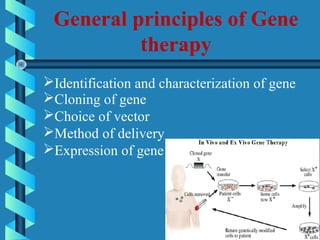
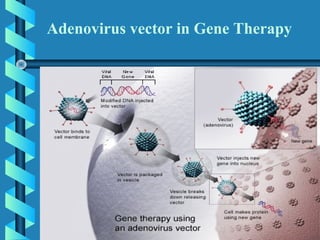
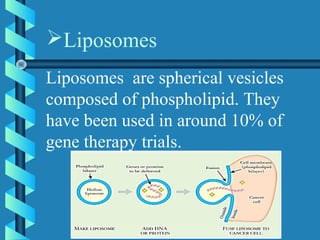
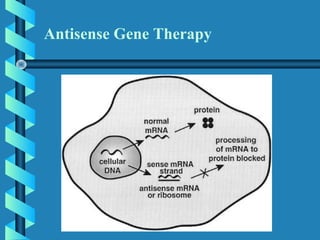
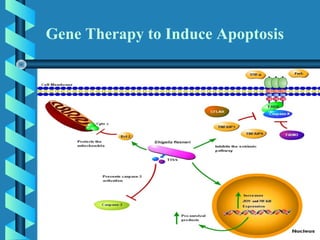
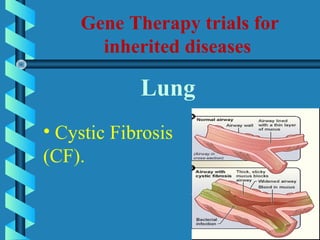
This document provides an overview of gene therapy, including definitions, aims, delivery methods, approaches, problems, and applications. Gene therapy involves inserting, altering or removing genes in a patient's cells to treat disease. It aims to correct defective genes. Delivery is mainly through viral vectors like adenoviruses or retroviruses, or non-viral methods like particle bombardment or liposomes. Gene therapy approaches include antisense therapy, inducing apoptosis, or anti-angiogenesis. Problems include short-lived effects, immune responses, vector safety, and challenges of multigene disorders. Diseases being investigated include cystic fibrosis, ADA deficiency, Alzheimer's, hemophilia and others.