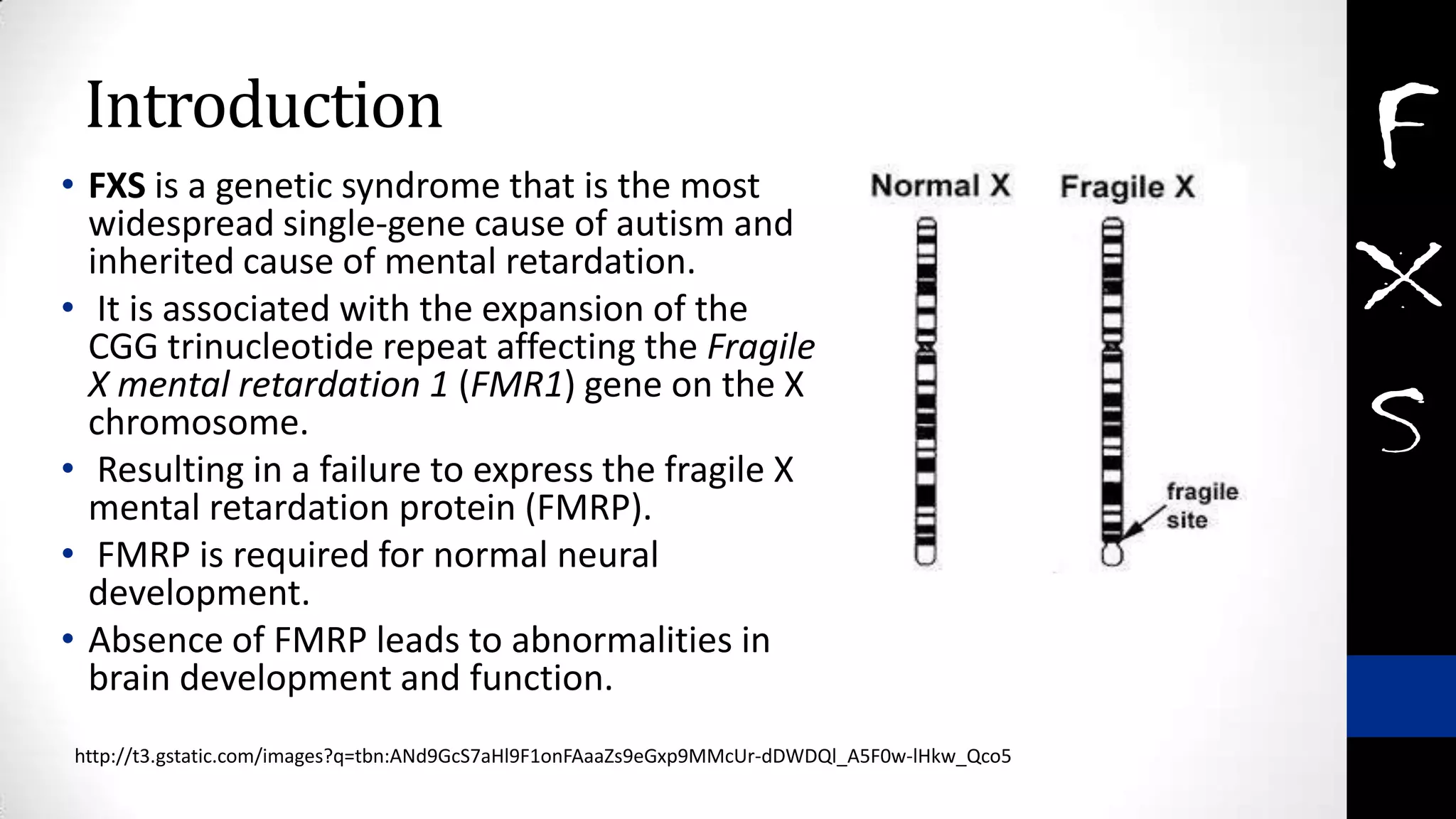
