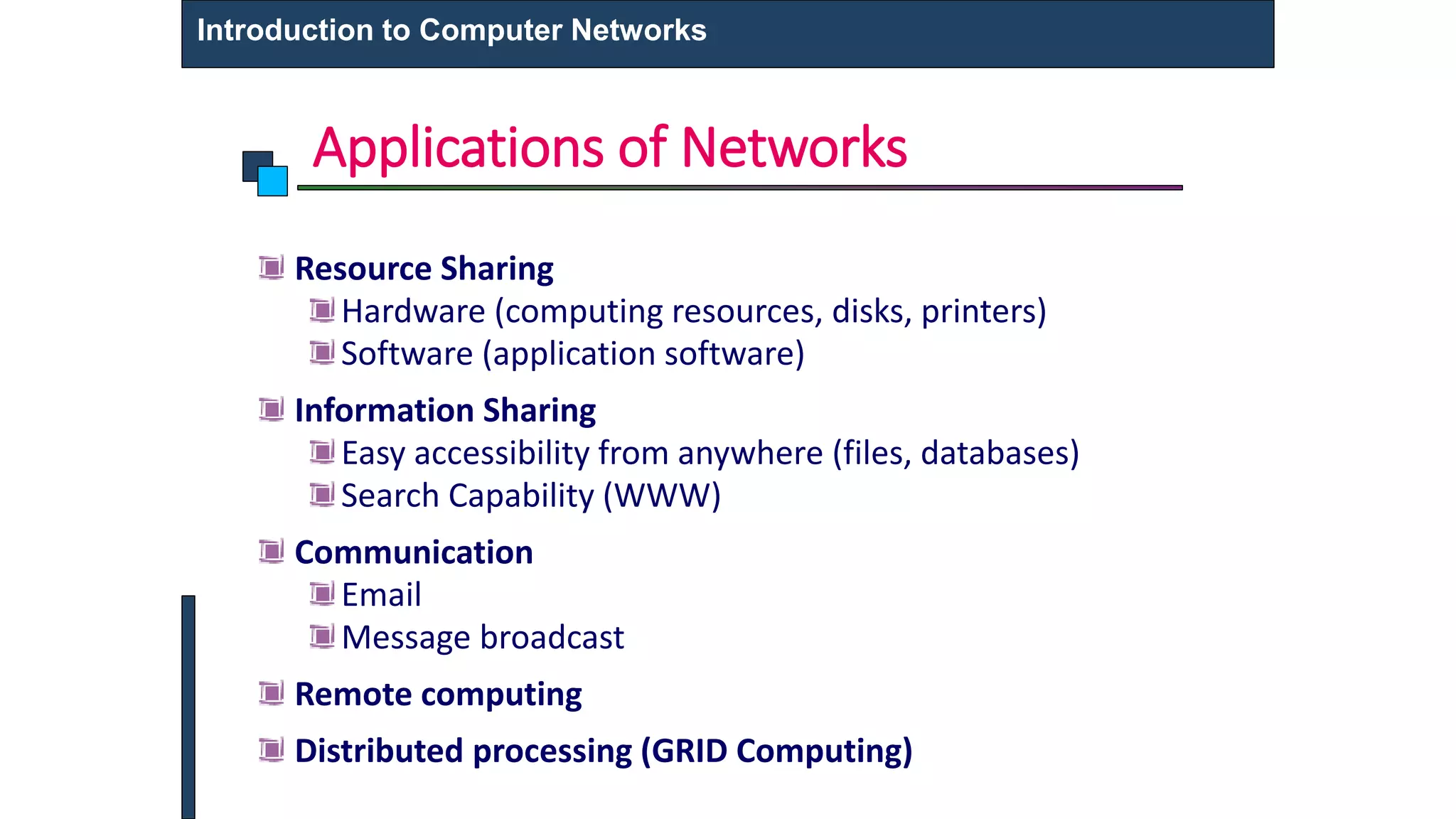
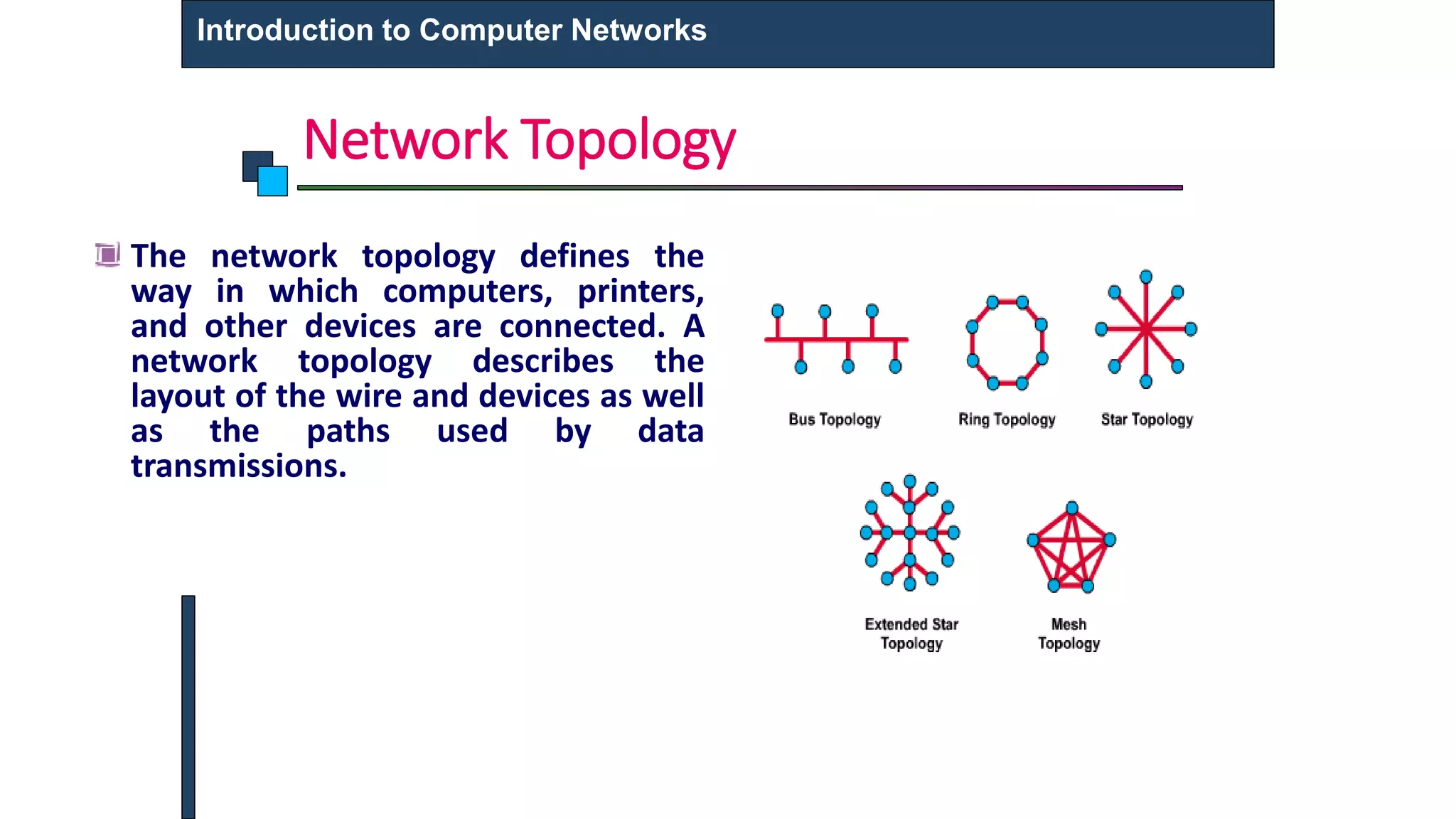
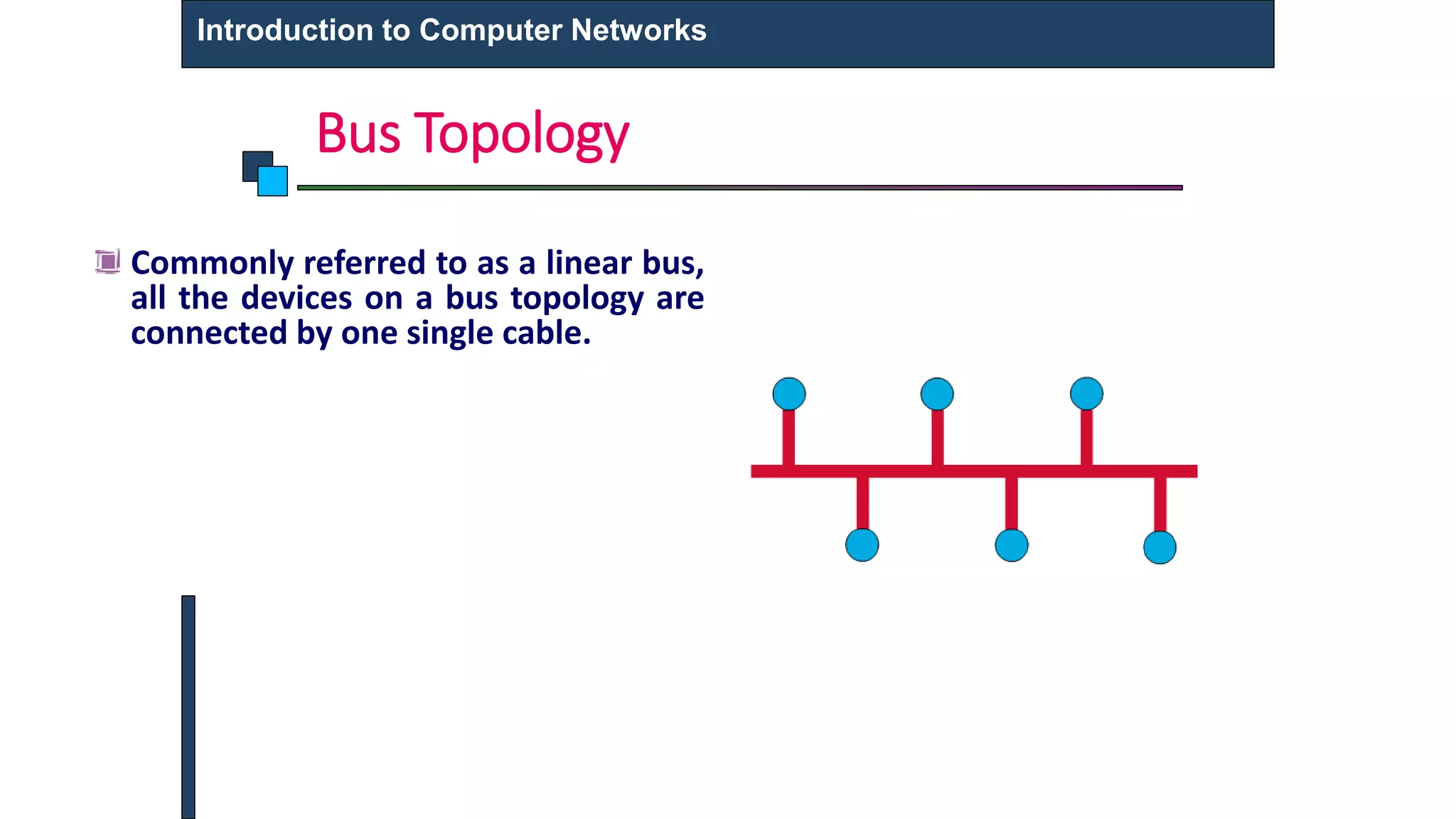
