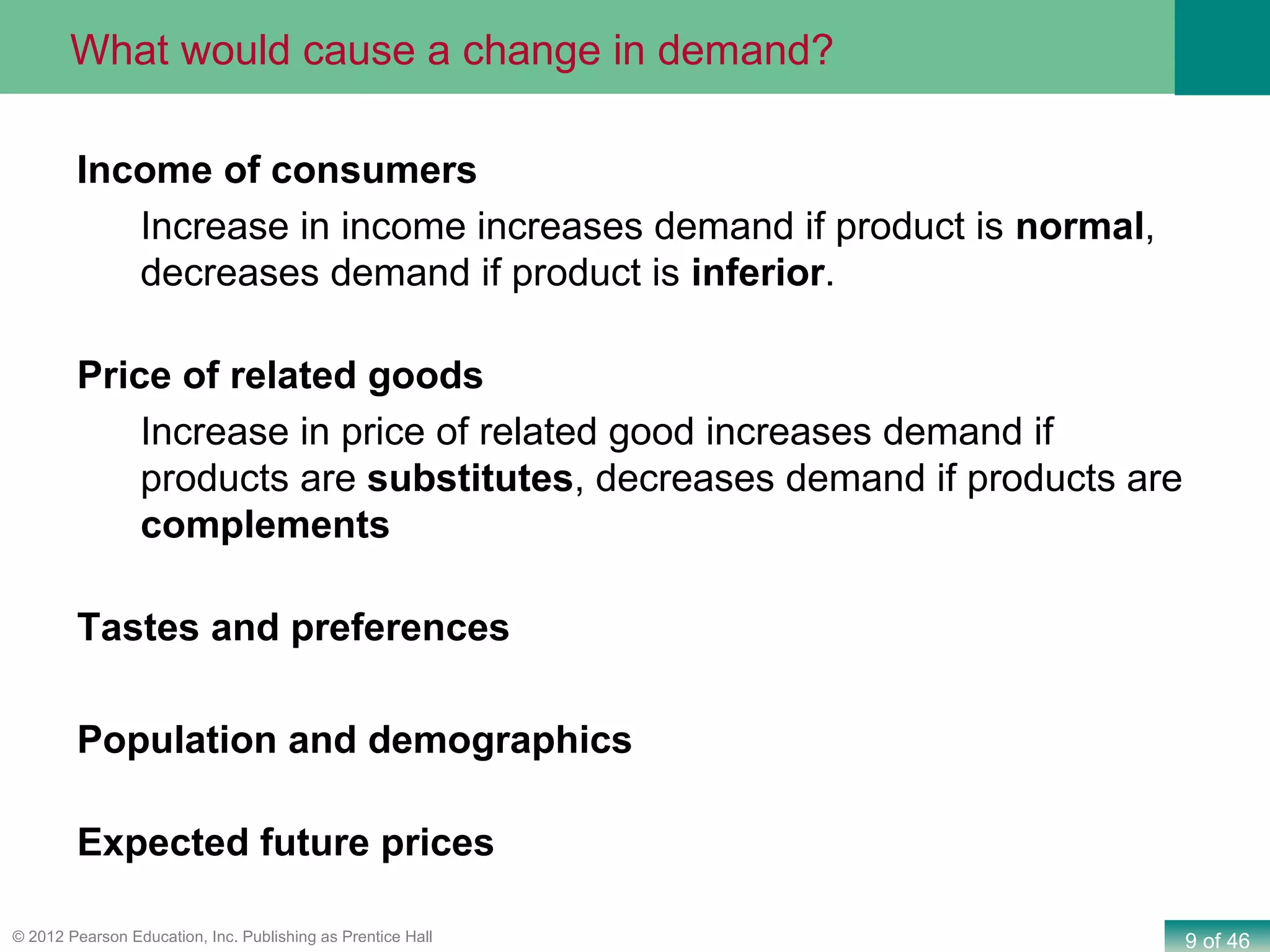
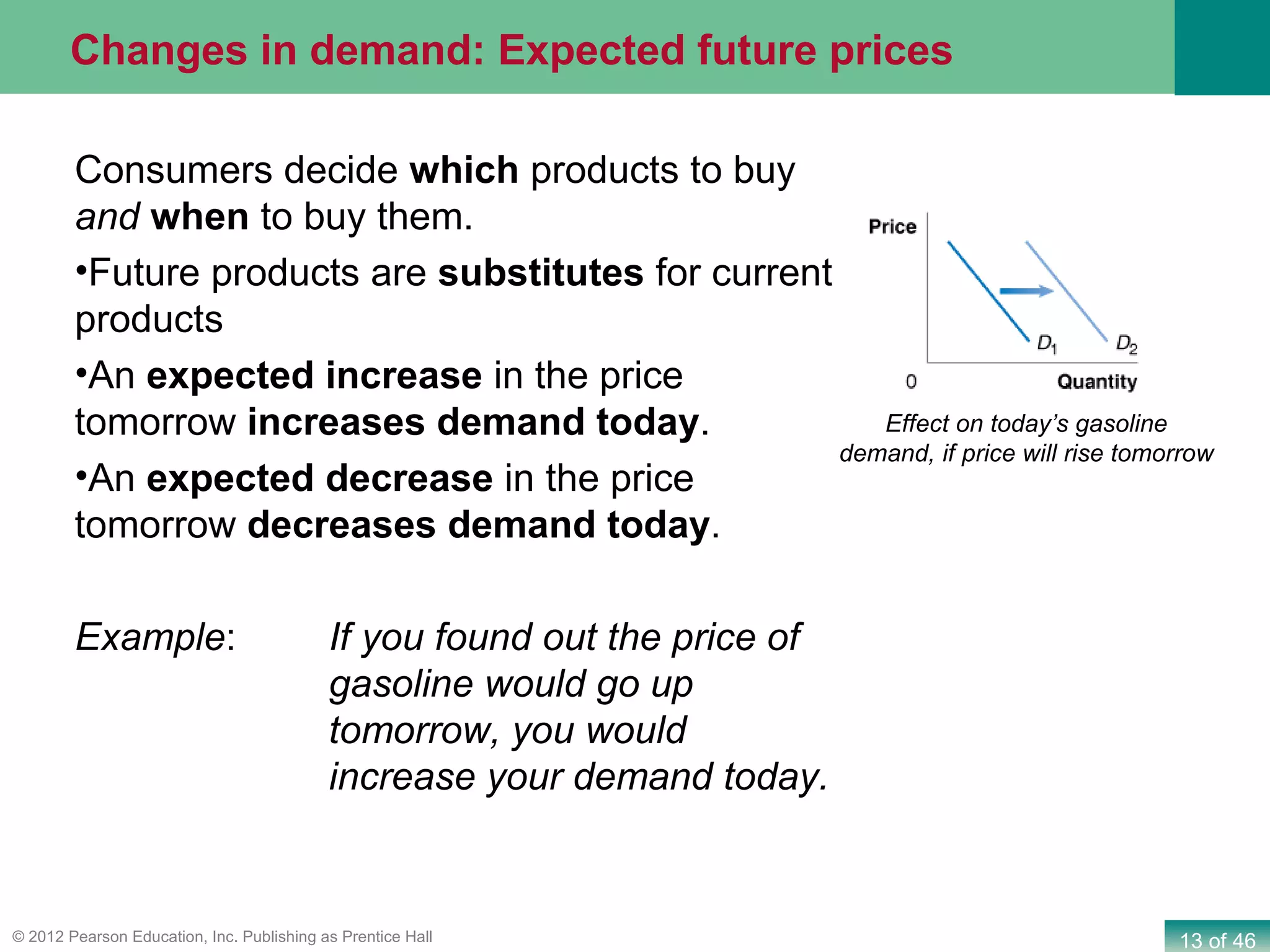
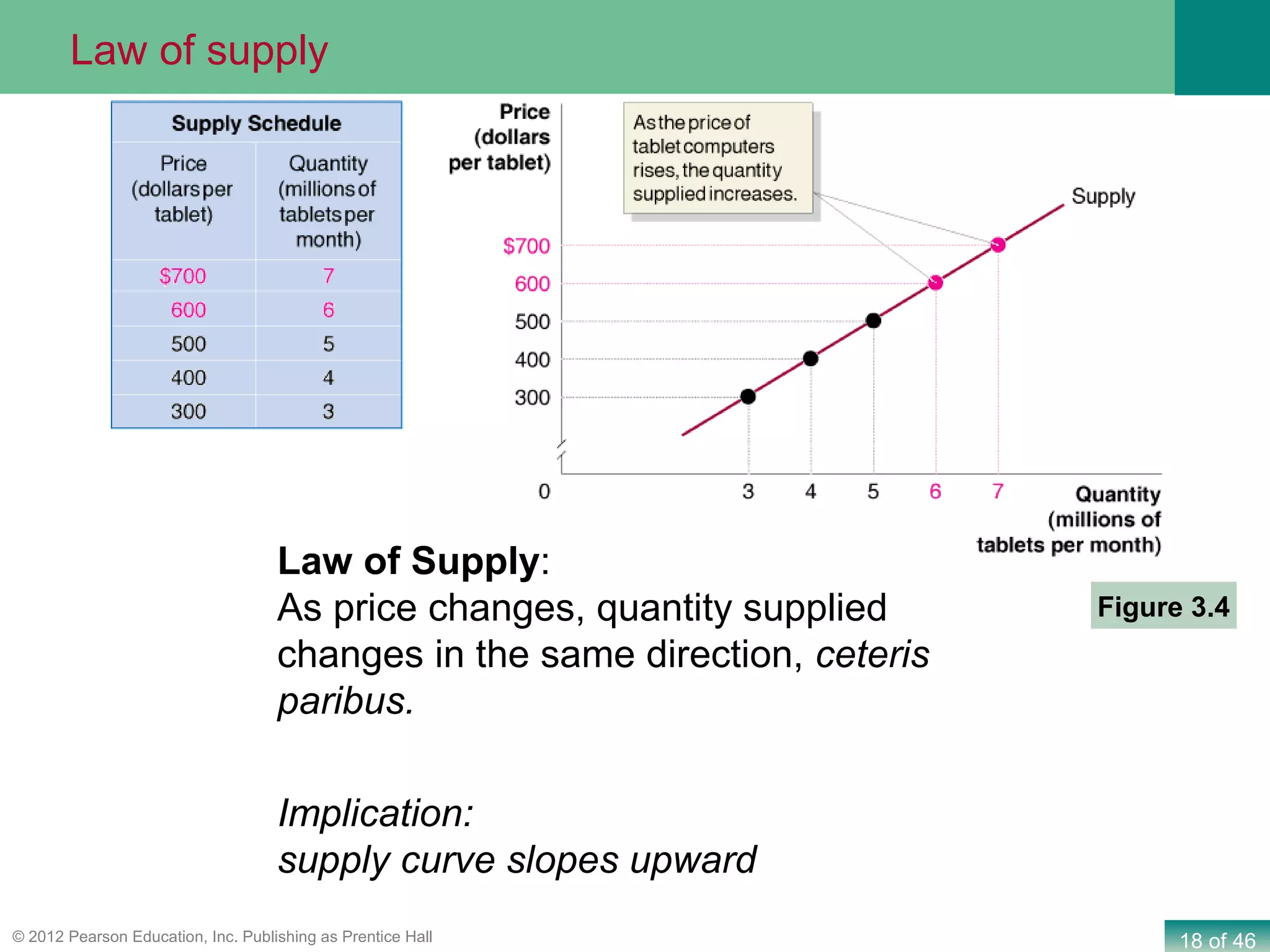
