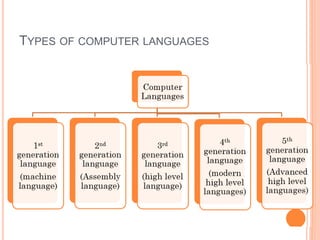
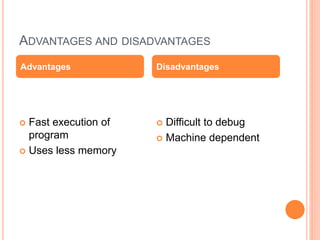
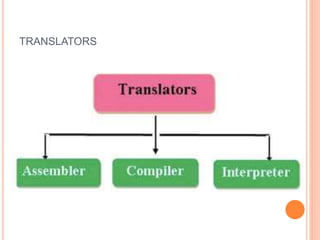
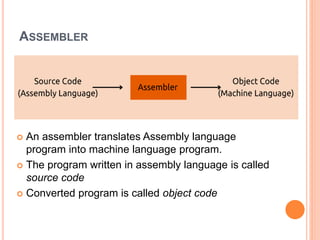
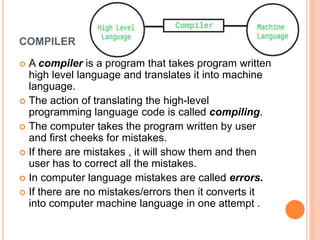
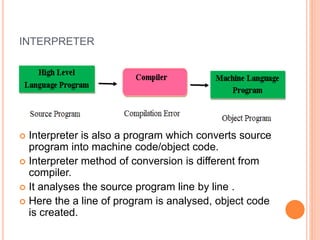
The document explains computer programming and various generations of programming languages, categorizing them into five generations from low-level machine languages to advanced high-level languages used in artificial intelligence research. It discusses the features, advantages, and disadvantages of each generation, including their execution speed, ease of debugging, and dependency on machines. Additionally, it describes the roles of translators such as assemblers, compilers, and interpreters in converting source code into machine language.