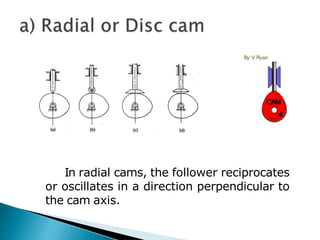
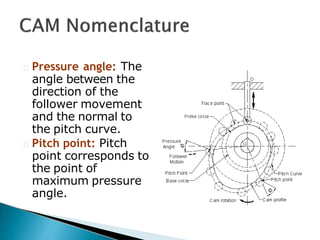
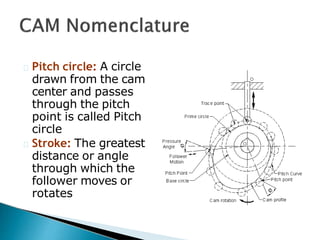
Cams are used to convert rotary motion to oscillatory motion or vice versa. They are commonly used in internal combustion engines to operate inlet and exhaust valves. The objectives of this chapter are to learn fundamental cam concepts and how to design cams. Cams can be classified based on their input/output motion types and shapes. Followers are the elements that receive motion from cams and can have different shapes. Key terms related to cam design include the cam profile, base circle, trace point, pitch curve, prime circle, pressure angle, and pitch point.