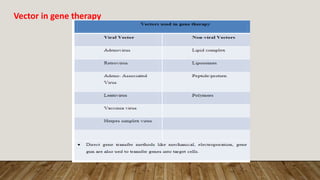
This document provides an overview of gene therapy including its principles, approaches, development, types, vectors, delivery methods, examples, advantages, and disadvantages. Gene therapy involves inserting genes into cells to treat diseases caused by defective genes. There are two main approaches - germline gene therapy, which alters the germ cells and is passed to offspring, and somatic gene therapy, which alters non-reproductive cells only in the individual. Gene therapy development involves pre-clinical and clinical trials. Vectors like viruses are used to deliver therapeutic genes. Examples include treating severe combined immunodeficiency. While gene therapy has potential benefits, there are also risks like immune responses and ensuring genes reach the right cells.