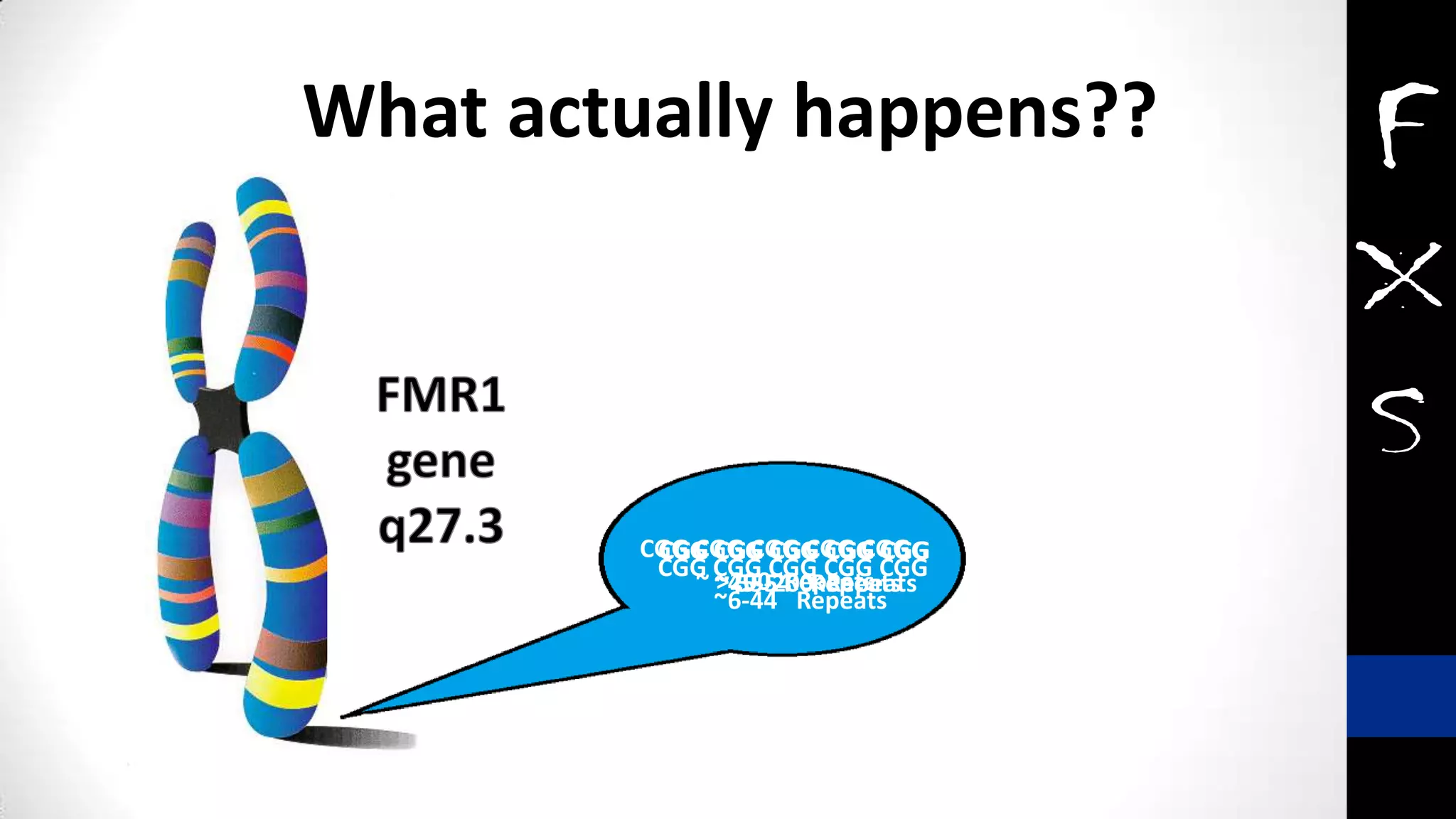
