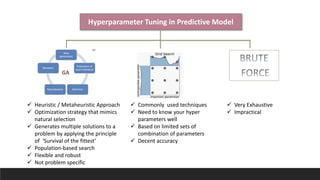
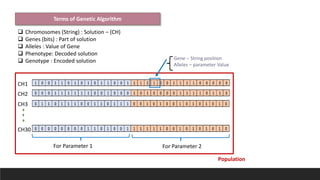
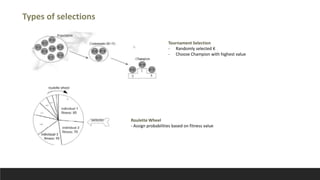
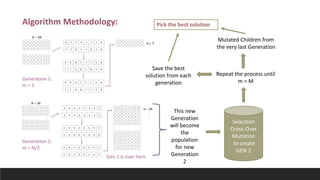
This document discusses using genetic algorithms to tune hyperparameters in predictive models. It begins by providing an overview of genetic algorithms, describing them as a heuristic approach that mimics natural selection to generate multiple solutions. It then defines key terms related to genetic algorithms and chromosomes. The document outlines the genetic algorithm methodology and provides pseudocode. It applies this approach to tune hyperparameters C and gamma in an SVM model and finds it achieves higher accuracy than grid search in less computation time. In an appendix, it references related work and describes a spam email dataset used to classify emails as spam or not spam.






![Application : Determine whether a given email is spam or not.
Relevant Information: Our collection of spam e-mails came from our postmaster and individuals who had filed spam.
Number of Instances: 4601 (1813 Spam = 39.4%)
Number of Attributes : 58 (57 continuous, 1 nominal class label)
Attribute Information :
1 nominal {0,1} class attribute : Denotes whether the e-mail was considered spam (1) or not (0)
48 continuous attributes : Percentage of words in the e-mail that match WORD
6 continuous attributes : Percentage of characters in the e-mail that match CHAR
1 continuous real [1,...] attribute : Average length of uninterrupted sequences of capital letters
1 continuous integer [1,...] attribute : Length of longest uninterrupted sequence of capital letters
1 continuous integer [1,...] attribute: Total number of capital letters in the e-mail
Missing Attribute Values: None
Class Distribution:
Spam 1813 (39.4%)
Non-Spam 2788 (60.6%)
Source:
This data at the UCI Machine Learning Repository:
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/spambase/
Spam email dataset description-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticalgorithmforhyperparametertuning-191026220328/85/Genetic-algorithm-for-hyperparameter-tuning-12-320.jpg)

