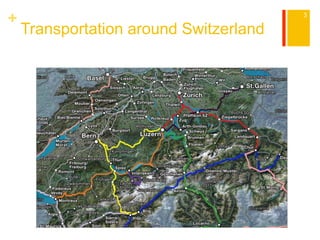
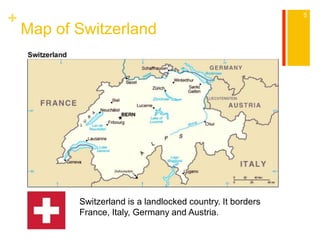
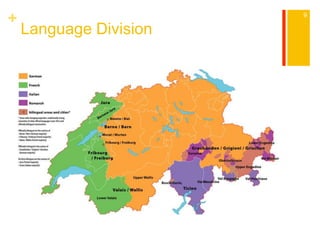
This document provides information about Switzerland, including its geography, history, culture, cities, and tourist attractions. It begins with details about traveling to Switzerland from Canada and transportation within the country. The rest of the document covers Switzerland's population, climate, terrain, languages spoken, religions practiced, cuisine, etiquette, music, major cities, and popular attractions in places like Geneva, Bern, Zurich, St. Moritz, Lugano, Lucerne, Interlaken, and Zermatt. In conclusion, it lists some travel restrictions and requirements for visiting Switzerland.