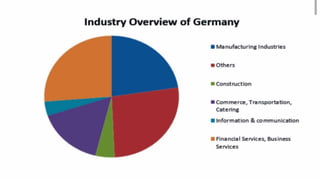
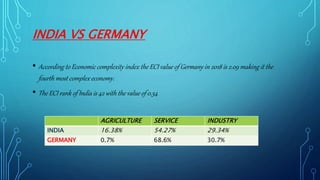
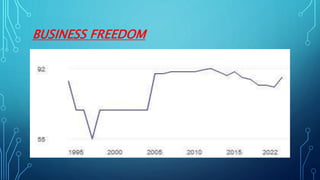
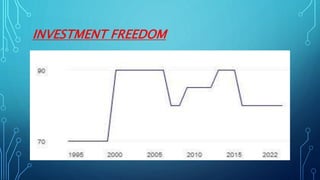
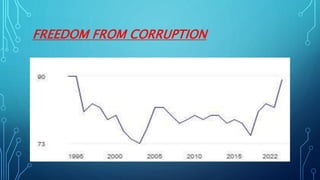
Germany has the largest economy in Europe based on GDP. It transformed from a largely rural economy in the 1800s to a modern industrial powerhouse by 1900, led by heavy industries. Today, Germany excels in automobiles, machinery, chemicals and electrical equipment and has a highly skilled labor force and focus on innovation. While Germany faces challenges like an aging population and dependence on exports, it has a strong economy based on principles of social market economy, investment in infrastructure and education, and a culture of transparency and low corruption.