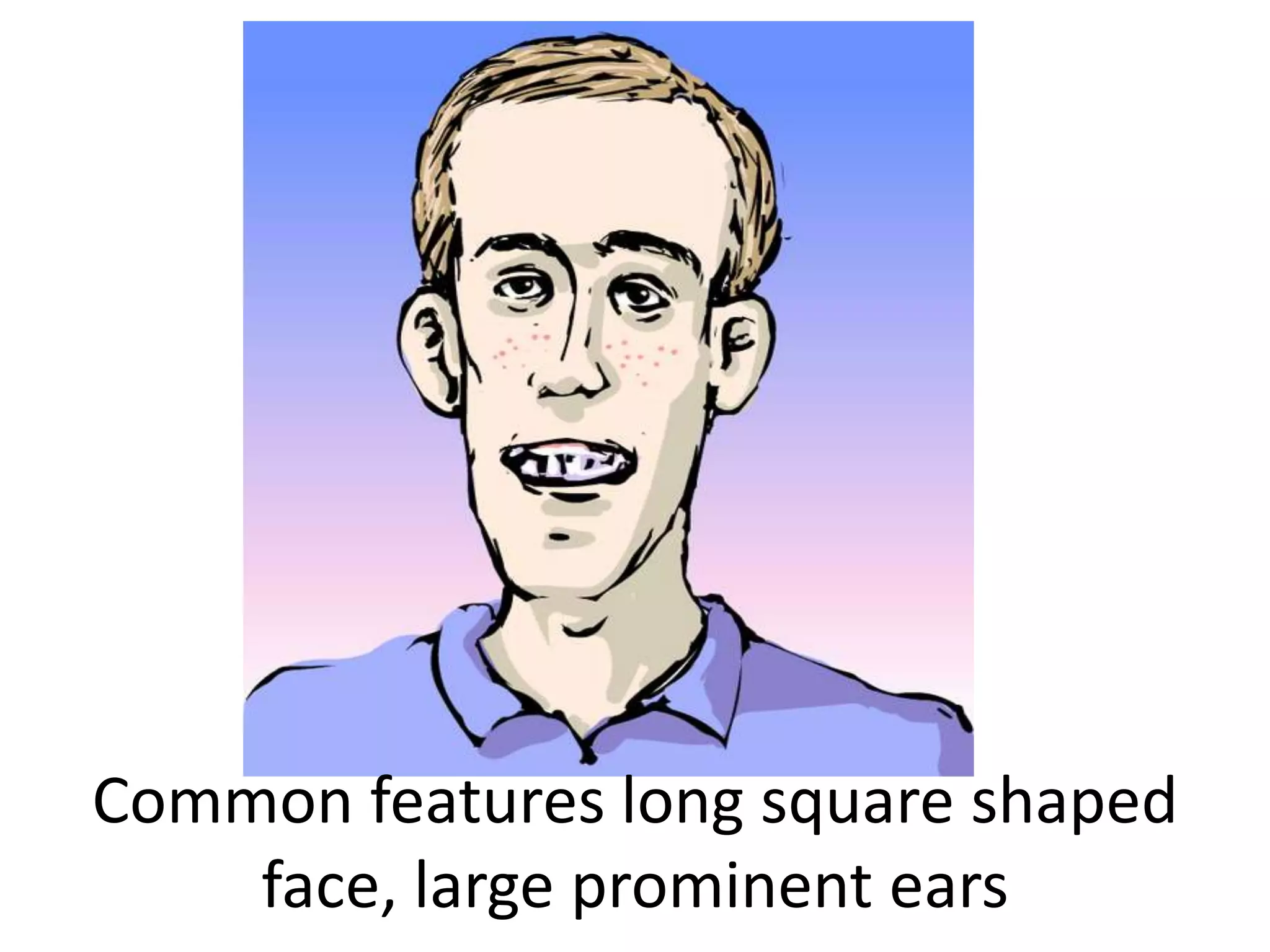
The two brothers presented with moderate to severe developmental delays and were referred to the hospital for evaluation. They exhibited features such as long square faces, prominent ears, hyperactivity, poor attention spans, and mental retardation. Their mother's aunt also displayed mental retardation. A diagnosis of fragile X syndrome was suggested due to the familial inheritance pattern and common features presented. Fragile X syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene, specifically the expansion of the CGG repeat sequence in this gene beyond normal limits. Prenatal diagnosis can be done via analysis of DNA from fetal tissue samples to detect the CGG repeat expansion.