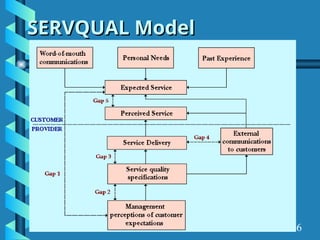
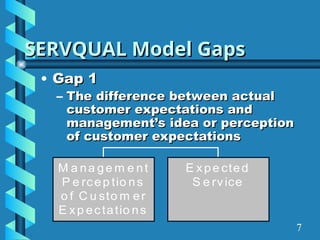
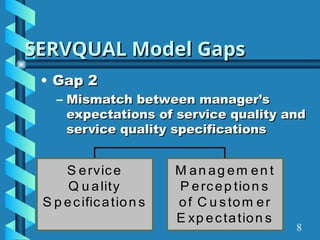
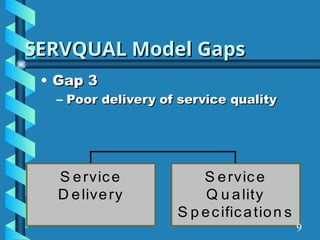
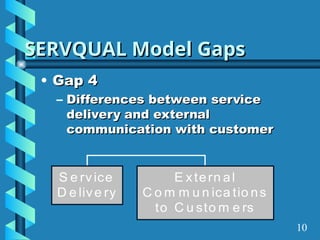
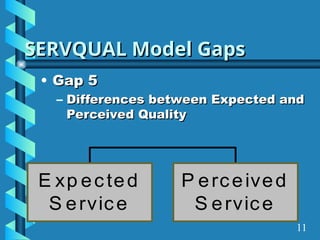
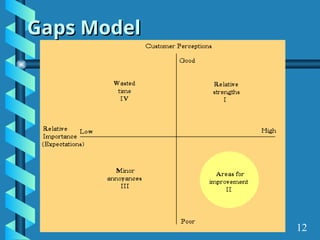
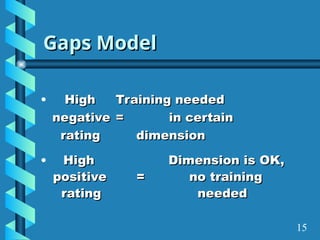
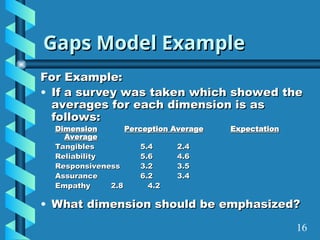
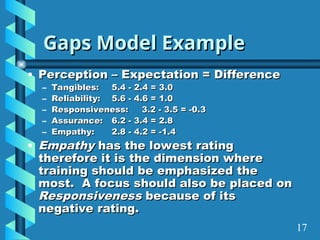
The document presents a comprehensive overview of gap analysis, defining it as a formal method to identify and rectify discrepancies between desired and actual performance levels within organizations. It discusses the Servqual model with its five identified gaps, emphasizing the importance of customer expectations versus service delivery, and outlines the application of ISO 9001:2000 as a tool for identifying and addressing these gaps. Ultimately, the document posits that gap analysis is crucial for process improvement and recognizing areas needing enhancement.