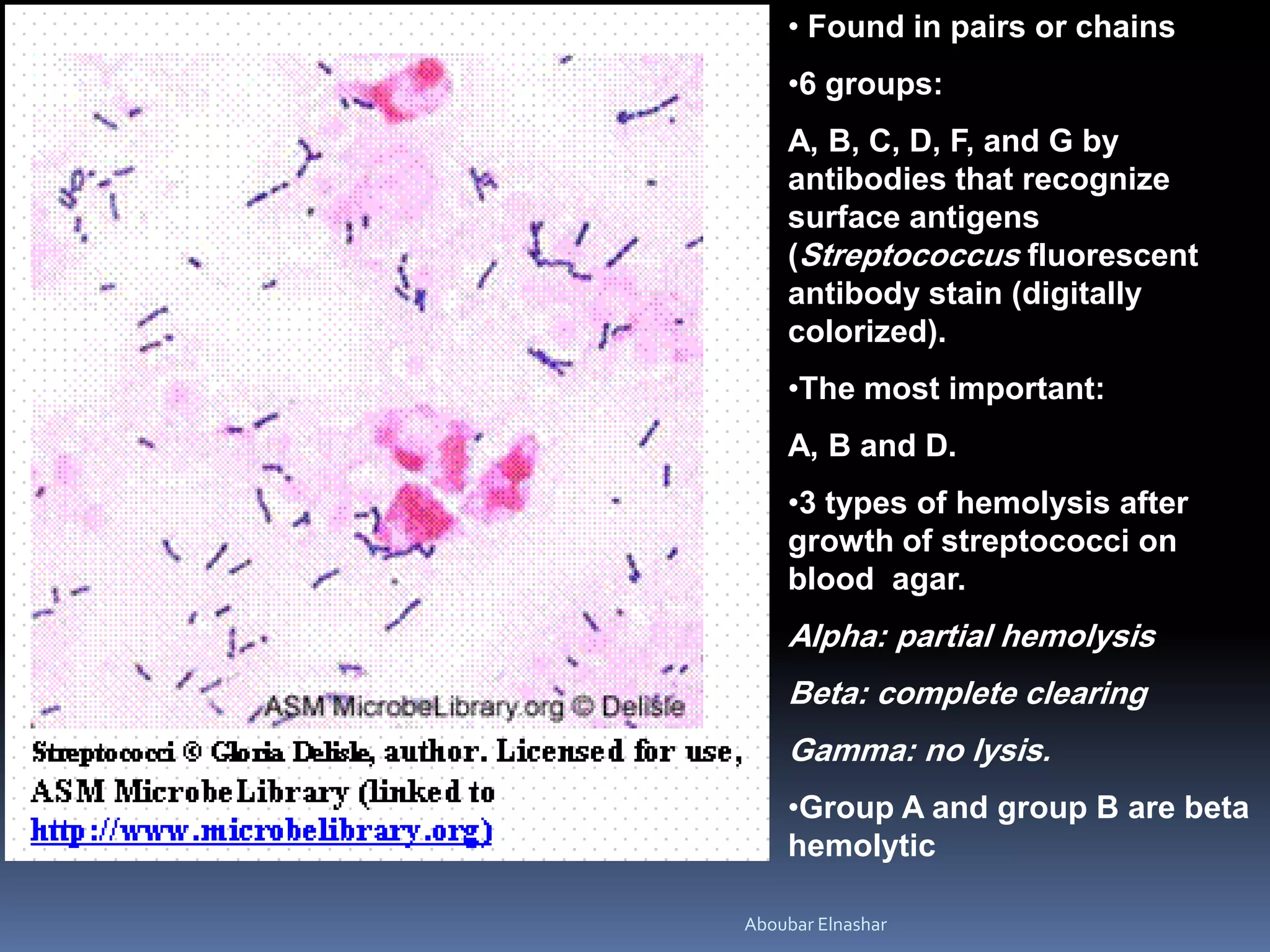
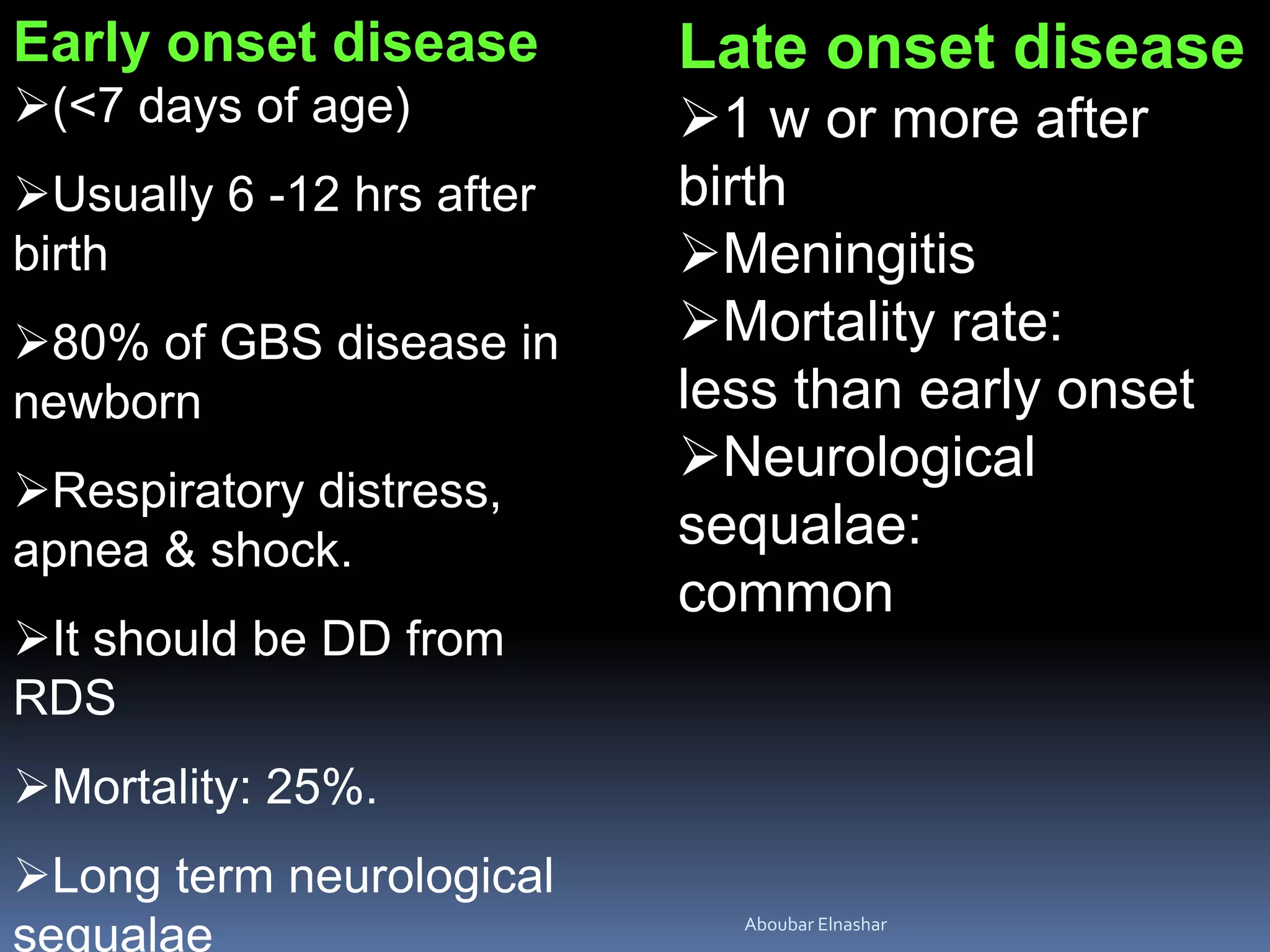
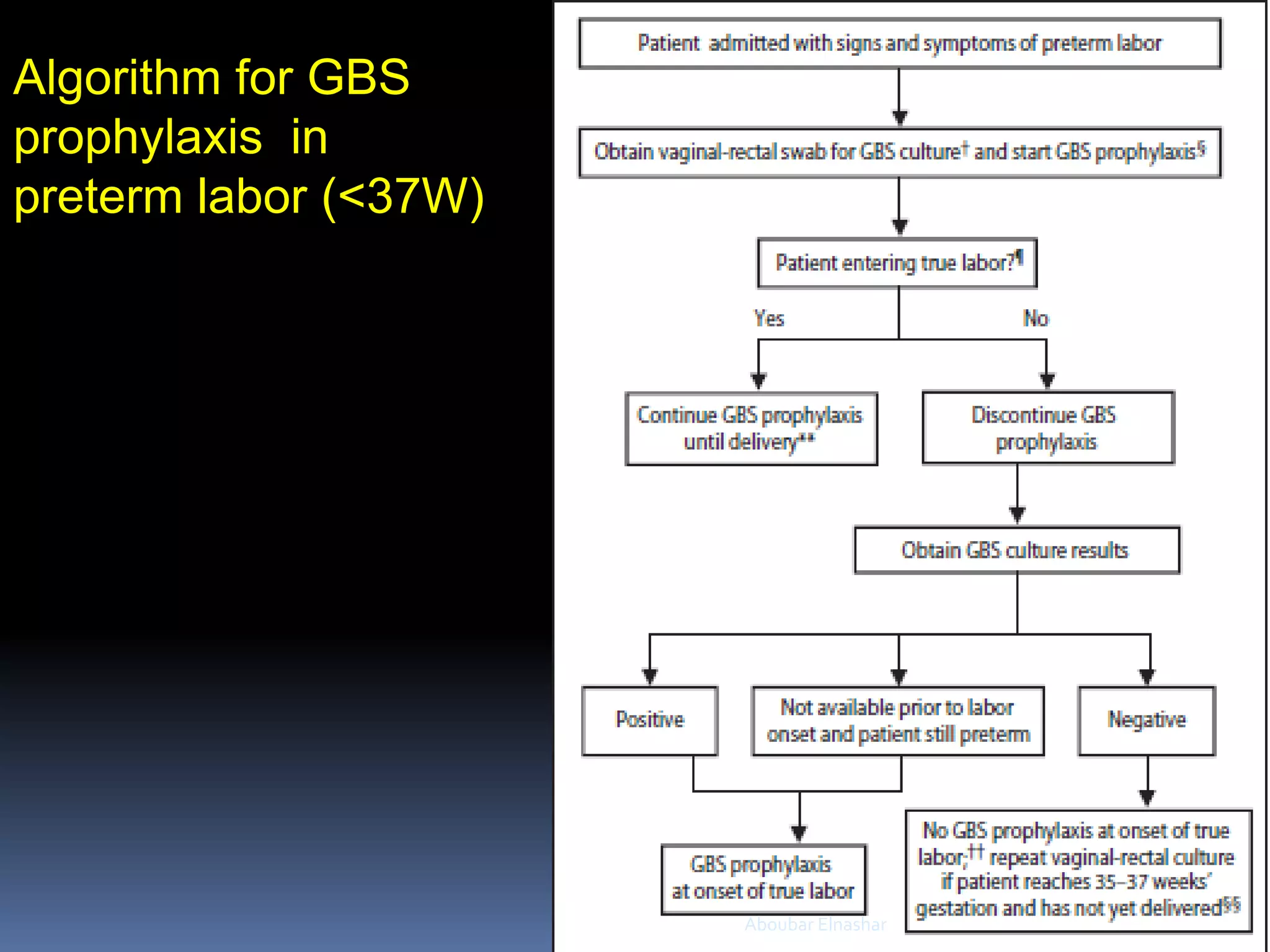
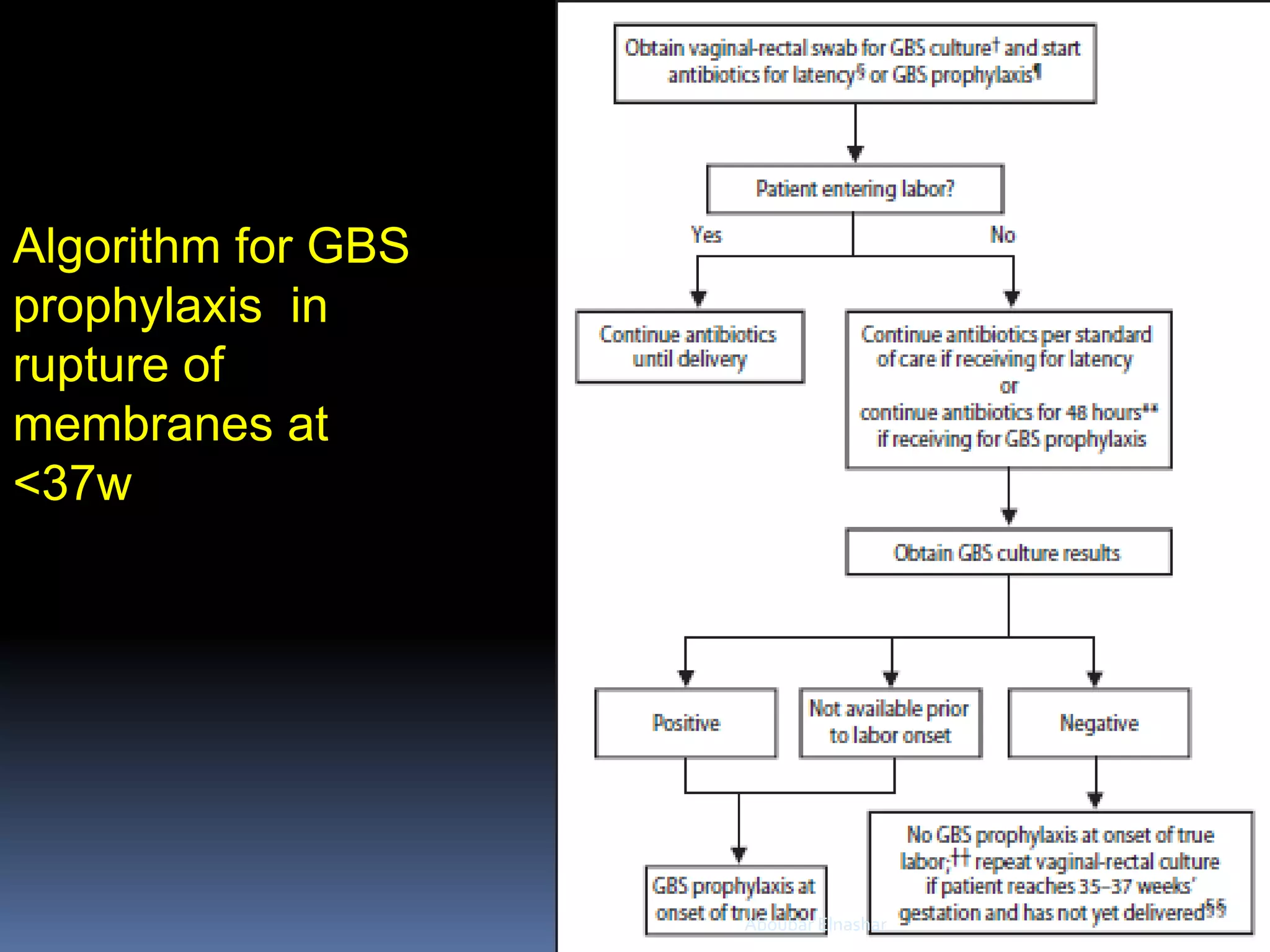
