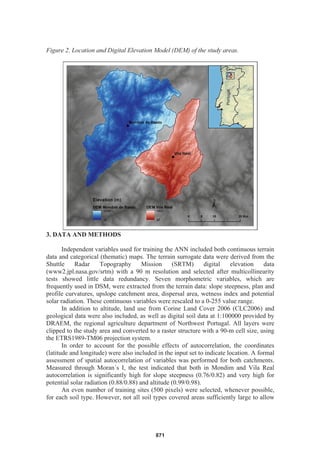
This document discusses the importance of sampling design for the accuracy of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in digital soil mapping. It evaluates the impact of different training site sampling methods on ANN predictive accuracy in two study areas in Portugal. Results show that sampling method significantly affects ANN performance, with stratified sampling reflecting spatial autocorrelation of soil properties achieving the highest accuracy. Sampling training sites close together based on their spatial relationship learns faster than random sampling, allowing the ANN model to converge to a better solution more quickly. The predictive accuracy of ANNs for soil mapping is highly dependent on the sampling approach used to select training data.