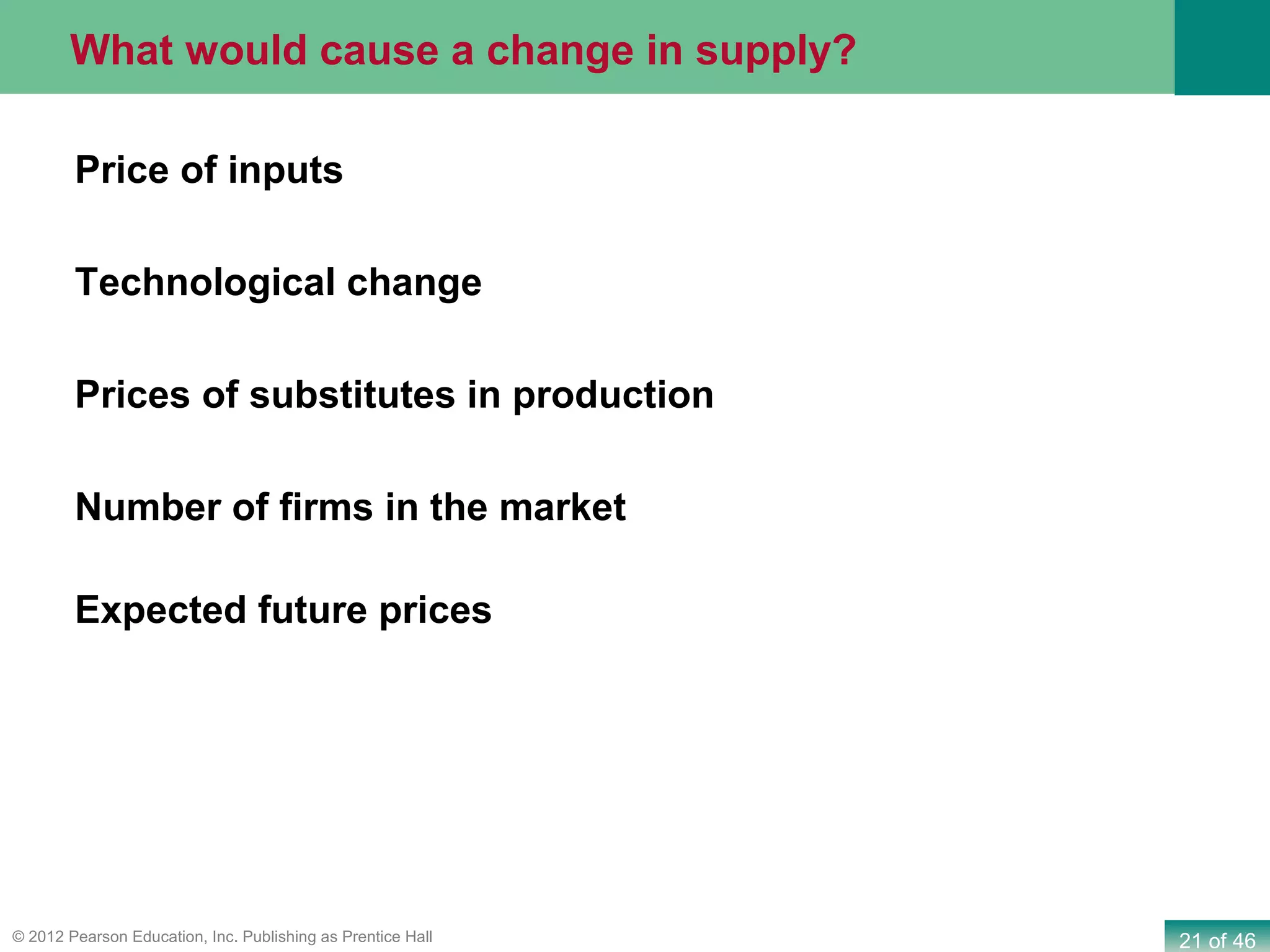
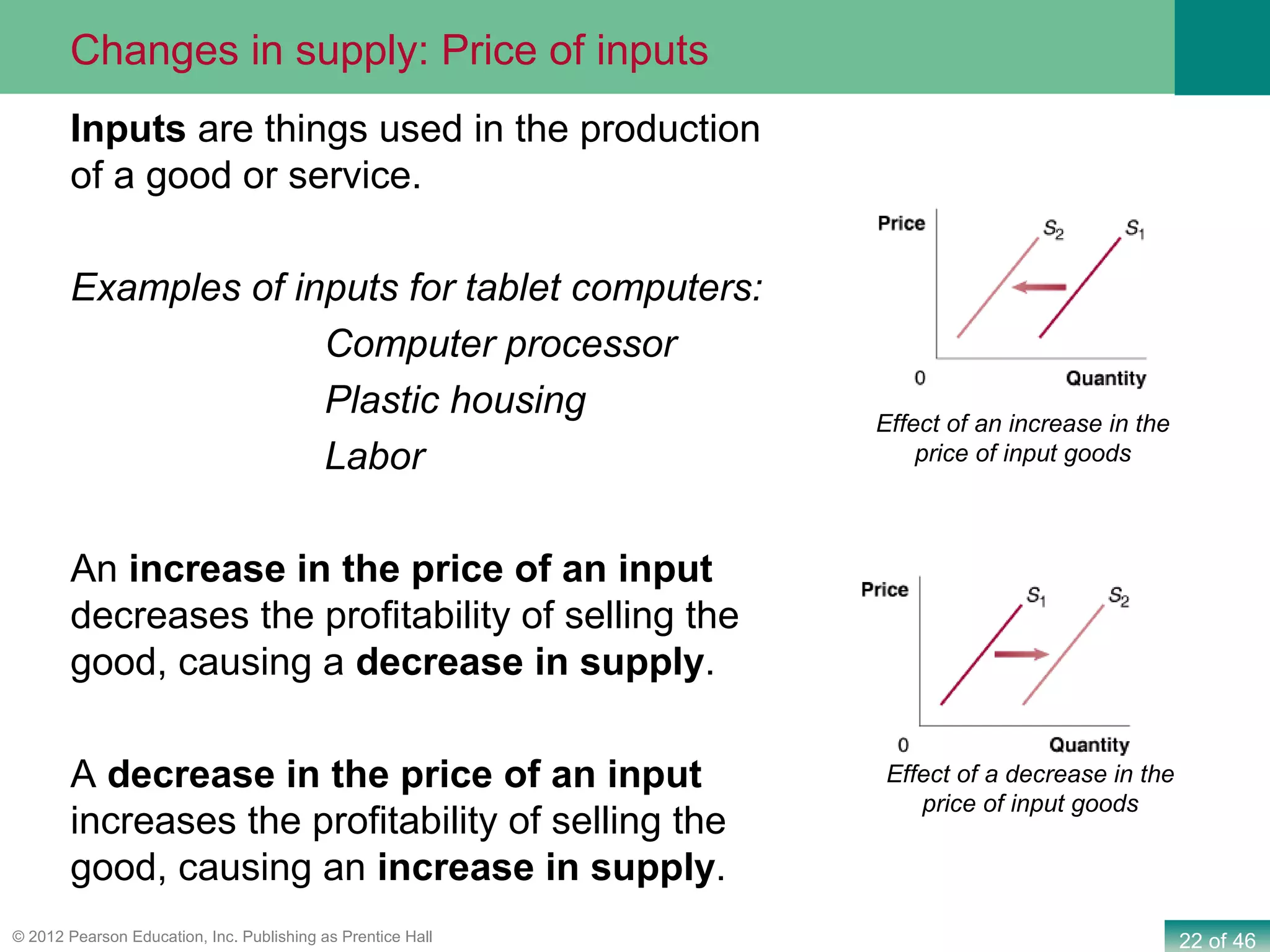
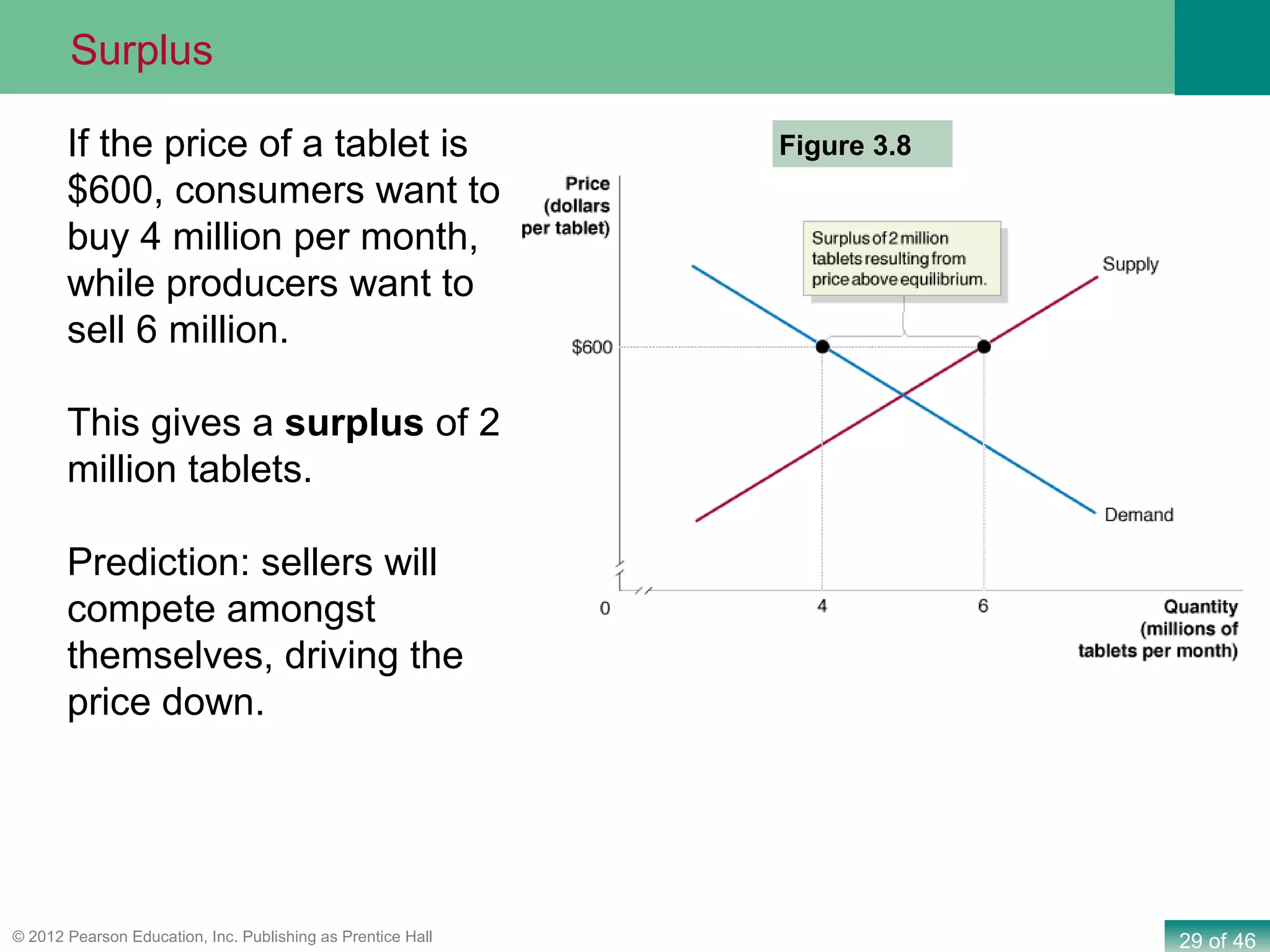
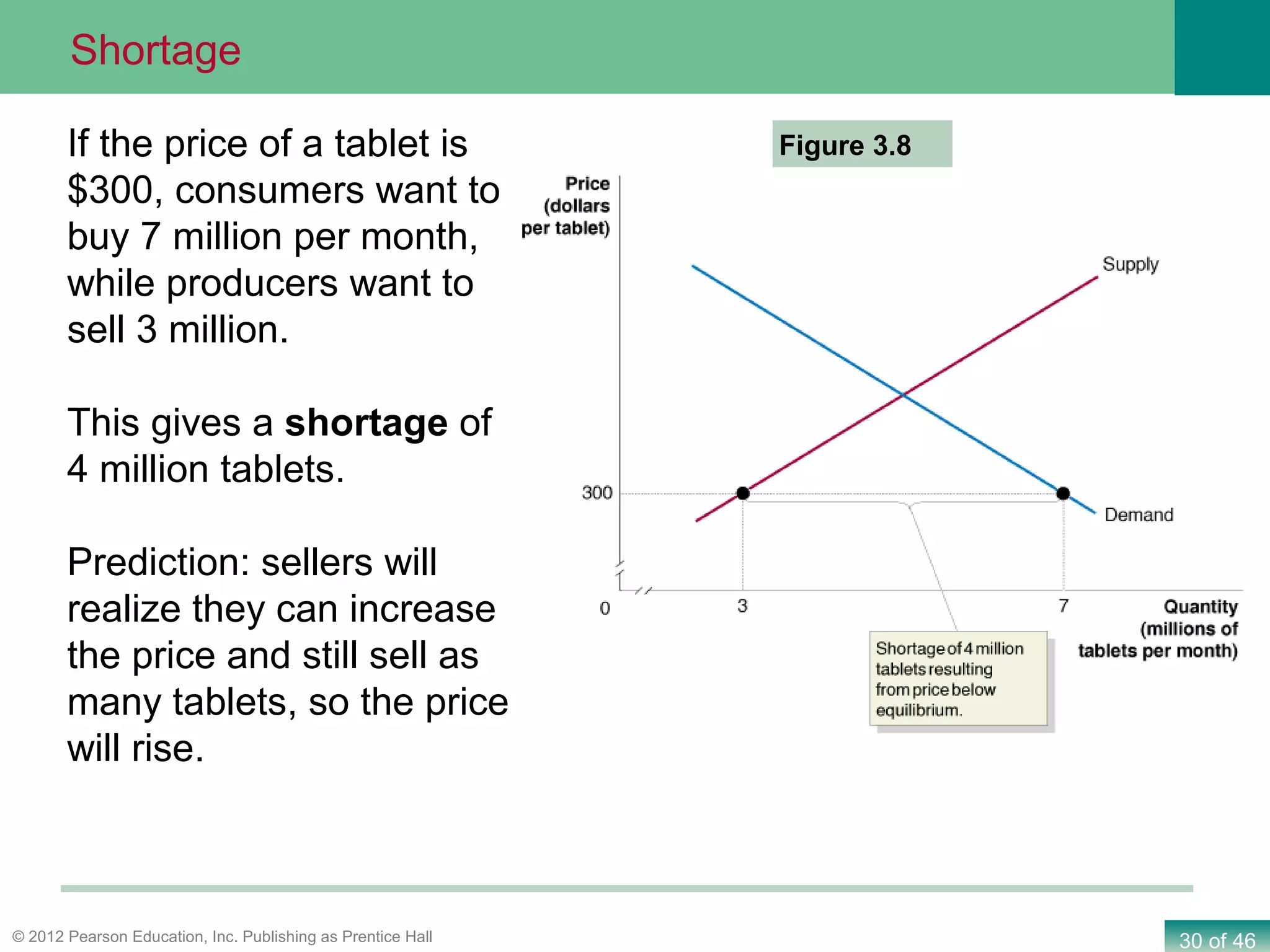
