Embed presentation
Download as DOCX, PPTX



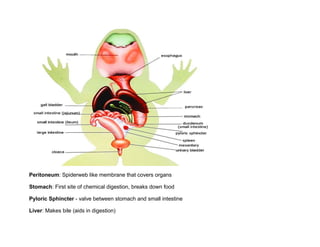

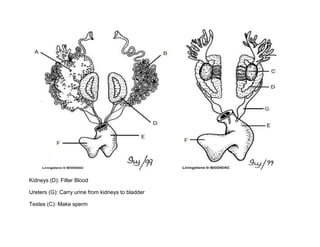

The document summarizes the anatomy of a frog through a dissection. It describes the major external features of the mouth, including the vomerine and maxillary teeth used for holding prey, as well as the internal nares, eustachian tubes, glottis, esophagus, and tongue. Internally, it outlines the organs of the abdominal cavity such as the peritoneum, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small and large intestines, mesentery, and cloaca. It also provides an overview of the urogenital system including the kidneys, ureters, testes, oviducts, ovary, urinary bladder, and cloaca.






