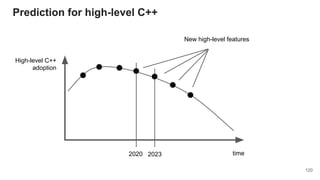
This document discusses the concepts and evolution of functional programming in C++. It covers key elements such as the philosophy, design patterns, and limitations of functional programming, as well as specific C++ features like lambdas, recursion, and type-level programming. The document also seeks to provide insights into the future direction of functional programming in C++ alongside its integration with modern C++ standards.




























 { return i + 1; }
i -> i + 1
i => i + 1
lambda i: i + 1
| i | -> i + 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-31-320.jpg)
![𝝺ambdas in C++
<>(int x, int y) -> int {return x + y;}
[|b|]() { return |b| -> set_text("World"); }
i => i + 1
[](auto i) { return i + 1; }
[]<>(auto i) { return i + 1; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-32-320.jpg)
![𝝺ambdas in C++
Idea of the feature
Standard issuing
Feature adoption
Feature improvements
== You are standing here ==
Feature improvements
<>(int x, int y) -> int {return x + y;}
[|b|]() { return |b| -> set_text("World"); }
i => i + 1
[](auto i) { return i + 1; }
[]<>(auto i) { return i + 1; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-33-320.jpg)
![𝝺ambdas in C++
Idea of the feature
Standard issuing
Feature adoption
Feature improvements
== You are standing here ==
Feature improvements
2011
...2000...
2014, 2017
...2011...
2020
2019
<>(int x, int y) -> int {return x + y;}
[|b|]() { return |b| -> set_text("World"); }
i => i + 1
[](auto i) { return i + 1; }
[]<>(auto i) { return i + 1; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-34-320.jpg)
![Idea of the feature
Pondering and thinking
Reference implementation
Discussions in Committee
Drafting in Standard
Implementation in compilers
Standard issuing
Feature adoption
Feature improvements
== You are standing here ==
Feature improvements
𝝺ambdas in C++
2011
...2000...
<>(int x, int y) -> int {return x + y;}
[|b|]() { return |b| -> set_text("World"); }
i => i + 1
[](auto i) { return i + 1; }
[]<>(auto i) { return i + 1; }
2014, 2017
...2011...
2008 - 2011
2006 - 2008
2020
2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-35-320.jpg)


 { sum += i; });
std::cout << sum; // 10
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-38-320.jpg)
 {
return x;
};
auto K = [](auto x) {
return [=](auto y) {
return x;
};
};
auto S = [](auto x) {
return [=](auto y) {
return [=](auto z) {
return (x(z))(y(z));
};
};
};
Ix = x
Kxy = x
Sxyz = xz(yz)
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-39-320.jpg)
 { return i * 2; }
auto mul2 = [](auto i) { return i * 2; }
constexpr auto mul2 = [](auto i) { return i * 2; }
auto mul2 = []<typename T>(T i) { return i * 2; }
auto mul2 = i => i * 2;
C++11
C++14
C++17
C++20
C++??
Lambda expressions
Polymorphic lambdas
Constexpr lambdas
“Familiar” syntax
Abbreviated syntax
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-40-320.jpg)


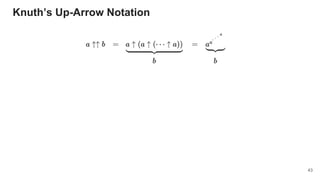





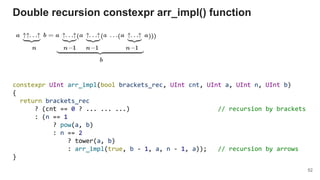



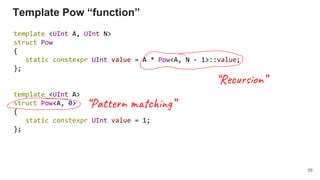
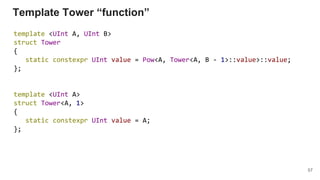







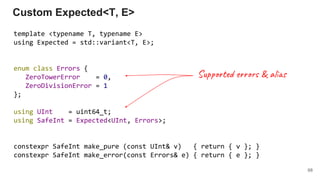
















 { return make_pure(pow(a, v)); }
);
}
Monadic binding*
86
* Almost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-86-320.jpg)
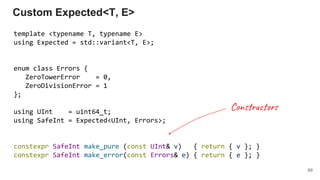
 { return make_pure(pow(a, v)); }
);
}
Monadic binding*
87
* Almost
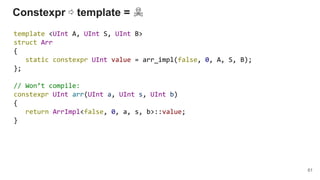
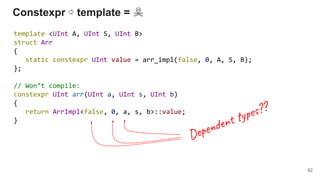
SafeInt mbind (SafeInt, Func<SafeInt, UInt>)
mbind :: SafeInt -> (UInt -> SafeInt) -> SafeInt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-87-320.jpg)