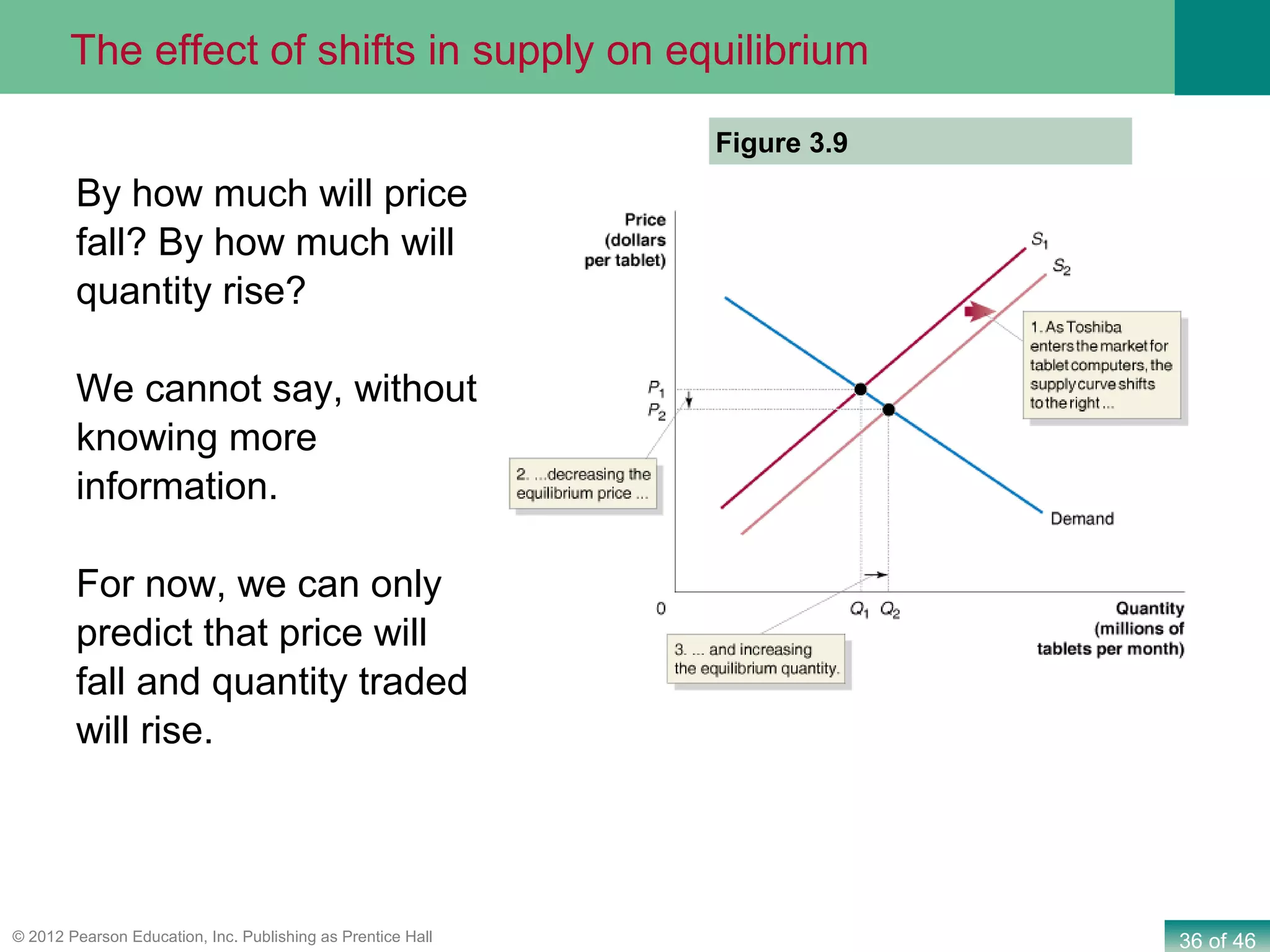
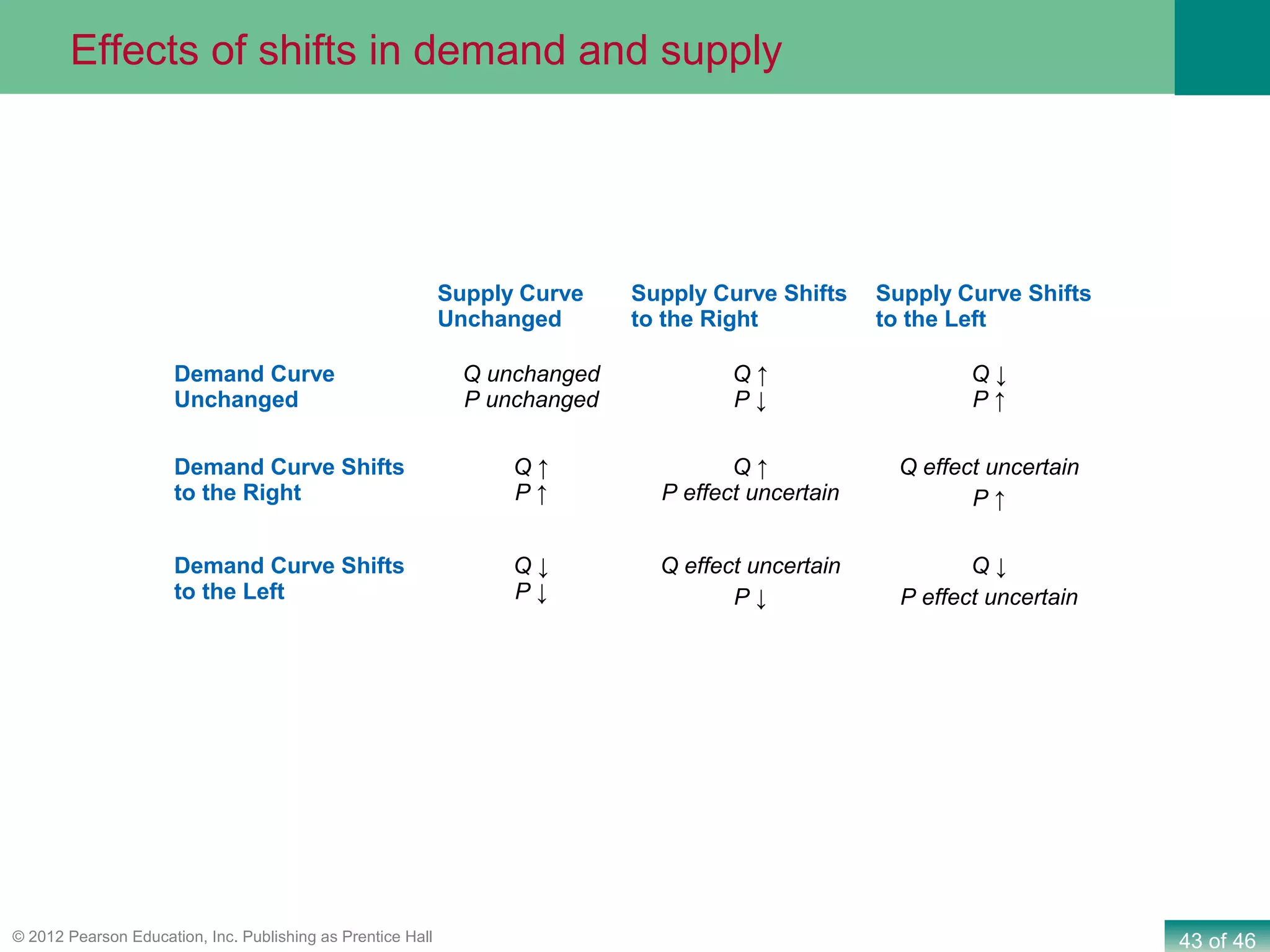
If both supply and demand increase simultaneously:
- The equilibrium quantity will unambiguously increase, as both curves shifting outward pushes the equilibrium point to a higher quantity.
- The effect on the equilibrium price is ambiguous and depends on the relative magnitudes of the supply and demand shifts. If demand increases more than supply, price will rise. If supply increases more than demand, price will fall. But if the shifts are equal in magnitude, price will remain the same.
The key point is that while a change in equilibrium quantity is assured in this scenario, the direction of change in price cannot be determined without knowing more details about the specific supply and demand shifts.