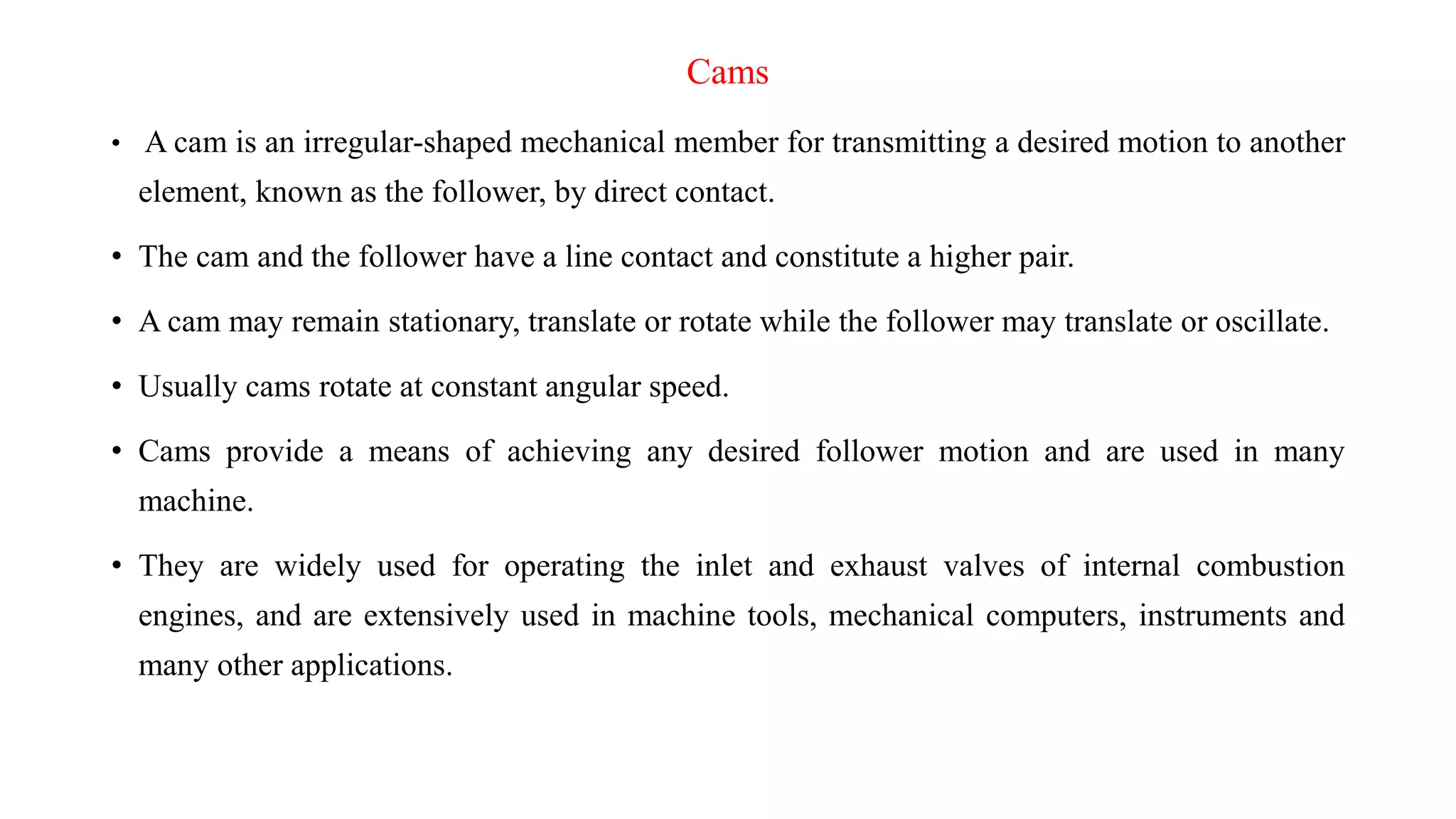
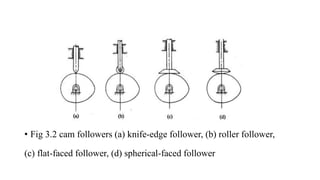
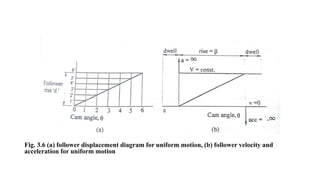
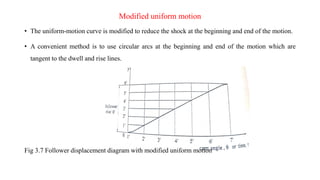
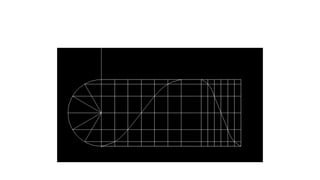
A cam is a mechanical device used to convert rotational motion into linear or oscillating motion. It works through direct contact with a follower. Cams can be classified based on the follower's surface, type of motion, and position relative to the cam's center. Common follower surfaces include knife-edge, roller, and flat or spherical faces. Follower motion may be translatory, oscillatory, or a combination. The document provides examples of displacement diagrams and motions including uniform, modified uniform, parabolic, simple harmonic, and cycloidal. It also defines cam nomenclature and describes the process for designing a cam profile based on a given follower motion specification.