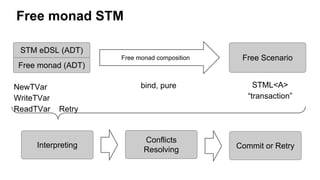
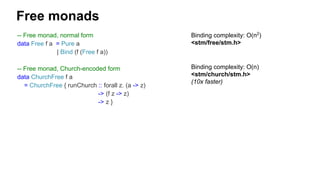
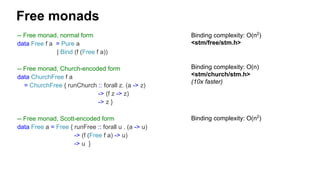
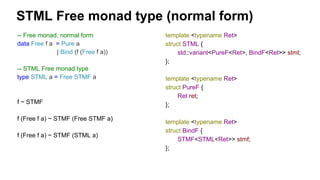
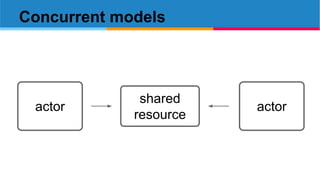
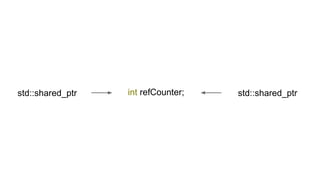
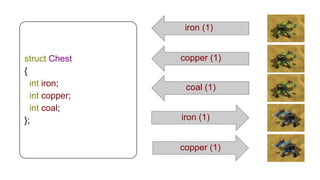
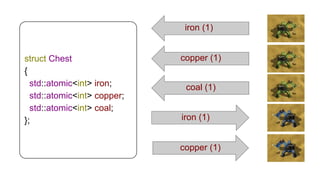
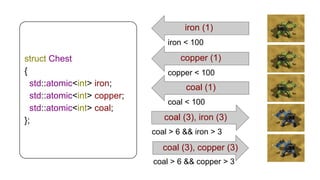
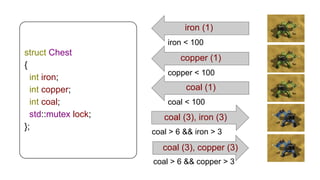
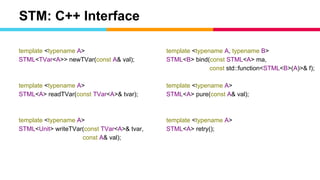
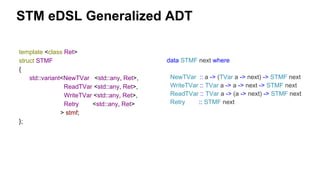
The document discusses several advanced concepts in functional programming using C++, focusing on concurrent models and software transactional memory (STM). It includes code snippets and explanations for monadic STM, resource management, and the implementation of various operations related to concurrency. Key topics include actor models, STM-based concurrency, and the design of a functional approach within C++.
















 {
return readTVar(tvar);
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinc-lambdansk-180802153055/85/Functional-programming-in-C-LambdaNsk-25-320.jpg)
 { return t2; });
}
STML<Unit> extractResource (TVar<int> resource, int count) {
STML<int> trans1 = readTVar (resource);
return bind (trans1, [=](int value) {
return value >= count
? writeTVar (recource, value - count)
: retry();
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinc-lambdansk-180802153055/85/Functional-programming-in-C-LambdaNsk-26-320.jpg)




{
return bind (readTVar (tvar), [=](int v1)
{
return bind (pure (10), [=](int v2)
{
return pure (v1 + v2);
});
});
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinc-lambdansk-180802153055/85/Functional-programming-in-C-LambdaNsk-33-320.jpg)

{
return bind (readTVar (tvar), [=](int v1)
{
return bind (pure (10), [=](int v2)
{
return pure (v1 + v2);
});
});
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinc-lambdansk-180802153055/85/Functional-programming-in-C-LambdaNsk-34-320.jpg)
![STML<int>
[](){}
↳ STML<TVar<int>>
[](){}
↳ STML<int>
[](){}
↳ STML<int>
[](){}
↳ STML<int>
Recursive STML type (lambda-enclosed)
STML<int> transaction()
{
return bind (newTVar (42), [=](TVar<int> tvar)
{
return bind (readTVar (tvar), [=](int v1)
{
return bind (pure (10), [=](int v2)
{
return pure (v1 + v2);
});
});
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fpinc-lambdansk-180802153055/85/Functional-programming-in-C-LambdaNsk-35-320.jpg)