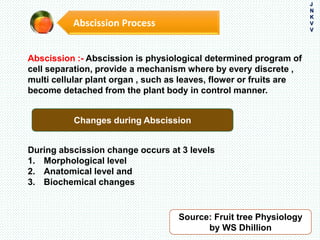
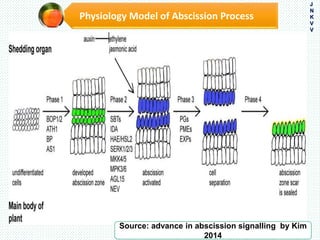
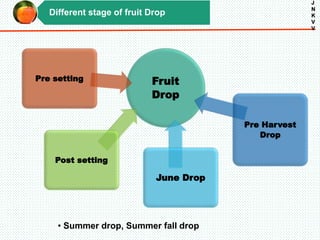
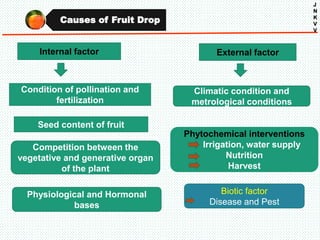
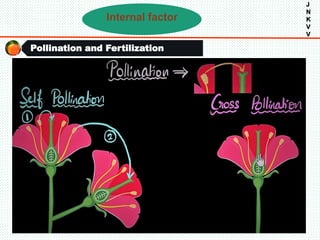
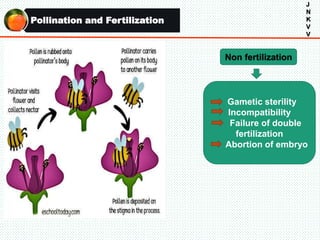
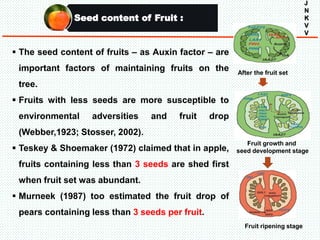
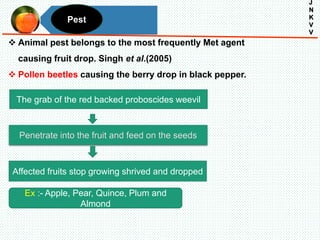
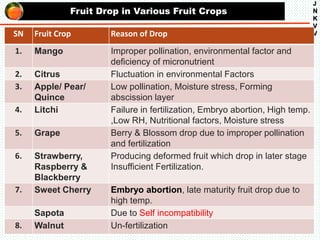
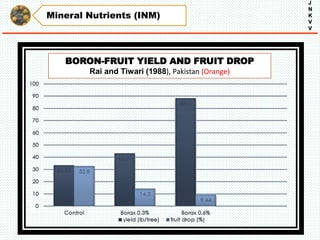
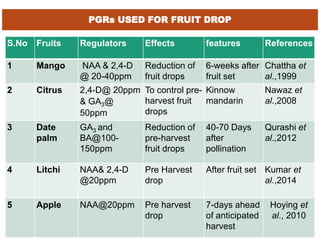
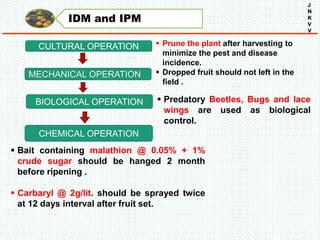
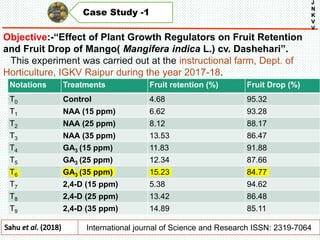
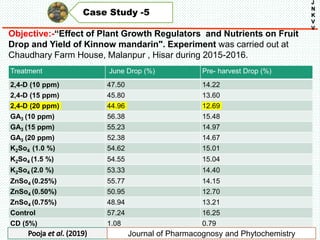
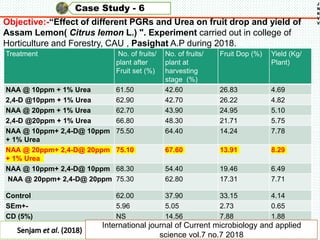
The document discusses the problem of fruit drop in various fruit crops, outlining its causes, types, and potential remedies. It explains the physiological process of abscission responsible for fruit drop and identifies internal and external factors influencing this issue. Case studies are provided to illustrate the effects of plant growth regulators and nutrient applications on fruit retention and drop rates in specific fruit varieties.