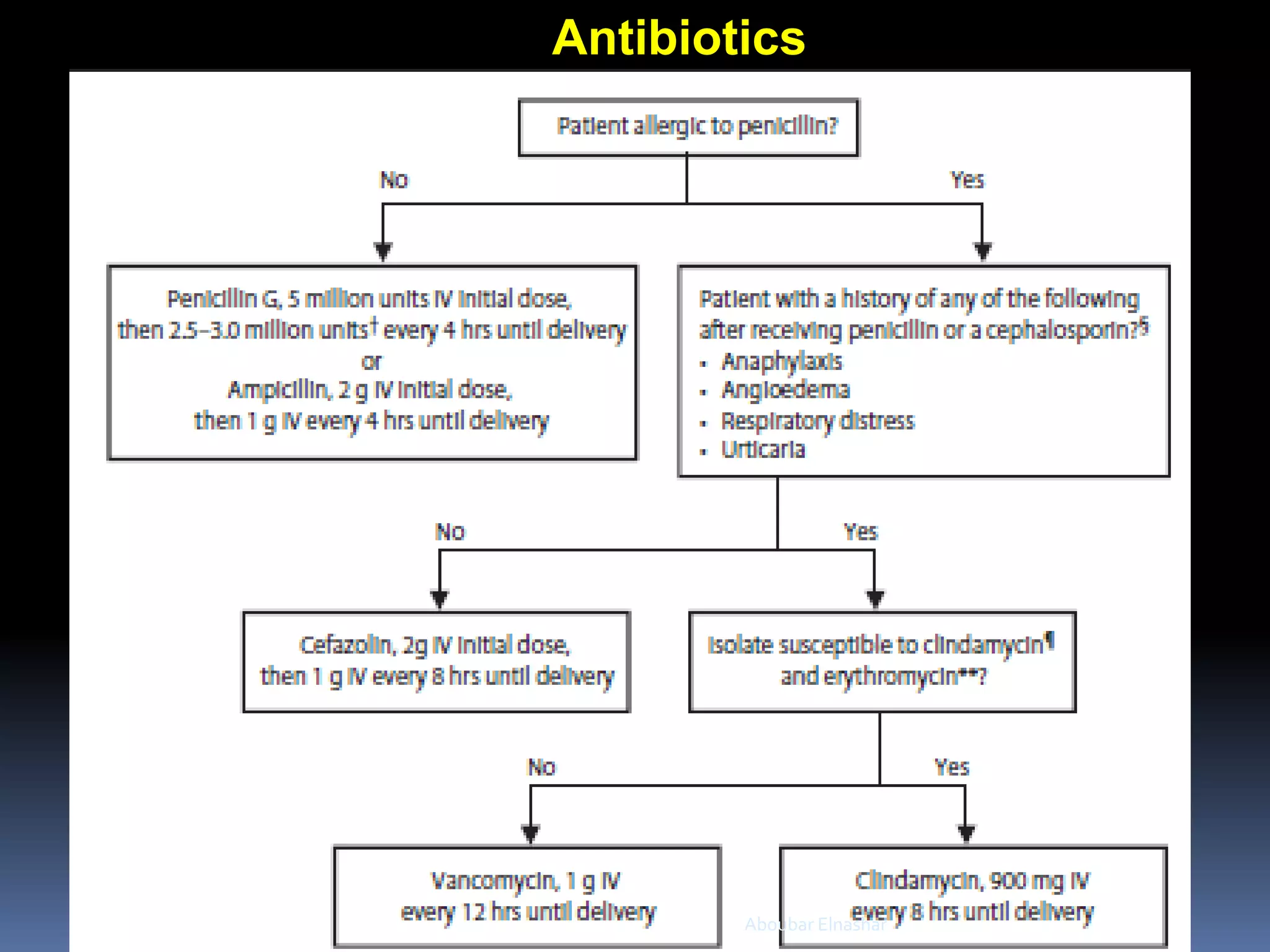
This document discusses Group B Streptococcus (GBS) prevention of early-onset disease in newborns. It covers that 10-30% of pregnant women asymptomatically carry GBS. GBS is the leading cause of neonatal bacterial sepsis in the US and most frequent cause of neonatal infection in the UK. The document outlines recommendations for intrapartum GBS prophylaxis based on previous infections, current pregnancy GBS test results, gestational age and other risk factors. It recommends screening all pregnant women between 35-37 weeks gestation for vaginal and rectal GBS colonization. Antibiotics such as ampicillin are recommended for GBS prophylaxis based on screening results and risk factors.