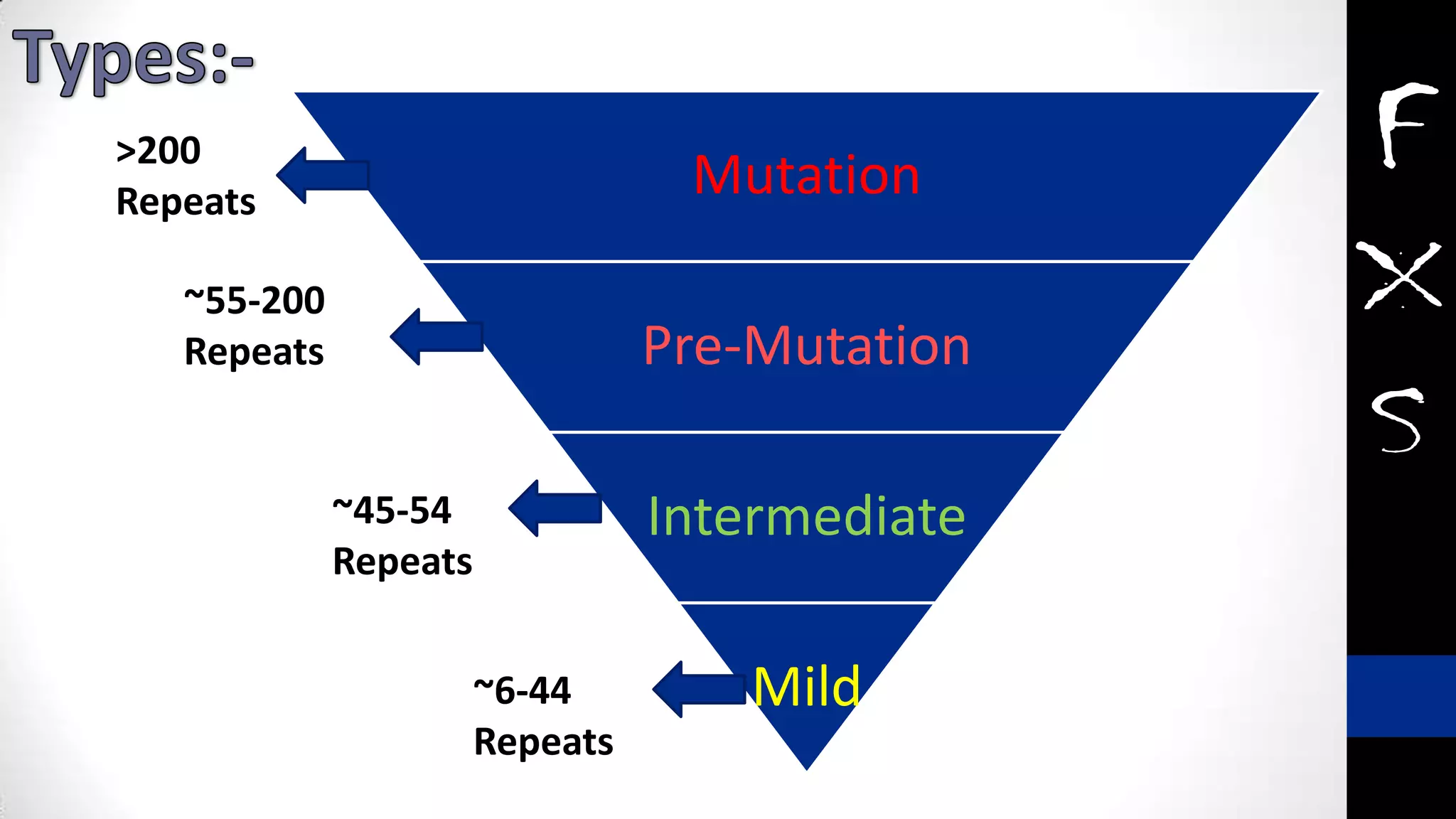
