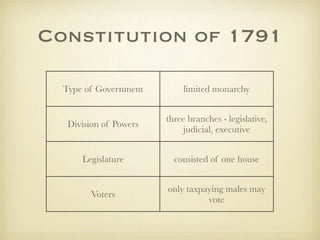
The document summarizes key events of the French Revolution including the "Great Fear" peasant uprising, the storming of the Bastille, emigres fleeing the country and plotting against the revolution, the women's march on Versailles, reforms establishing departments and elections, the Declaration of Rights of Man, the limited constitutional monarchy established in 1791, foreign invasion threatening France, and the end of the monarchy.