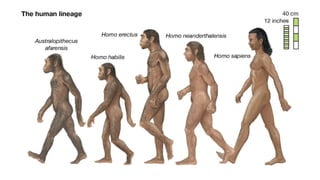
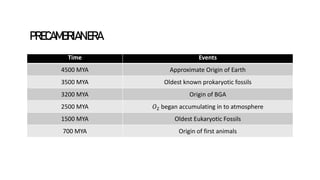
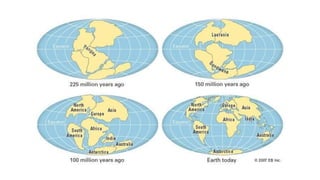
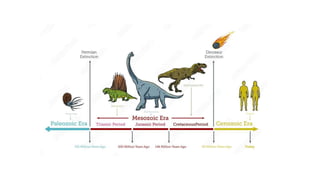
The geological timescale divides Earth's history into periods defined by major geological or biological events. It represents over 4.6 billion years and is divided into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. The earliest eon was the Precambrian, which saw the formation of oceans, atmosphere and early life like bacteria. The Paleozoic era saw an explosion of marine life including trilobites, fish, and amphibians. During the Mesozoic, reptiles like dinosaurs became dominant and the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event wiped out the dinosaurs. The current Cenozoic era is the age of mammals, and saw the evolution of early primates and eventually humans in the Quatern








![PALEOZOICERA
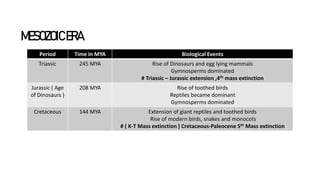
Period Time in MYA Biological Events
Cambrian 544 MYA
All the invertebrate phylums, Origin of first simple marine
invertebrate, Scanty Fossils
Origin of diverse algae
Origin of first animals
Ordovician 505 MYA
All vertebrate phyla established : Trilobites abundant. First origin of
jawless vertebrates ( Ostracoderm fishes ) . Marine algae abundant
* Origin of freshwater life from sea
Silurian 438 MYA
Diversity of jawless vertebrates . Origin of Vascular plants
# Ordovician-Silurian extinction;1st mass extinction due to cooling
sea level drop
Devonian
[Age of
Amphibians]
408 MYA
First origin of amphibians; Fishes flourished all over the world .
Origin of jawed fishes and winged insects
Carboniferous 360 MYA
Amphibians flourished, 1st origin of reptiles & seed plants :
Formation of coal deposits
# Late Devonian Extension, 2nd mass extinction
Permian 285 MYA
Rise of modern insects and radiation of repltiles
# Permian – Triassic extinction ; 3rd mass extinction
SlideSkimmers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geologicaltimescale-copy-230326062628-e5d0a05d/85/Geological-Time-Scale-11-320.jpg)







![Period Epoch Time in
MYA
Biological Events
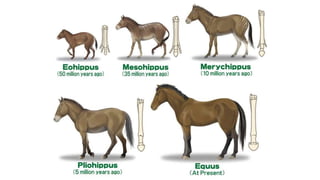
Tertiary Paleocene 65 MYA Origin of primitive primates
Eocene 57 MYA Diversification of Placental Mammals
*Horse originated called as Eohippus
Oligocene 34 MYA Rise of first monkeys and Apes [ Anthropoids ]
Mesohippus
Miocene 23 MYA Mammals at peak , First man like apes formed
Merychippus
Pliocene
Epoch of mammals
5 MYA 1st Hominidae appeared i.e. emergence of man
Formation of modern mammals , Pliohippus originated
Quaternary Pleistocene 1.8 MYA Extinction of great mammals
Human civilization
Modern horse i.e Equss appeared
Holocene
Age of Man
0.01 MYA Modern man, mammals, birds, fishes, insects dominant
Man flourished all over the world
#6th Mass extionction is on due to human activity
ERAOFMODERNLIFE
SlideSkimmers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geologicaltimescale-copy-230326062628-e5d0a05d/85/Geological-Time-Scale-23-320.jpg)