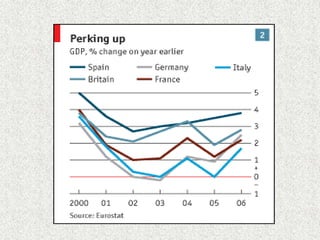
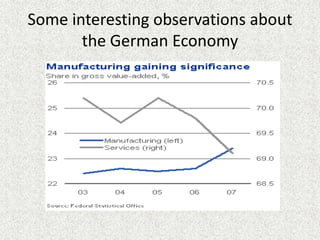
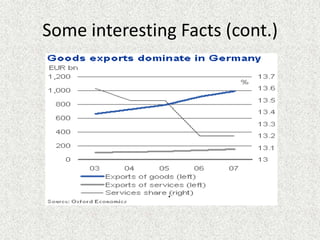
Germany is officially the Federal Republic of Germany, located in Western and Central Europe. It has a population of over 81 million people and its capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany has the largest economy in the European Union, with the world's 4th largest economy by GDP. It has a social market economy with a highly skilled workforce and is a leading exporter, particularly of automobiles, machinery, and chemicals. The service sector contributes over 70% of GDP, with financial, trade, and other services being largest subsectors.