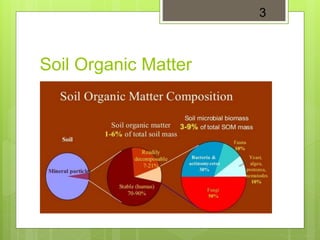
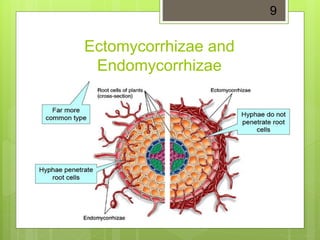
Fungal communities in soil play an important role in plant growth by increasing soil organic matter and aggregation while decreasing soil erosion. Fungi develop underground networks of hyphae that entangle soil particles and create links between them, improving soil structure. There are two main types of mycorrhizal fungi that form symbiotic relationships with plant roots - endomycorrhizae which infiltrate root cortical cells, and ectomycorrhizae which form structures outside roots. These relationships improve nutrient and water uptake for plants as well as increasing stress tolerance and plant health overall. Fungal networks also allow communication between plants as chemical signals and nutrients are exchanged through their interconnected mycelium.