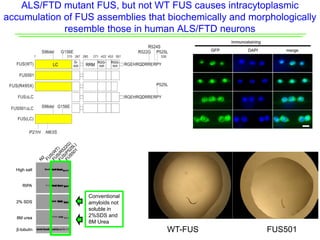
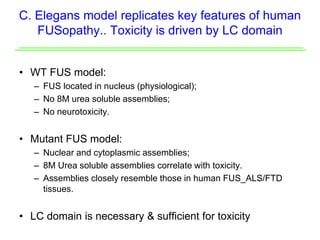
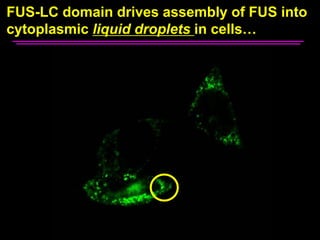
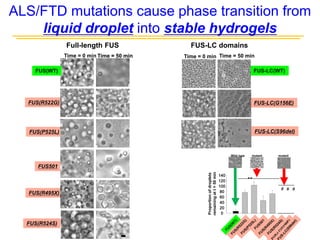
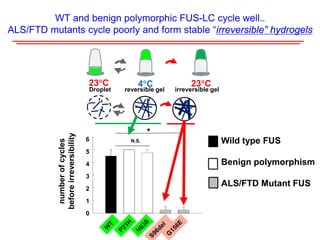
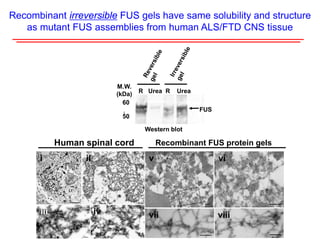
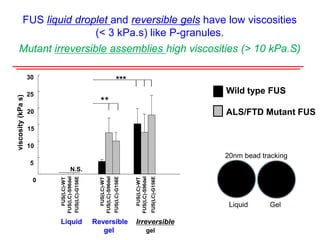
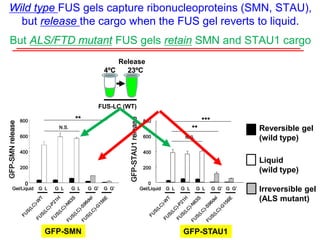
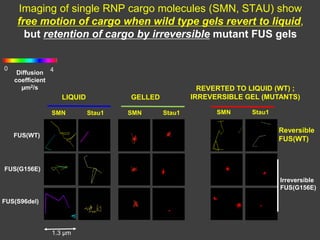
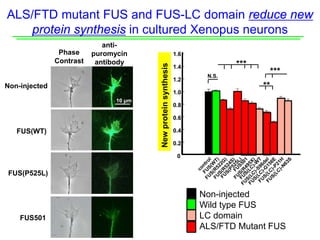
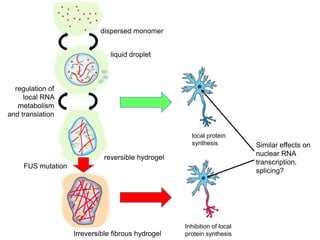
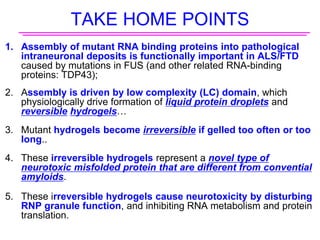
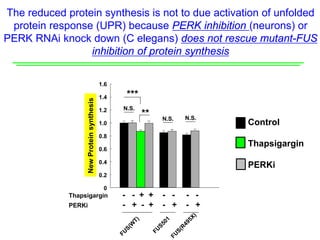
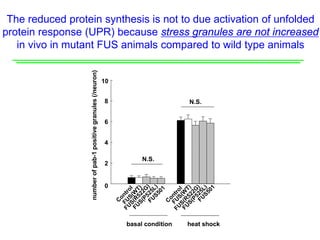
The document explores the role of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration, specifically focusing on the effects of mutant FUS proteins in ALS/FTD using a C. elegans model. Findings indicate that low complexity (LC) domains of FUS drive the formation of toxic hydrogel assemblies that disrupt RNA metabolism and protein synthesis. These assemblies differ from conventional amyloids and present a novel neurotoxic mechanism linked to pathologies in ALS/FTD.