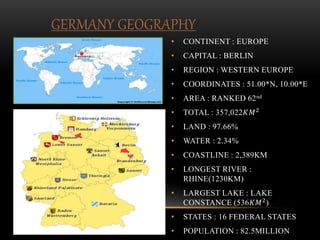
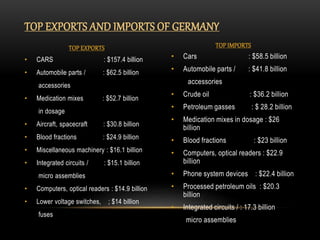
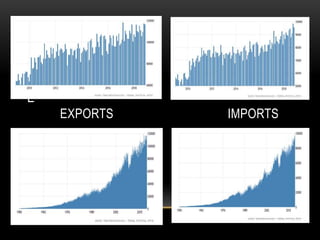
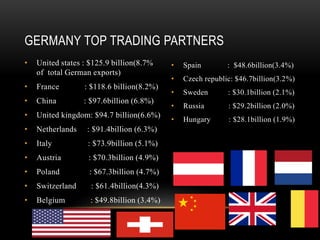
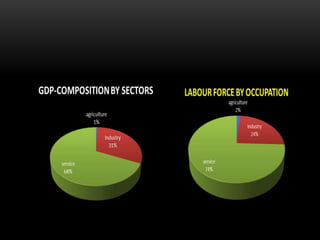
This document provides information about Germany in 3 main sections. It begins with geographical and demographic information, noting that Germany is located in Central Europe, has a population of over 82 million, and borders 9 countries. It then discusses Germany's economy, highlighting its strong manufacturing industry, top exports of cars and machinery, and important trading partners like the US and France. Finally, it covers aspects of German culture, such as its focus on rules and hierarchy, importance of punctuality, and conservative dress code.