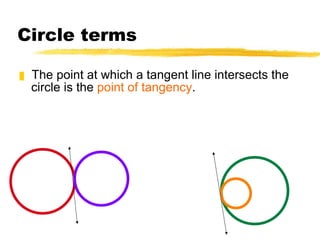
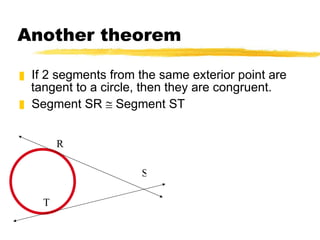
The document discusses key terms and theorems related to circles, including:
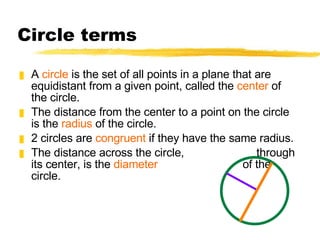
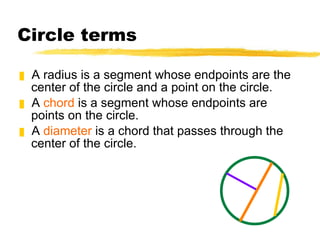
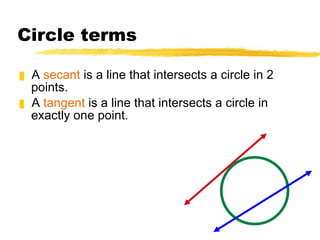
- Definitions of circles, radii, diameters, chords, secants, tangents
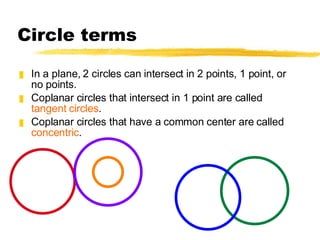
- Types of circle intersections and relationships (concentric, tangent)
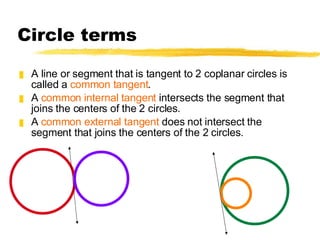
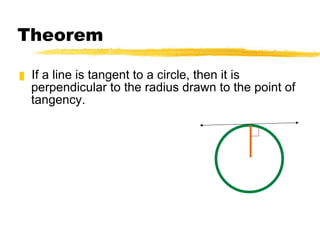
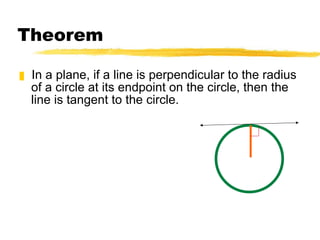
- Theorems about tangents being perpendicular to radii and lines perpendicular to radii being tangents
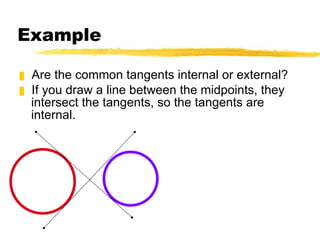
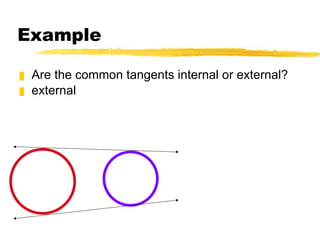
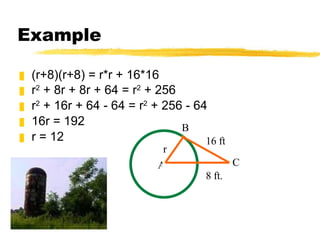
- Using properties of tangents, radii, and perpendicular lines to solve problems about circles
- The Pythagorean theorem can be used with right triangles formed with radii and tangent segments