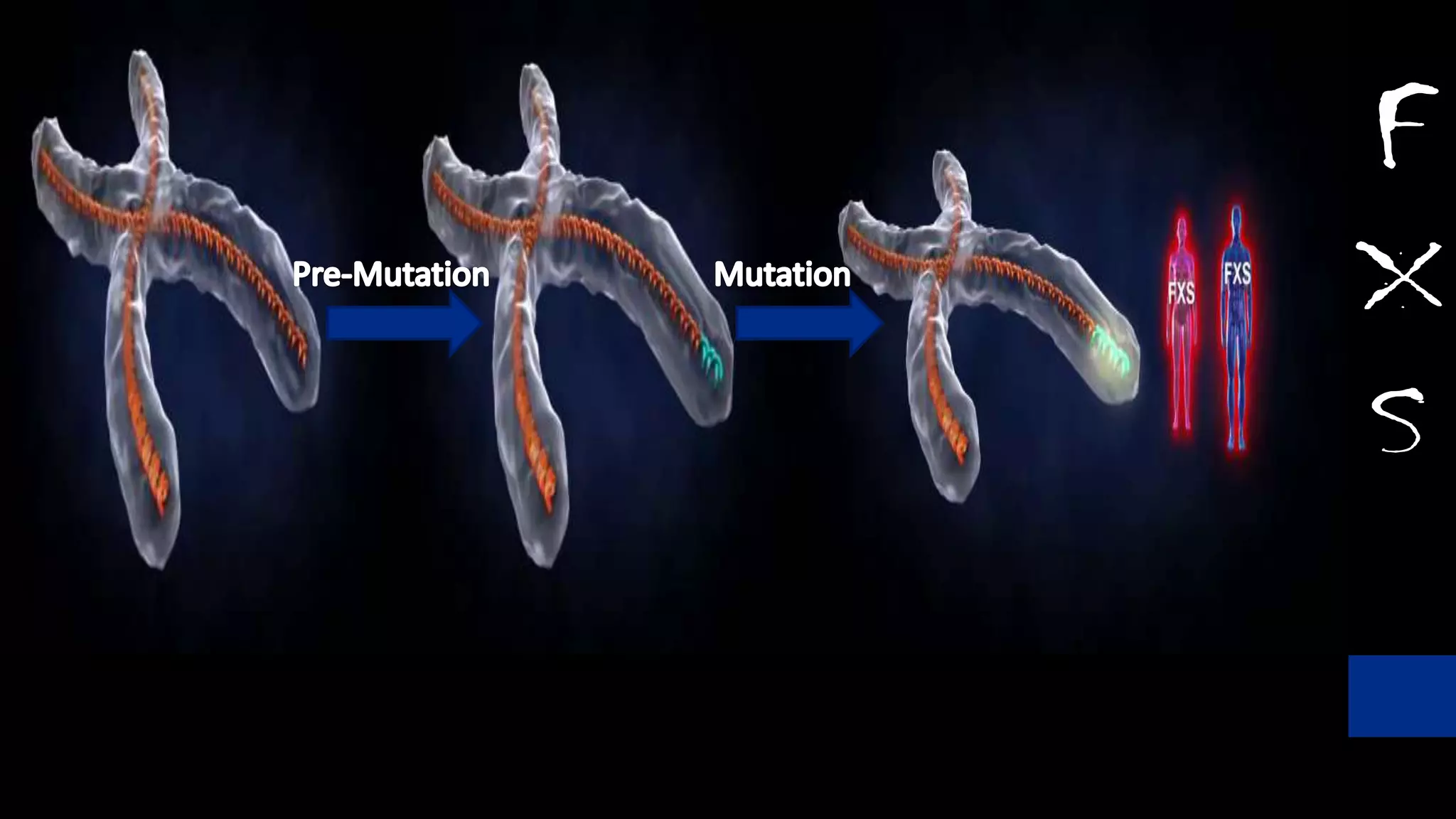