 { return make_pure(i * 10); };
SafeInt v1 = safe_tower(2, 0);
SafeInt v2 = mbind(v1, mul10);
std::visit(SafeIntVisitor(), v1); // error : 0
std::visit(SafeIntVisitor(), v2); // error : 0
Monadic chaining*, error path
89
* Almost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-89-320.jpg)
 { return make_pure(i * 10); };
SafeInt v1 = safe_tower(2, 3);
SafeInt v2 = mbind(
mbind(v1, mul10),
mul10
);
std::visit(SafeIntVisitor(), v1); // result: 16
std::visit(SafeIntVisitor(), v2); // result: 1600
Monadic chaining*, success path
90
* Almost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-90-320.jpg)
 { return make_pure(i * 10); };
SafeInt v1 = safe_tower(2, 3);
SafeInt v2 = mbind(
mbind(v1, mul10),
mul10
);
SafeInt v2 = do {
UInt i1 <- safe_tower(2, 3);
UInt i2 <- mul10(i1);
return mul10(i2);
}
Monadic chaining*, do-notation dream
91
* Almost
m i d
d e n “<-”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-91-320.jpg)



{ return x.age == p.age; } );
return ps.size();
}
}
Monads everywhere: optional<>
95
mbind :: expected<A, E> -> (A -> expected<B, E>) -> expected<B, E>
mbind :: optional<A> -> (A -> optional<B>) -> optional<B>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-95-320.jpg)





 {
return for_each(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) {
return for_each(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) {
return yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z,
make_tuple(x, y, z));
});
});
});
Pythagorean Triples in Ranges](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-103-320.jpg)
 {
return for_each(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) {
return for_each(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) {
return yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z,
make_tuple(x, y, z));
});
});
});
Pythagorean Triples in Ranges](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-104-320.jpg)
 {
return for_each(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) {
return for_each(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) {
return yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z,
make_tuple(x, y, z));
});
});
});
for(auto triple : triples | view::take(10)) {
cout << '('
<< get<0>(triple) << ','
<< get<1>(triple) << ','
<< get<2>(triple) << ')' << 'n';
}
Pythagorean Triples in Ranges
Output:
(3,4,5)
(6,8,10)
(5,12,13)
(9,12,15)
(8,15,17)
(12,16,20)
(7,24,25)
(15,20,25)
(10,24,26)
(20,21,29)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-105-320.jpg)
![106
Pythagorean Triples in Ranges, reformatted
auto triples =
for_each(iota(1), [] (int z) { return
for_each(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) { return
for_each(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) { return
yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z, make_tuple(x, y, z));
}); }); });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-106-320.jpg)
![107
Looks familiar...
auto triples =
for_each(iota(1), [] (int z) { return
for_each(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) { return
for_each(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) { return
yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z, make_tuple(x, y, z));
}); }); });
iota :: list<int>
for_each :: list<int> -> (int -> list<int>) -> list<int>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-107-320.jpg)
![108
for_each → mbind...
auto triples =
mbind(iota(1), [] (int z) { return
mbind(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) { return
mbind(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) { return
yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z, make_tuple(x, y, z));
}); }); });
iota :: list<int>
for_each :: list<int> -> (int -> list<int>) -> list<int>
mbind :: list<int> -> (int -> list<int>) -> list<int>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-108-320.jpg)
![109
Monads, again??
auto triples =
mbind(iota(1), [] (int z) { return
mbind(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) { return
mbind(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) { return
yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z, make_tuple(x, y, z));
}); }); });
auto triples =
do {
int z <- iota(1);
int x <- iota(1, z+1);
int y <- iota(x, z+1);
guard (x*x + y*y == z*z);
return make_tuple(x, y, z);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-109-320.jpg)
![110
auto triples =
mbind(iota(1), [] (int z) { return
mbind(iota(1, z+1), [=](int x) { return
mbind(iota(x, z+1), [=](int y) { return
yield_if(x*x + y*y == z*z, make_tuple(x, y, z));
}); }); });
auto triples =
do {
int z <- iota(1);
int x <- iota(1, z+1);
int y <- iota(x, z+1);
guard (x*x + y*y == z*z);
return make_tuple(x, y, z);
}
Monadic Pythagorean Triples in Haskell
triples = do
z <- [1..]
x <- [1..z]
y <- [x..z]
guard (x*x + y*y == z*z)
pure (x, y, z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-110-320.jpg)


 {
const auto& [x, y, z] = t;
return make_tuple(x, y * 10, z);
};
Functional composition with ranges
Output:
(3,40,5)
(6,80,10)
(5,120,13)
(9,120,15)
(8,150,17)
(12,160,20)
(7,240,25)
(15,200,25)
(10,240,26)
(20,210,29)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-113-320.jpg)
 {
const auto& [x, y, z] = t;
return make_tuple(x, y * 10, z);
};
Functional composition with ranges
Output:
(20,210,29)
(10,240,26)
(15,200,25)
(7,240,25)
(12,160,20)
(8,150,17)
(9,120,15)
(5,120,13)
(6,80,10)
(3,40,5)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190219105615/85/The-Present-and-The-Future-of-Functional-Programming-in-C-114-320.jpg)