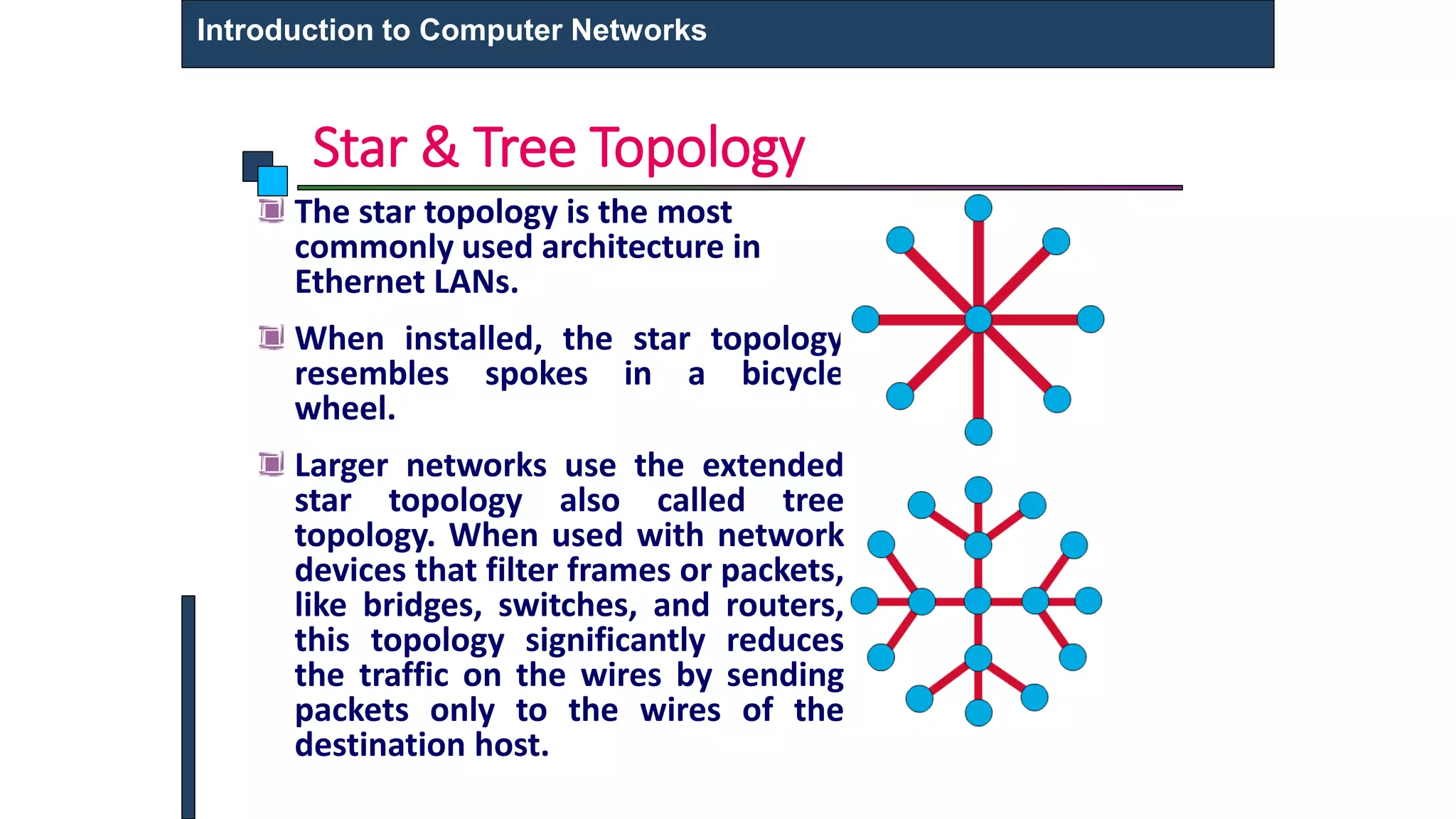
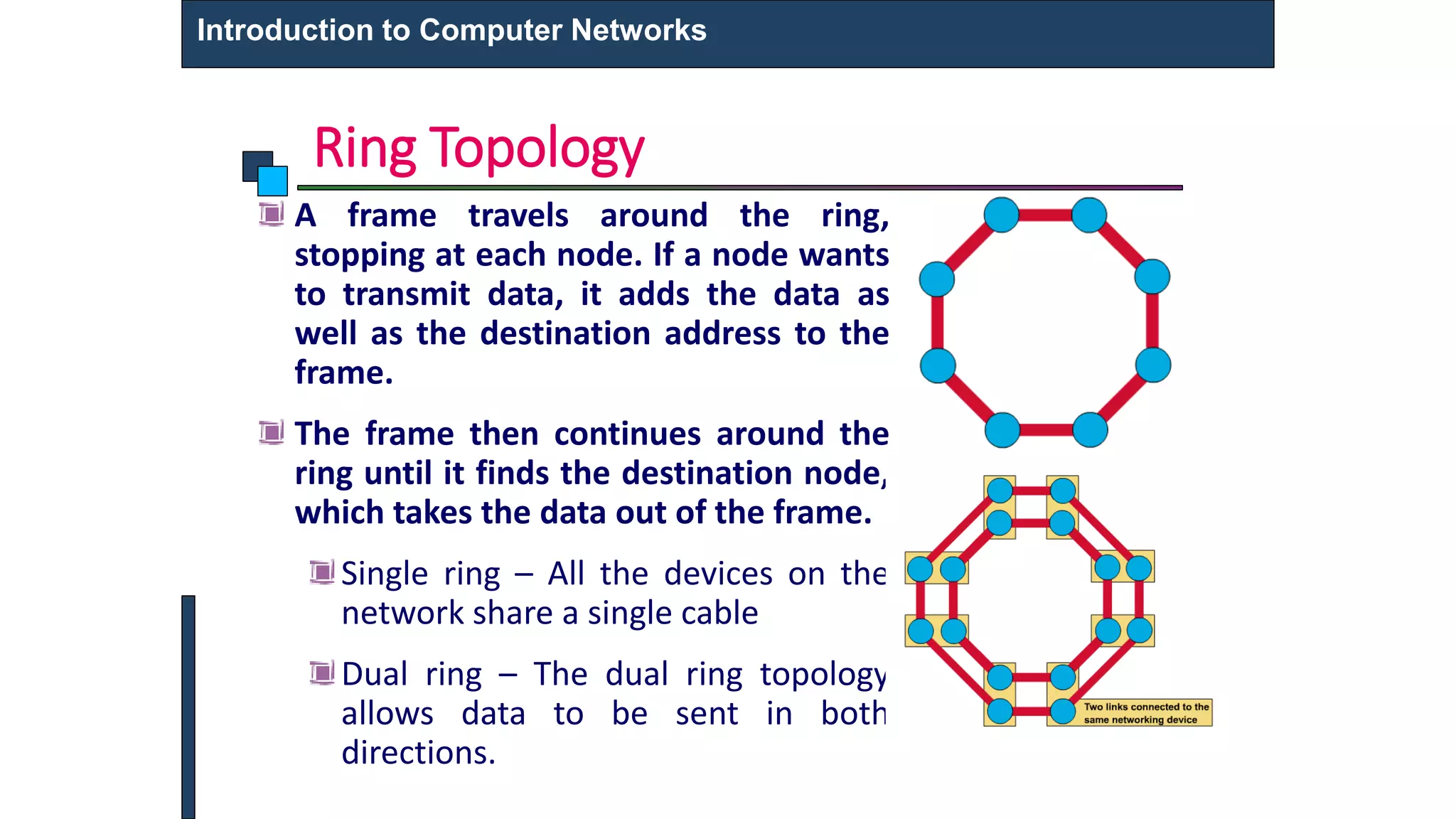