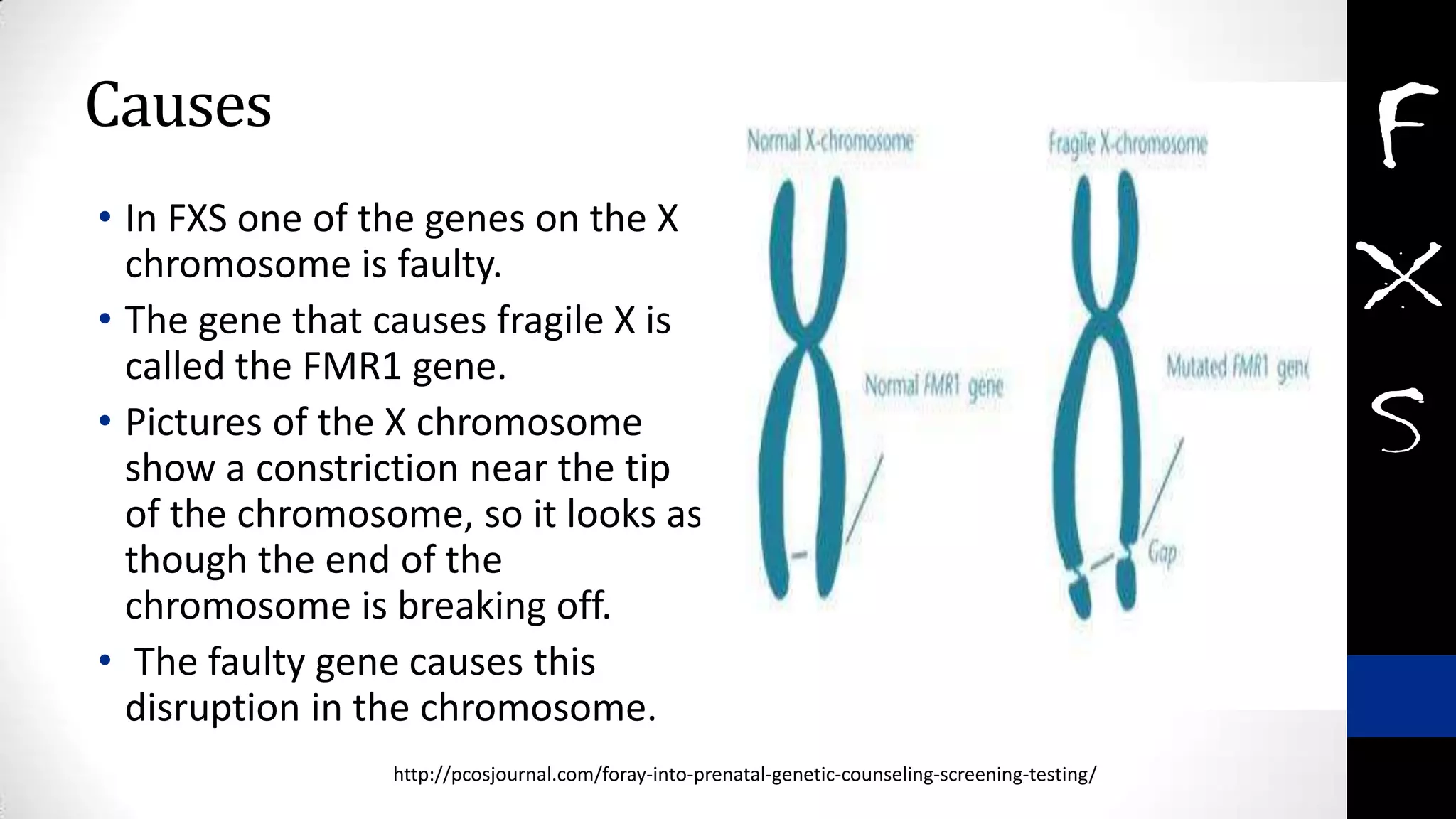
