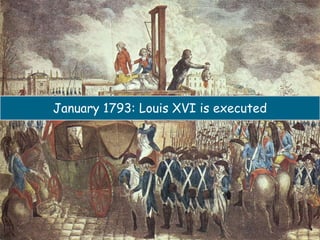The French Revolution overthrew the Estates system of the ancient regime, establishing a constitutional monarchy but eventually becoming a republic led by Maximilien Robespierre. Financial distress from war debts and poor harvests led to unrest among the Third Estate, who stormed the Bastille and established the National Assembly. The Assembly abolished feudalism and established civil liberties and rights of man, though the monarchy was eventually overthrown and Louis XVI was executed during the Reign of Terror led by Robespierre. The Revolution transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic and influenced other revolutions around the world.