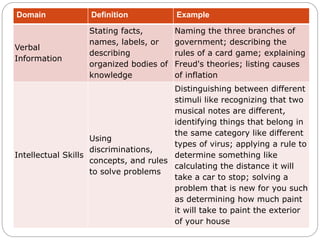
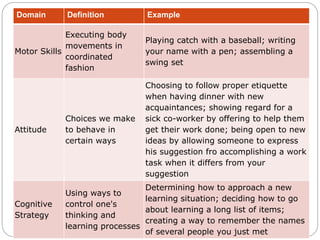
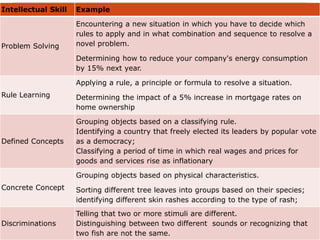
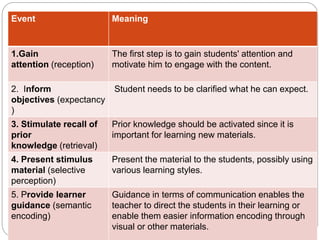
Robert Gagne was an experimental psychologist who studied learning and instruction. He identified five domains of learning outcomes - verbal information, intellectual skills, cognitive strategies, motor skills, and attitudes. Gagne proposed that different types of learning require different internal and external conditions, and identified nine events of instruction that can facilitate learning, including gaining attention, presenting material, providing guidance and feedback, and assessing performance. According to Gagne, learning is cumulative, building on previously acquired skills and knowledge, and different outcomes have different prerequisites that must be met for new learning to occur.