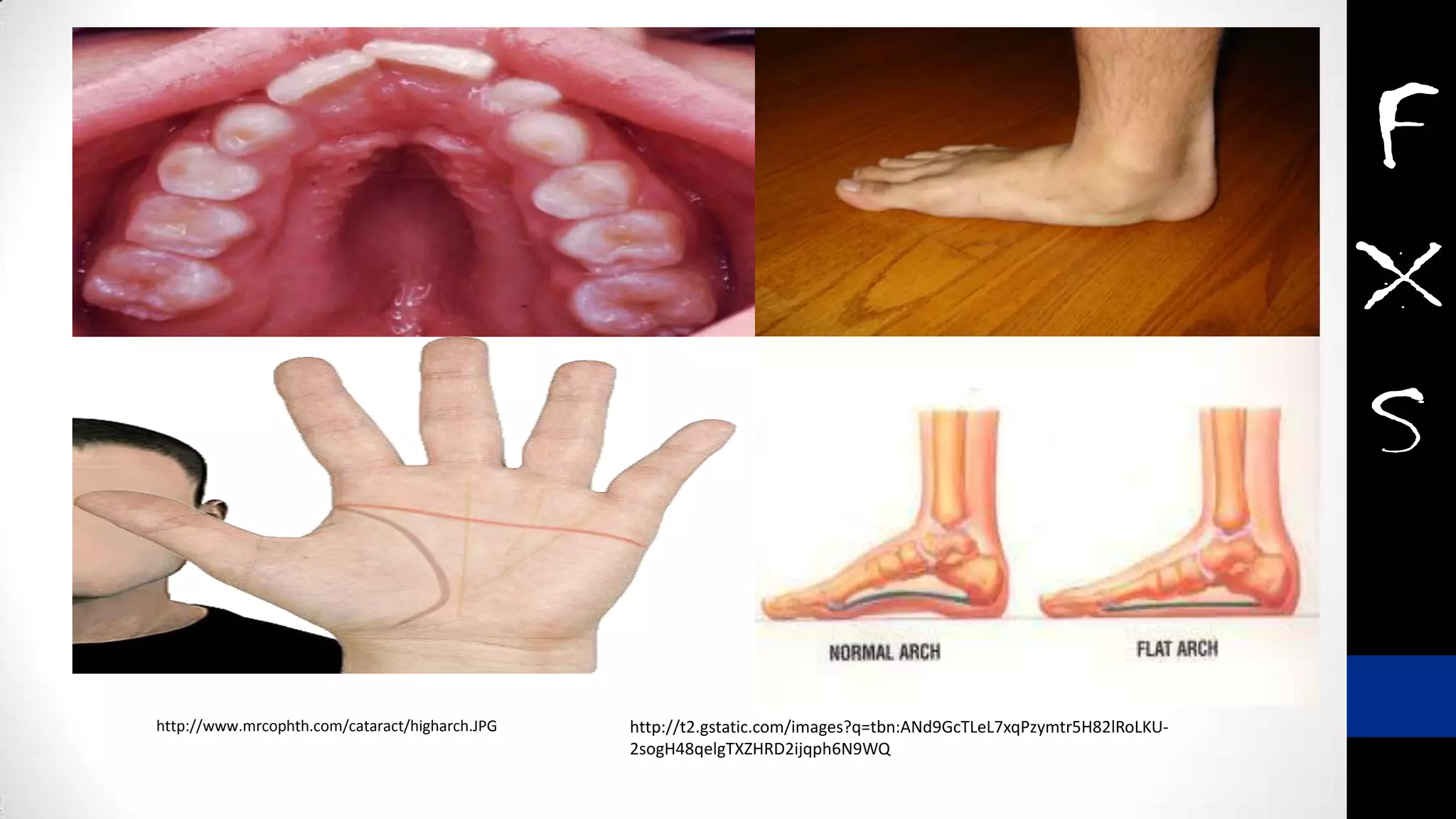
