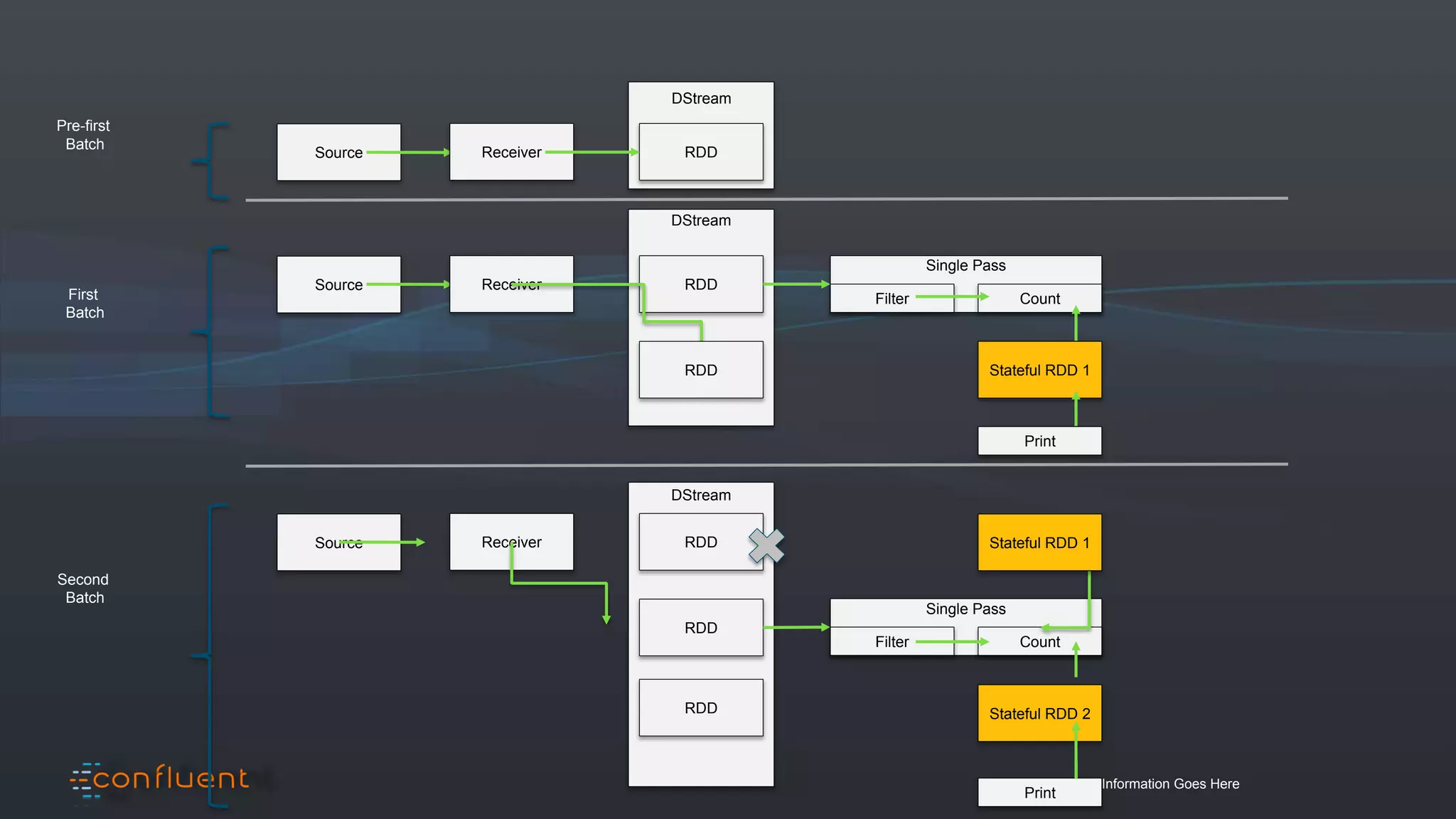
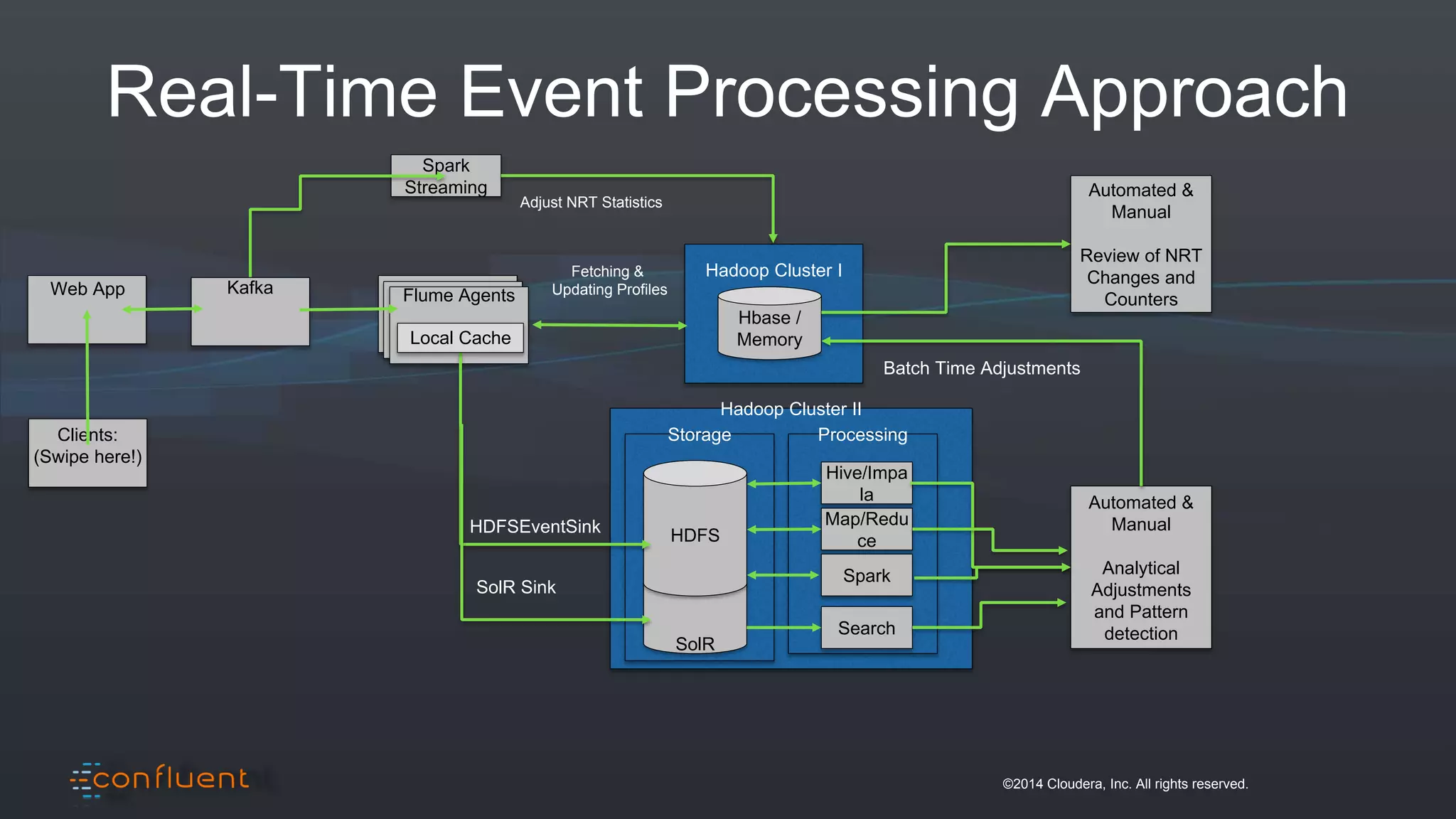
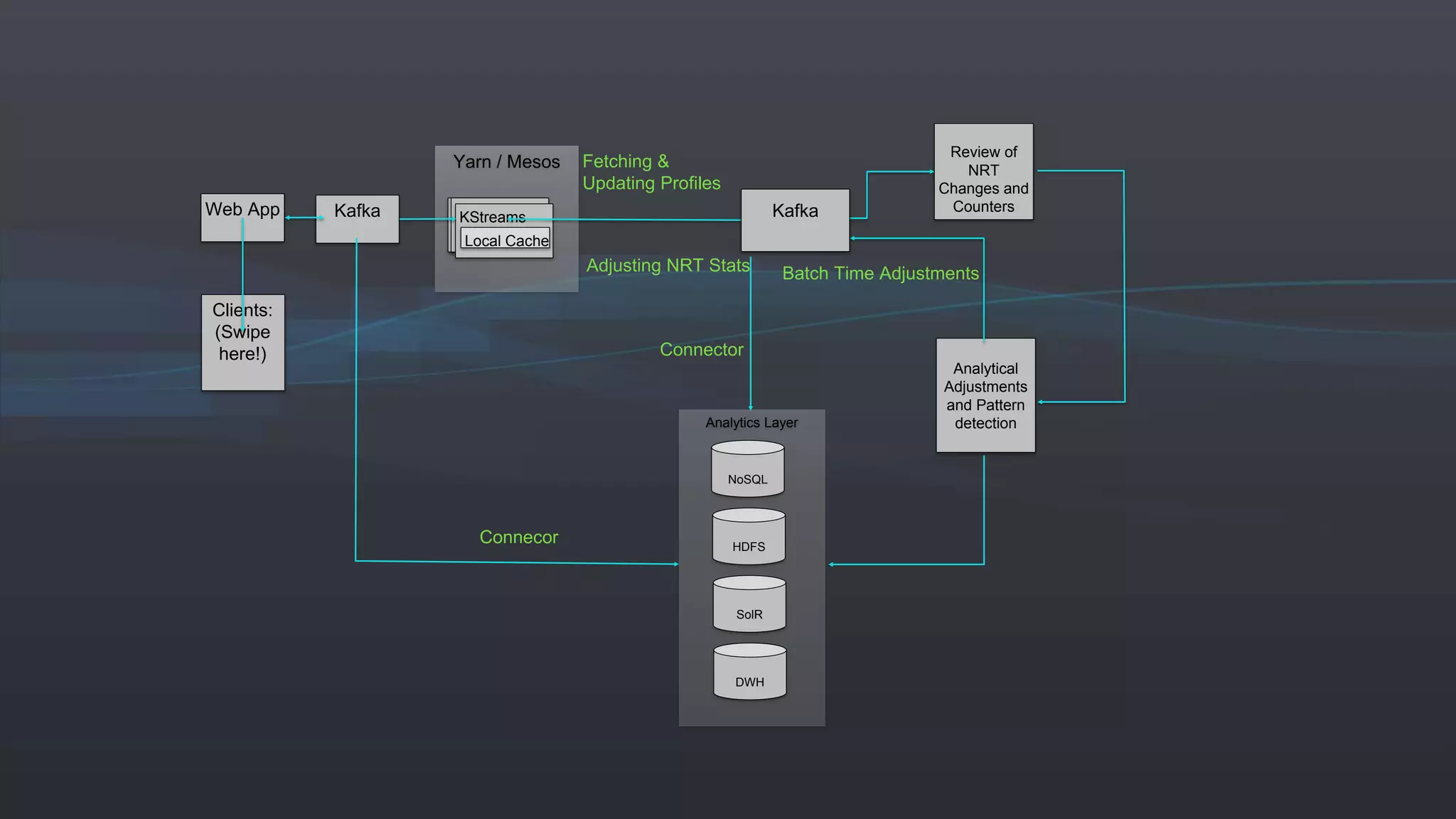
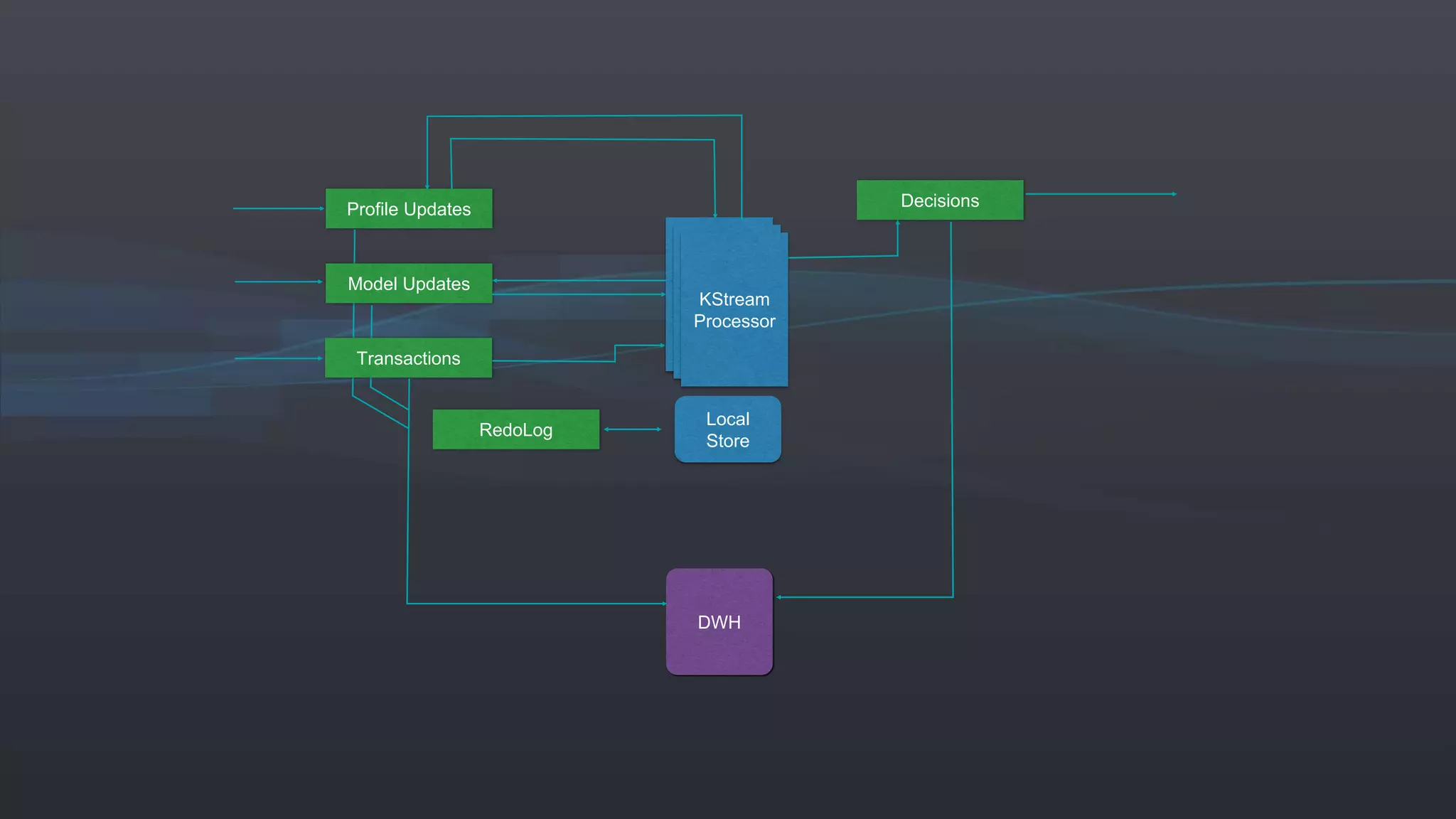
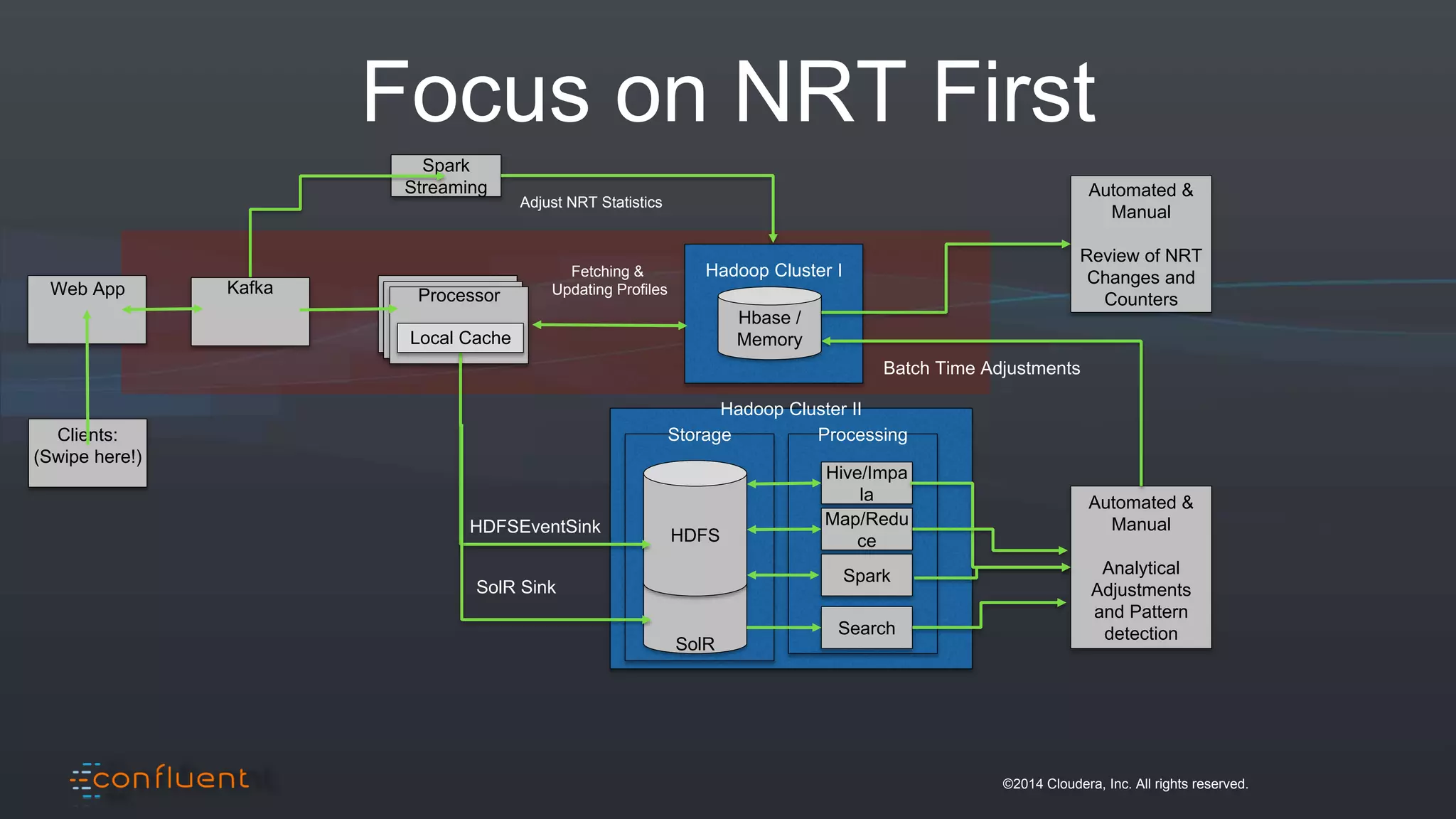
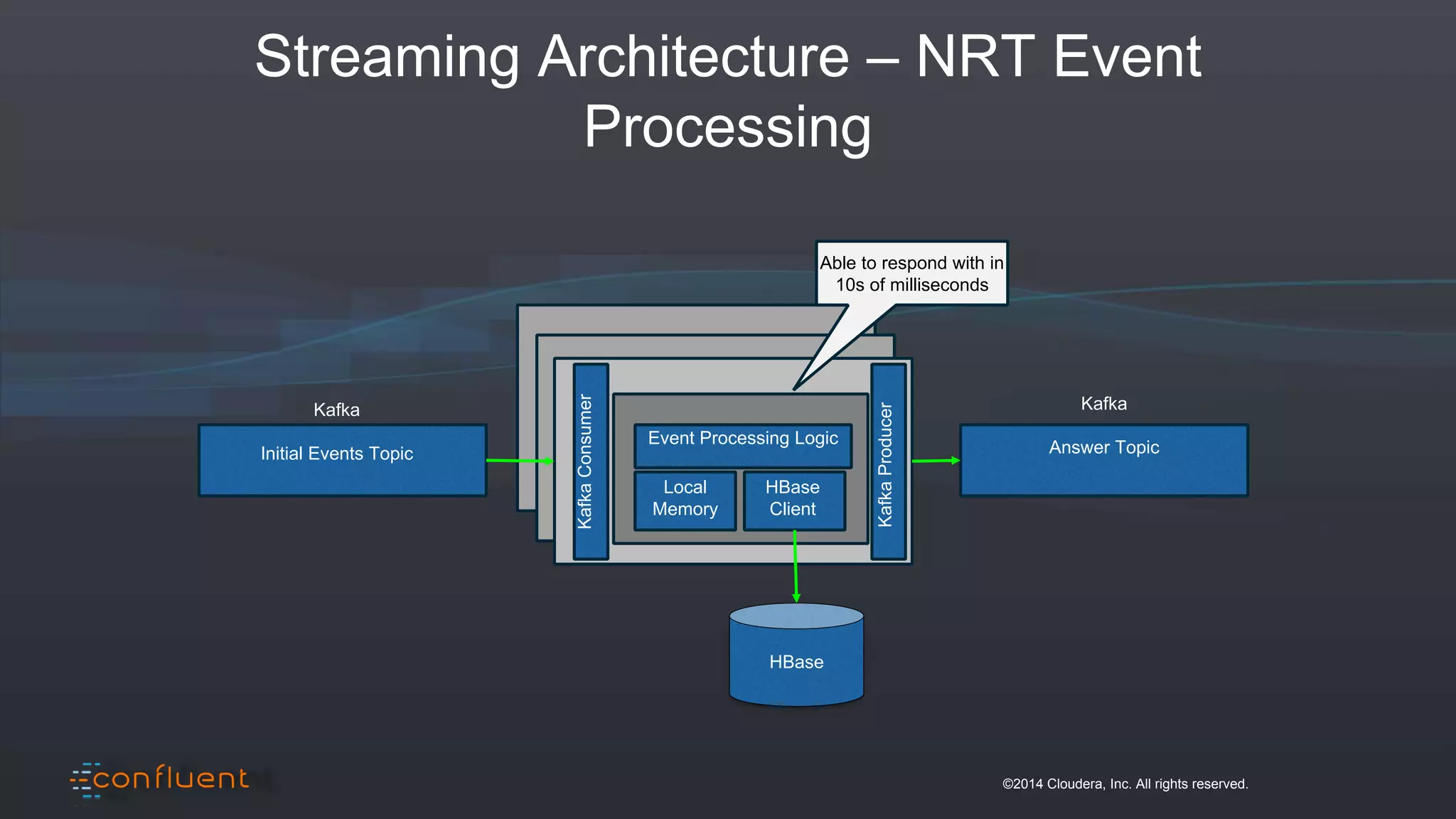
