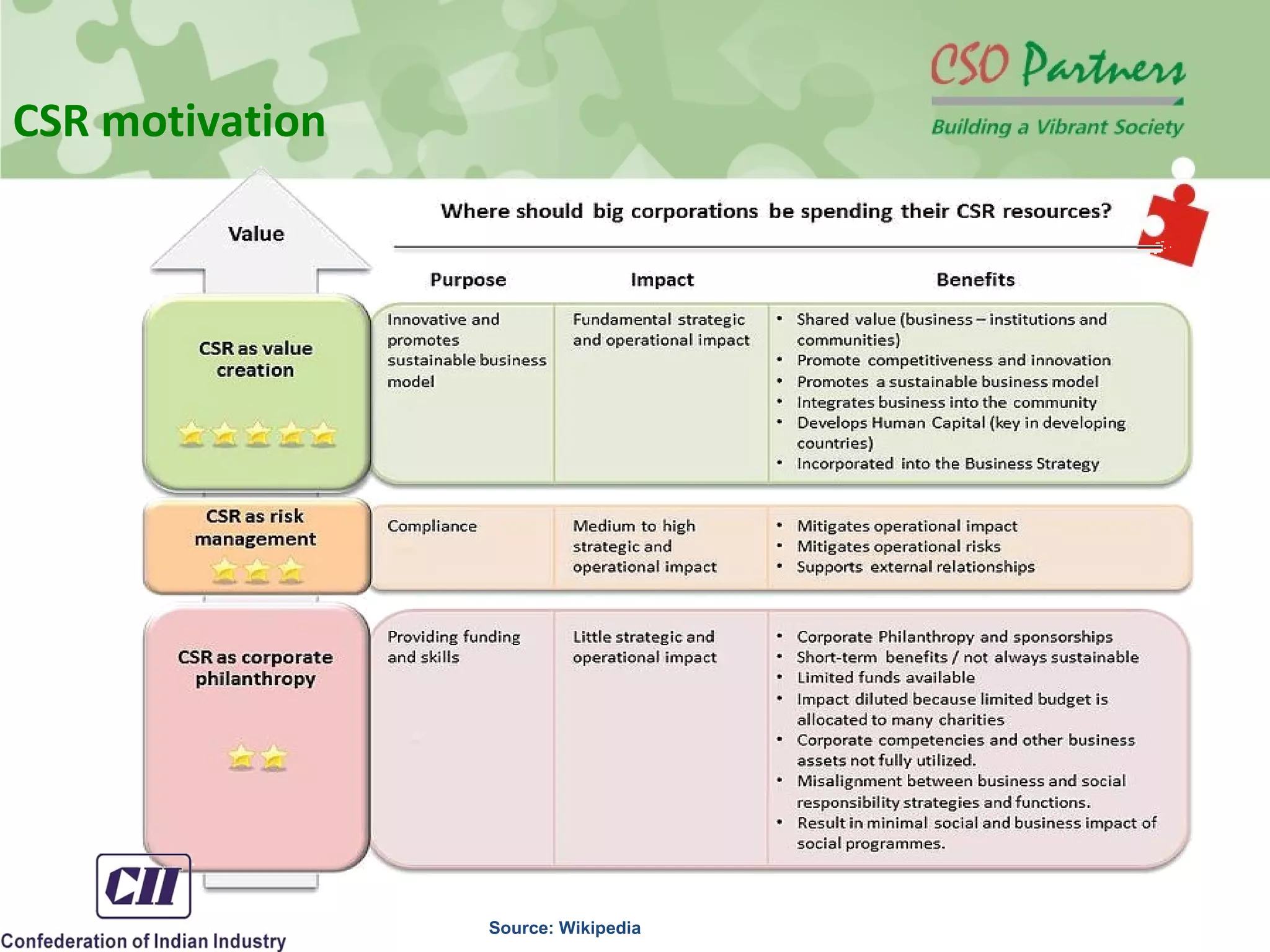
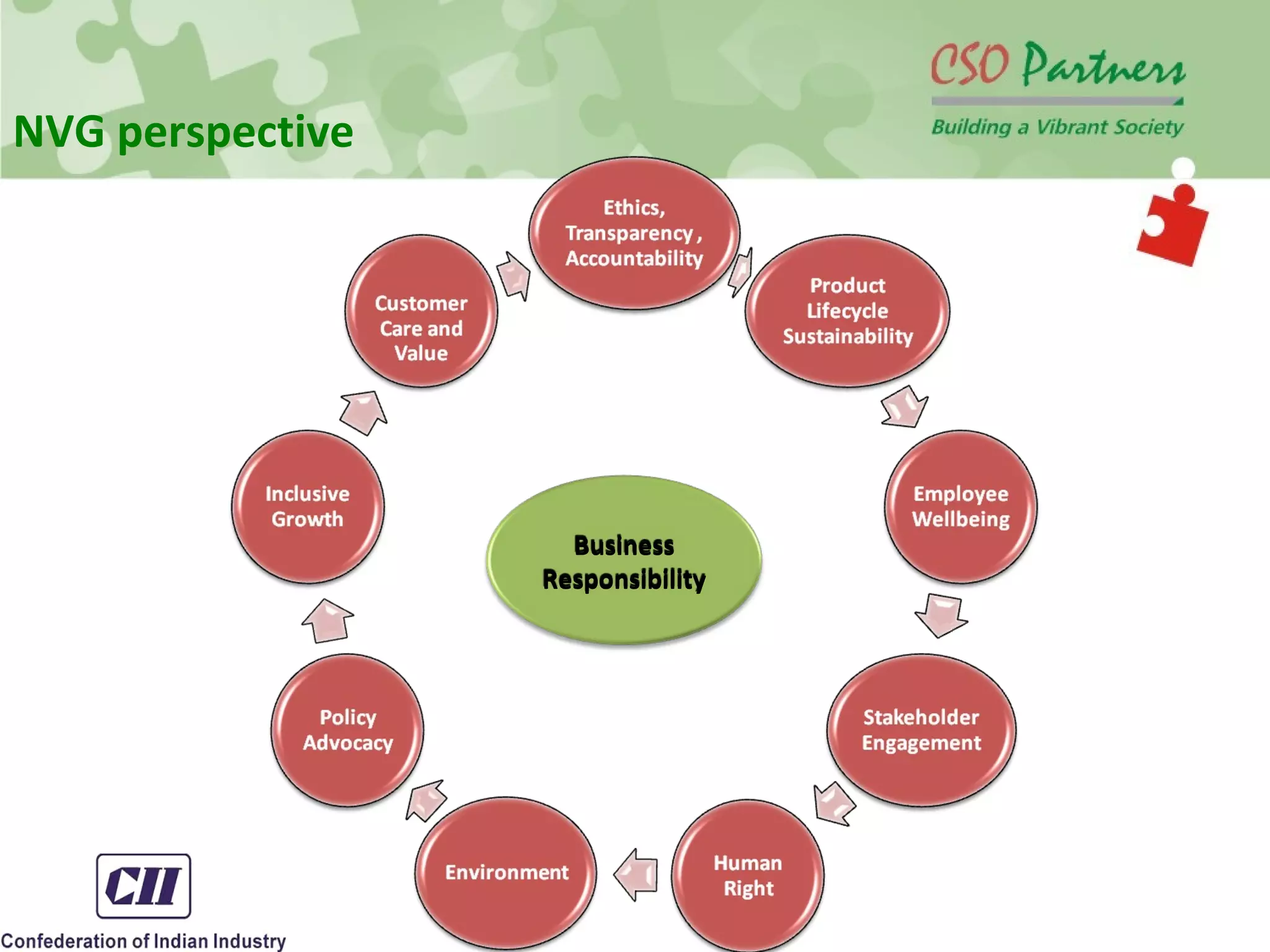
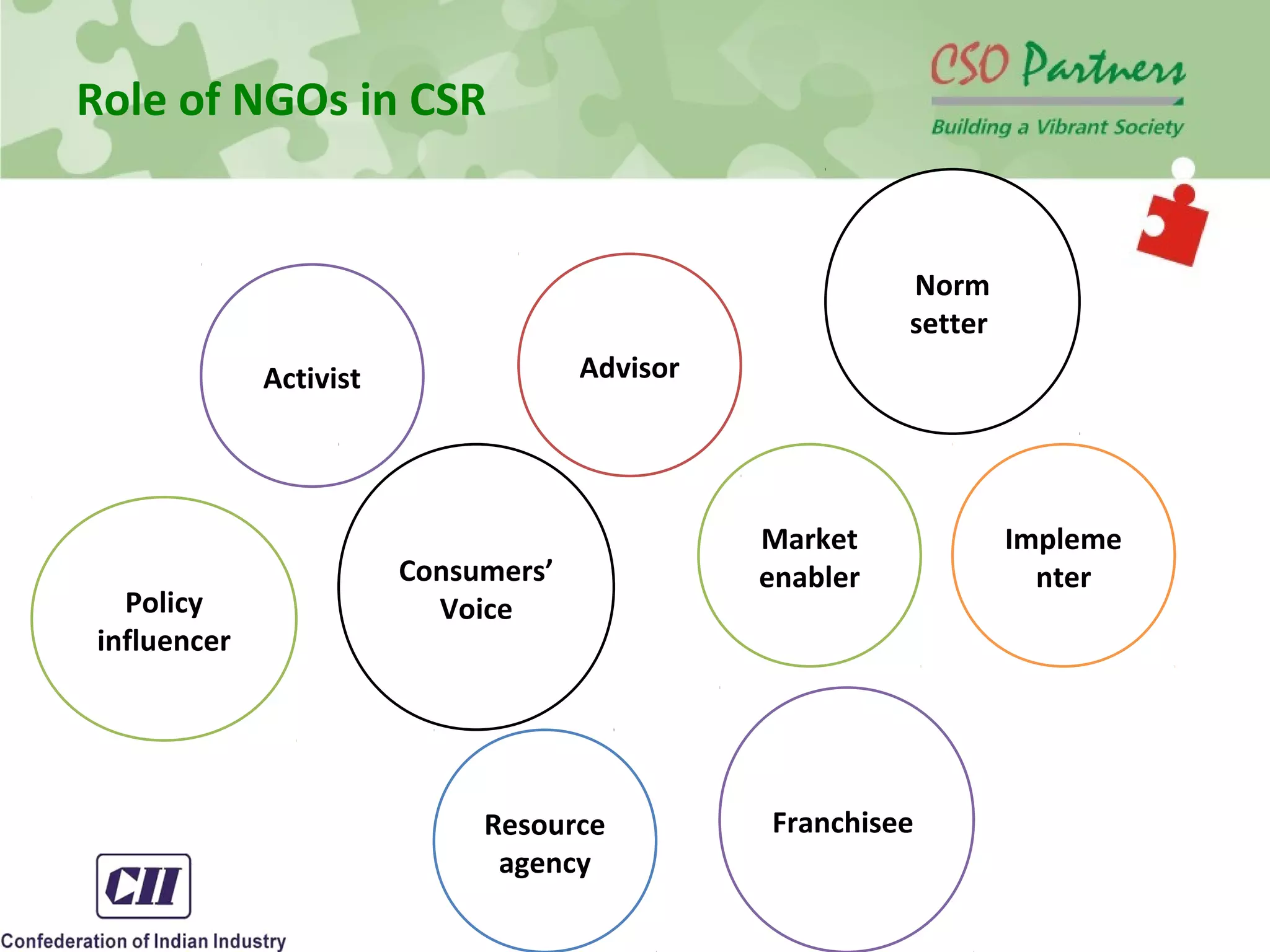
The document discusses the conceptual framework of corporate social responsibility and business responsibility, providing an overview of international standards and norms. It examines the role of non-governmental organizations in promoting business responsibility through activities like advocacy, resource provision, and implementing programs. The document also reviews cases where non-profits pressured companies to change practices, such as Nike reforming its labor policies after criticism of working conditions in overseas factories.