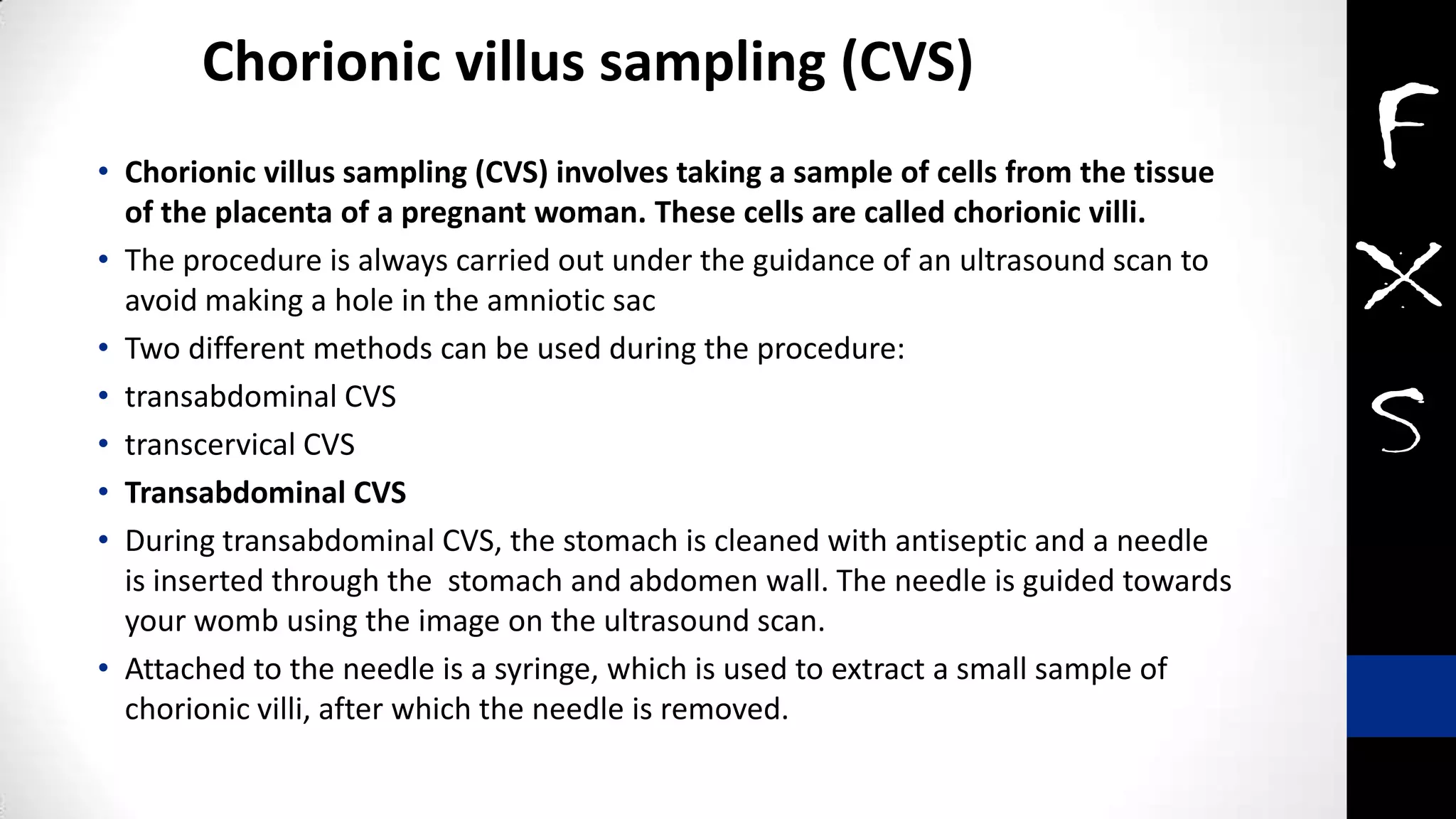
