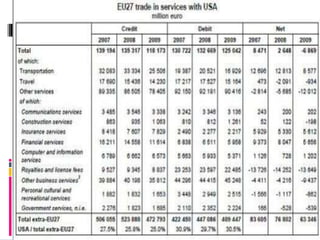
The document discusses EU-US trade and its significance. It played an important role in bringing former enemies like the US, Germany, and France together and helped build up Western Europe economically against the Soviet bloc. Together, the EU and US economies make up 40% of the world GDP. The document outlines the framework of EU-US trade including organizations like NATO, WTO, and OECD that are involved. It provides statistics on trade volumes and discusses the future Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership aimed at reducing trade barriers between the EU and US.