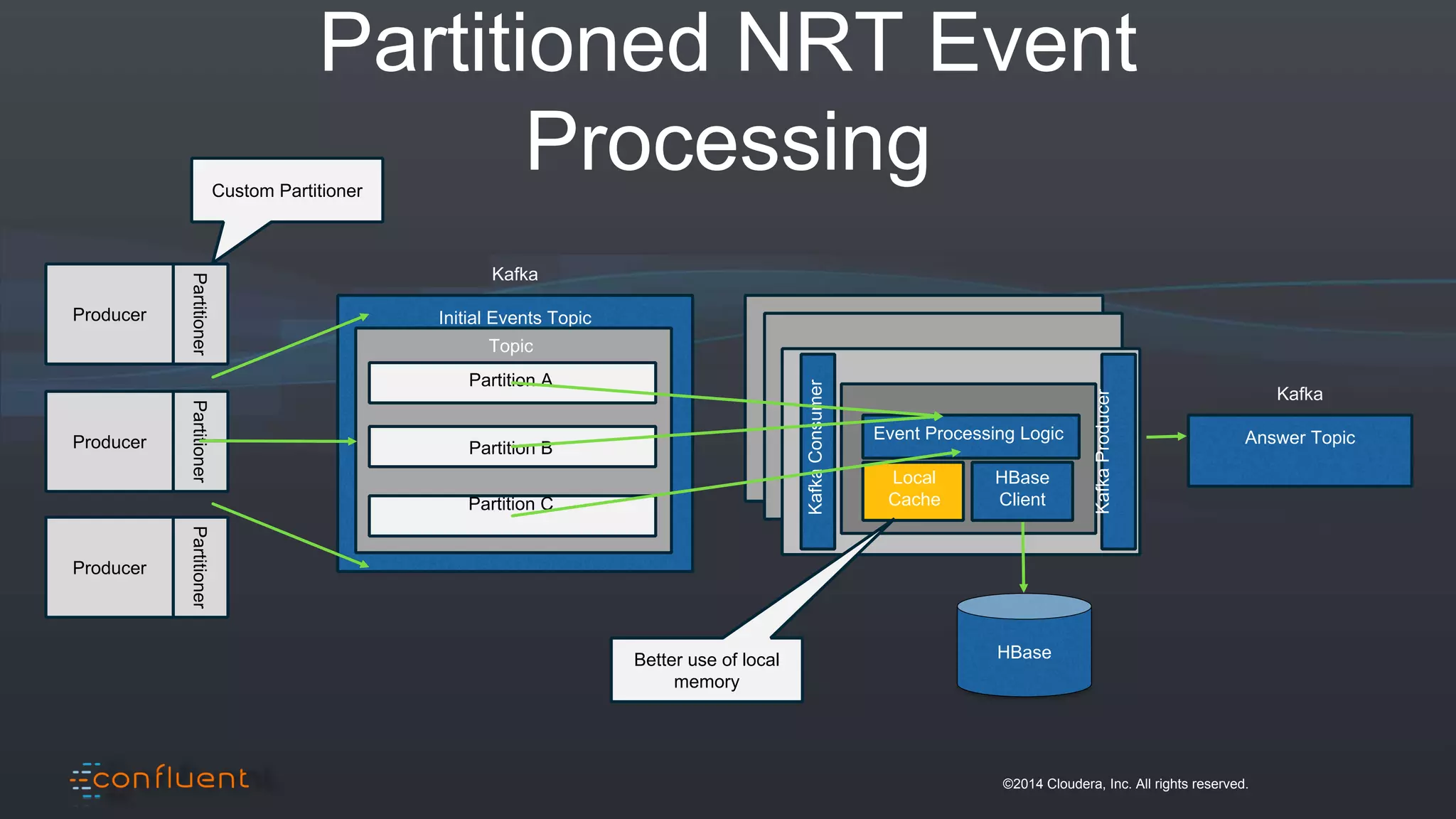
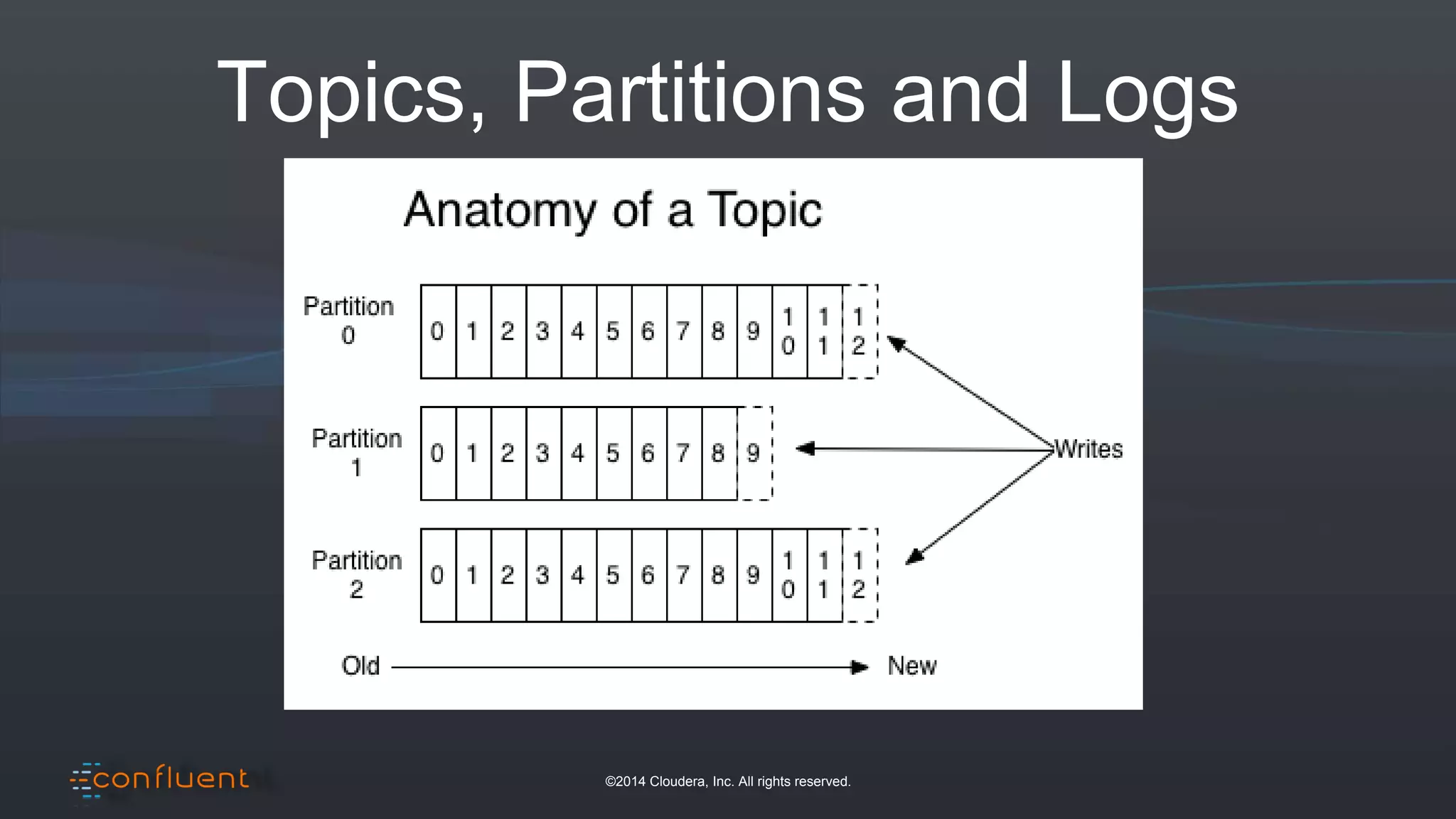
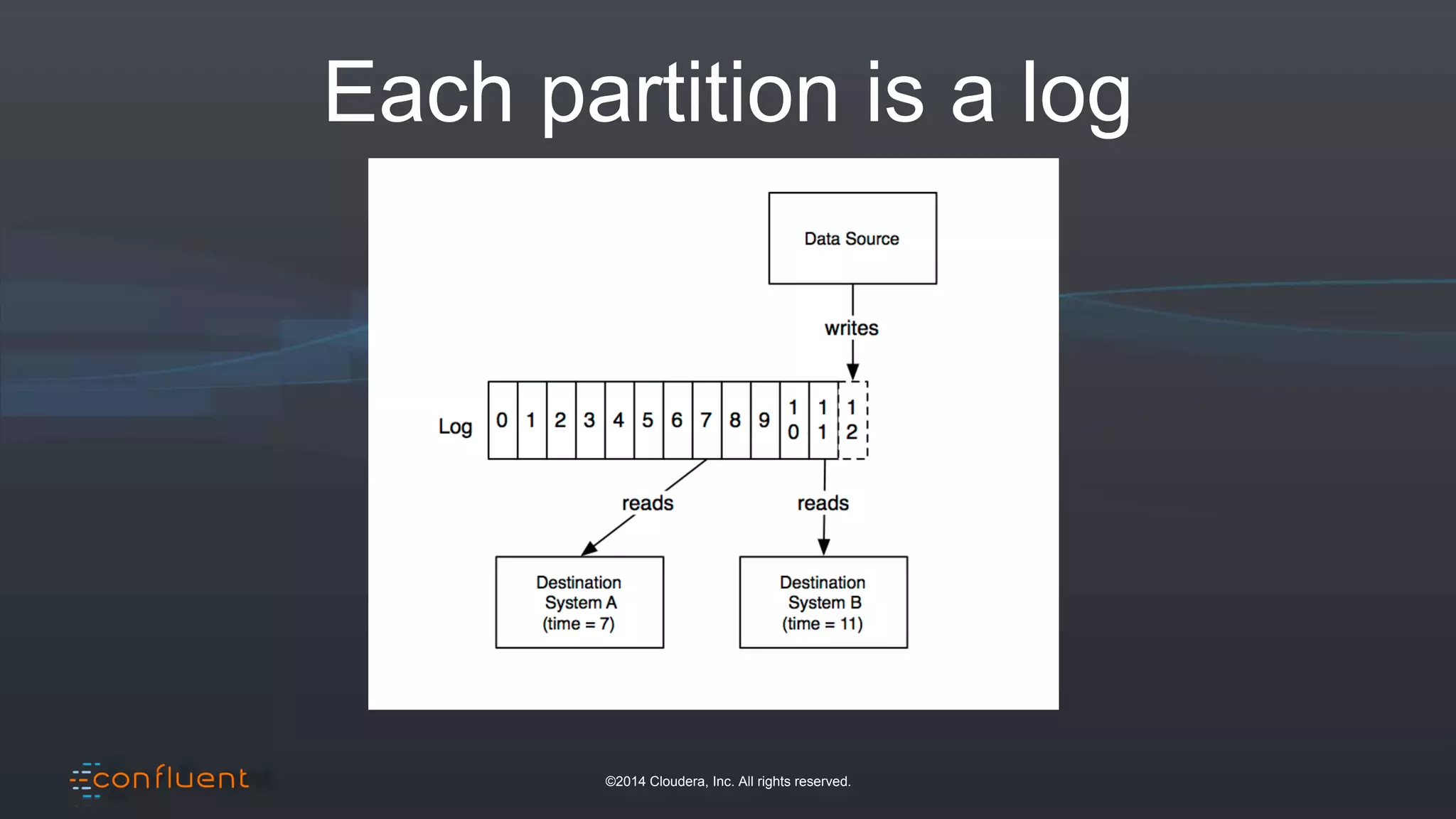
The document presents an overview of real-time anomaly detection using technologies like Kafka and Spark, focusing on high-level architecture and processing methodologies. It discusses various key technologies essential for handling stream data, including producers, consumers, and their operational structure. Additionally, it outlines the challenges posed by different types of fraud and emphasizes the importance of effective data management and analytics in addressing these issues.



















![©2014 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved.
Spark Example
1. val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]”)
2. val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
3. val lines = sc.textFile(path, 2)
4. val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
5. val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
6. val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
7. wordCounts.print()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/frauddetection-forisraelwebinar-160225183246/75/Fraud-Detection-for-Israel-BigThings-Meetup-29-2048.jpg)
![©2014 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved.
Spark Streaming Example
1. val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]”)
2. val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
3. val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
4. val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
5. val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
6. val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
7. wordCounts.print()
8. SSC.start()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/frauddetection-forisraelwebinar-160225183246/75/Fraud-Detection-for-Israel-BigThings-Meetup-30-2048.jpg)