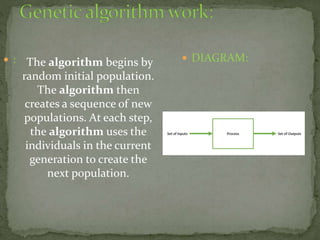
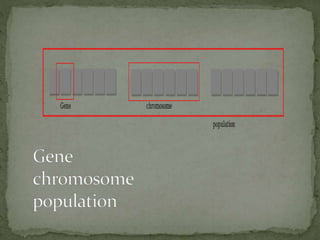
Genetic algorithms are a type of optimization technique inspired by natural selection and genetics. They are commonly used to find optimal or near-optimal solutions to complex problems by generating populations of solutions and using biologically inspired operators like mutation and crossover to select new solutions. Genetic algorithms maintain a population of potential solutions and evolve them over generations to find better solutions to optimization and search problems.