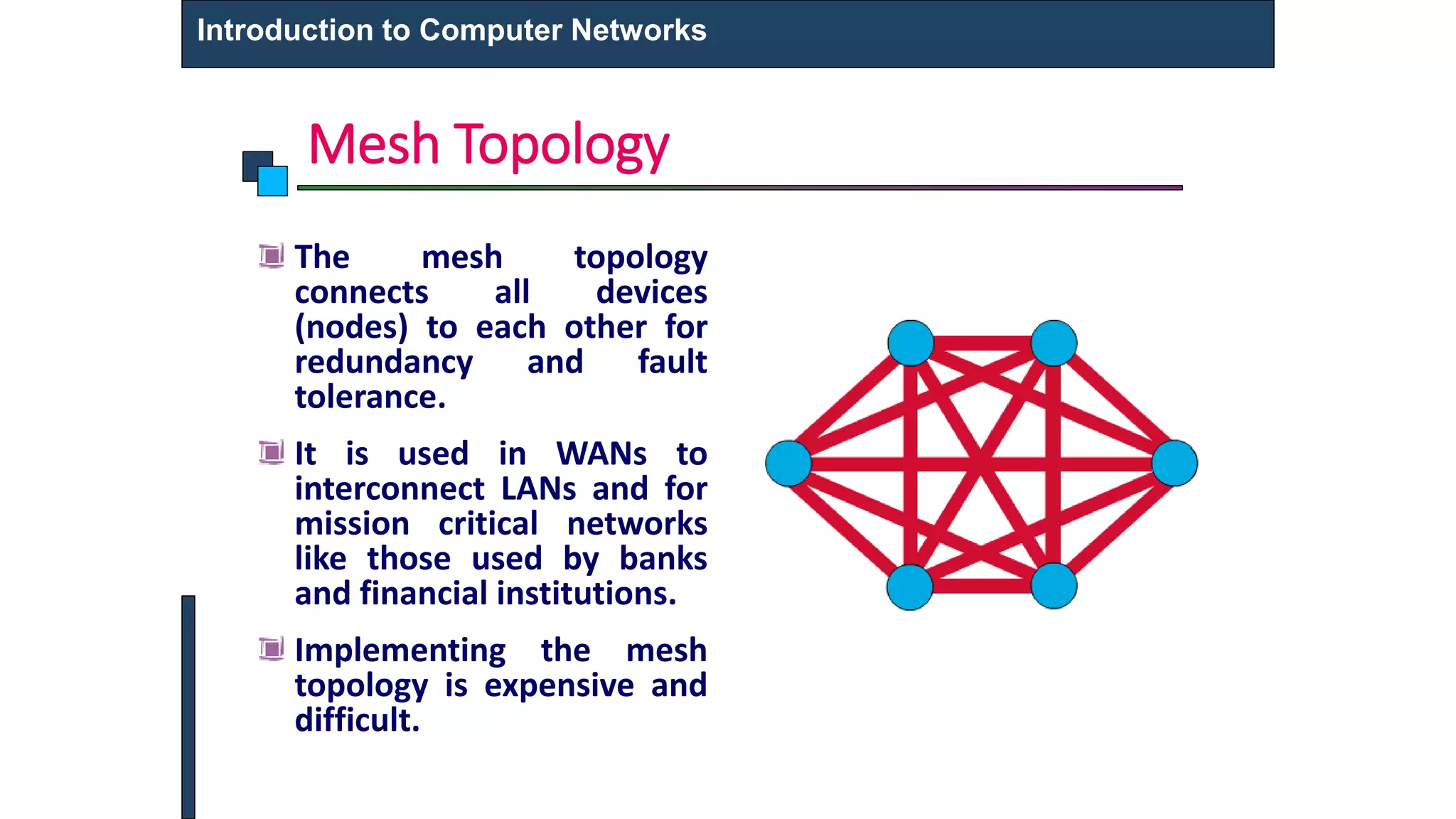
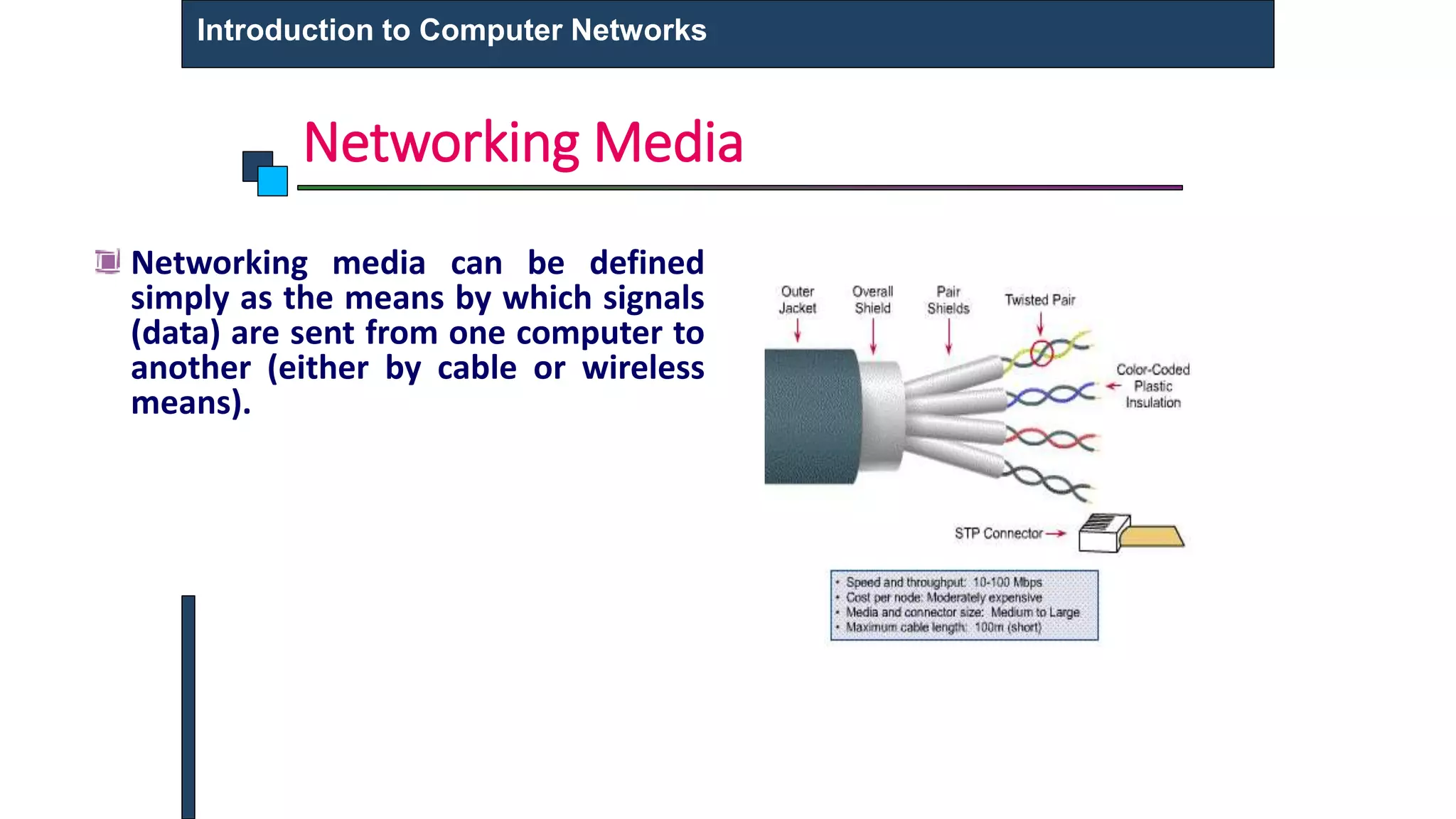
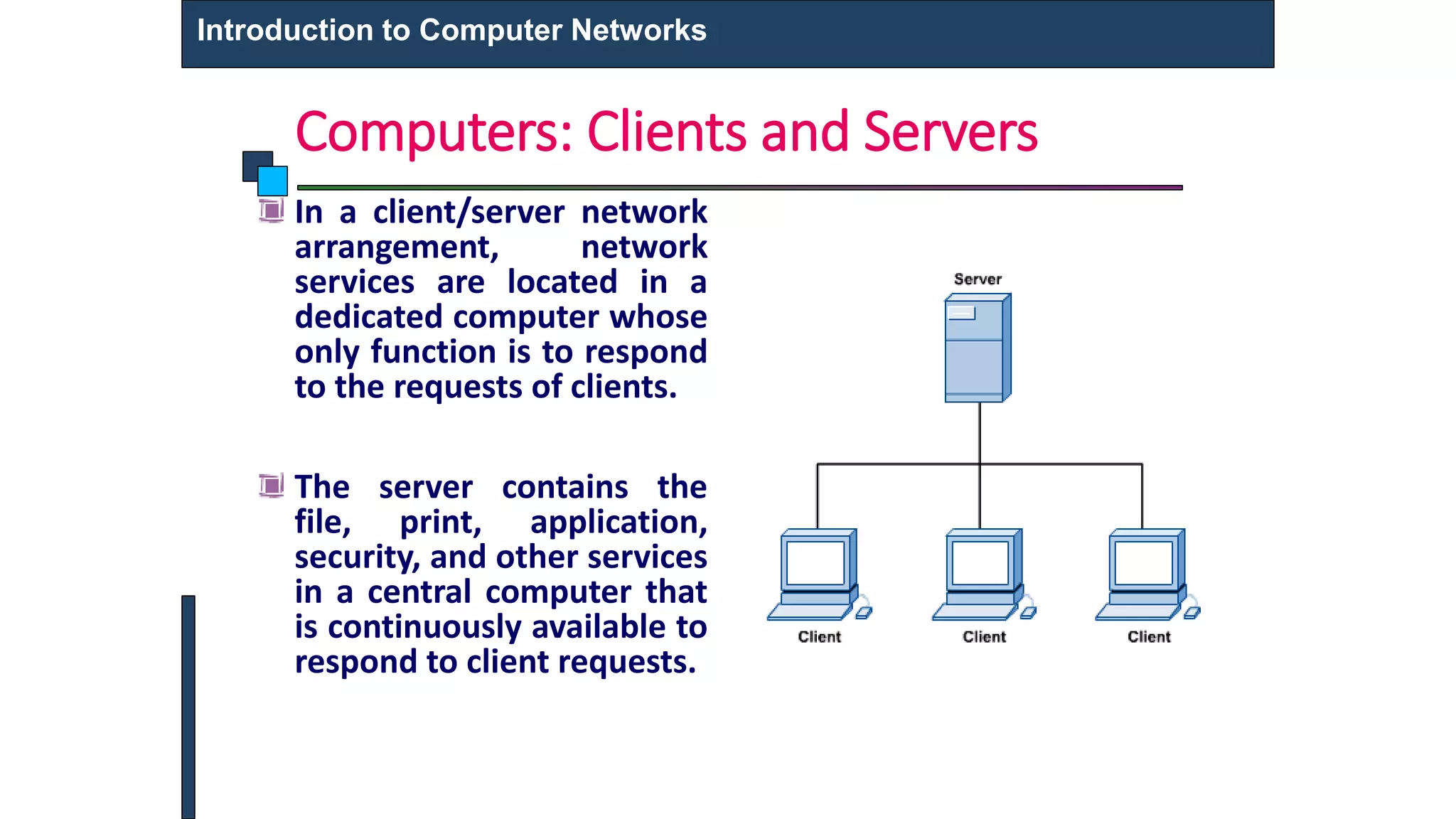
This document provides an introduction to computer networks. It defines what a computer network is and describes different types of networks including LAN, MAN, and WAN. It discusses applications of networks such as resource sharing, information sharing, and communication. It also outlines different network topologies including bus, star, ring, and mesh. Finally, it discusses key network components like physical media, networking devices, computers that can serve as clients or servers, and common network applications.