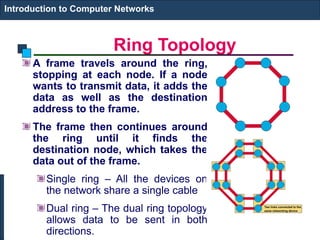
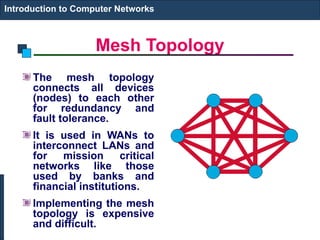
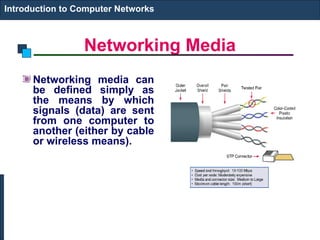
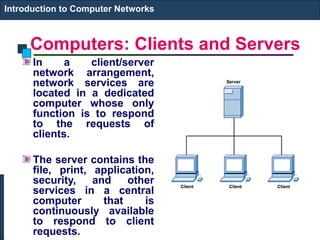
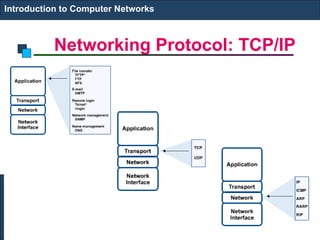
The document covers an introduction to computer networks, detailing various topologies such as ring and mesh. It explains components, networking media, devices, client/server arrangements, and protocols like TCP/IP. Additionally, it highlights network applications including e-mail, e-commerce, and internet telephony.