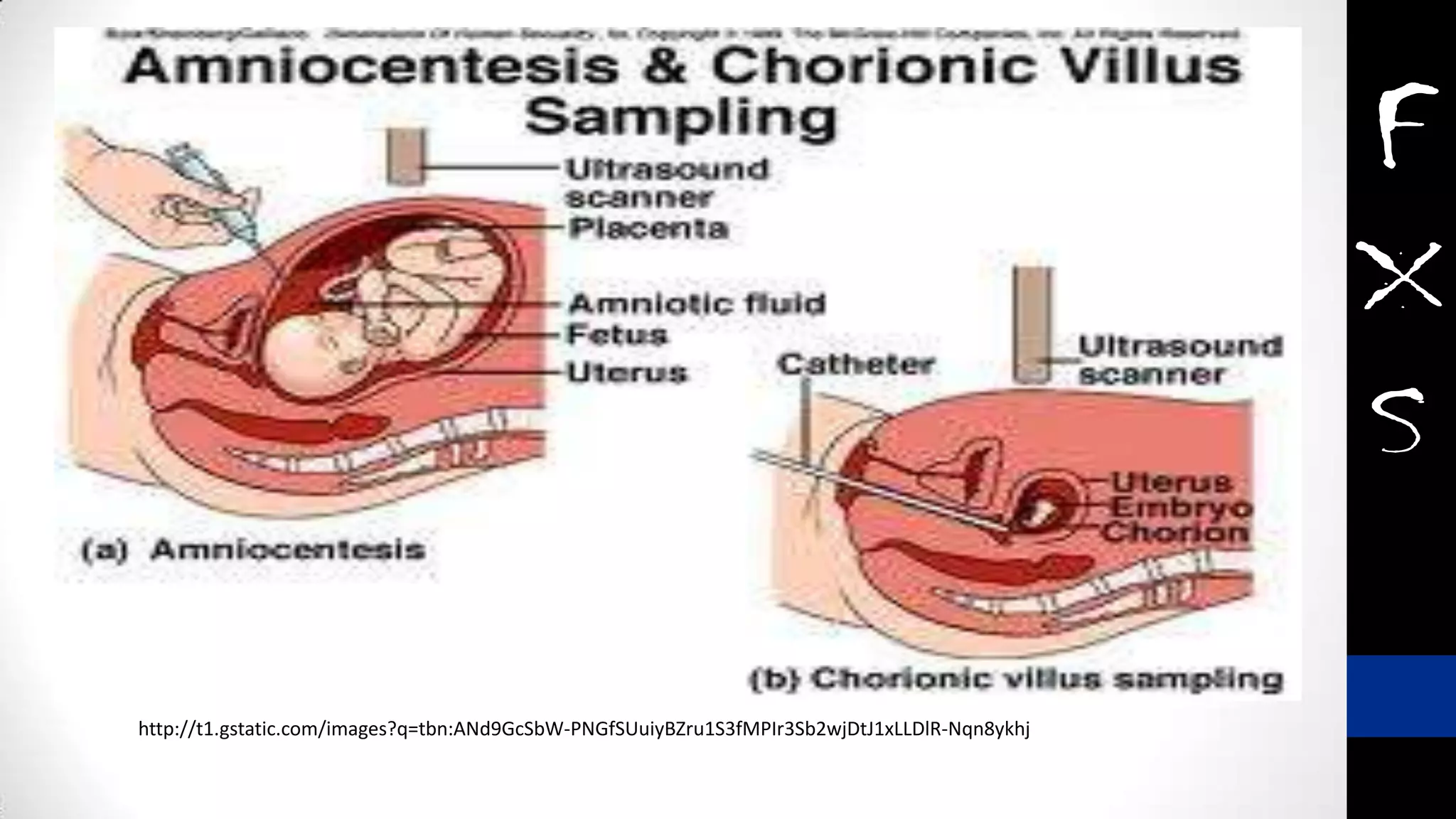
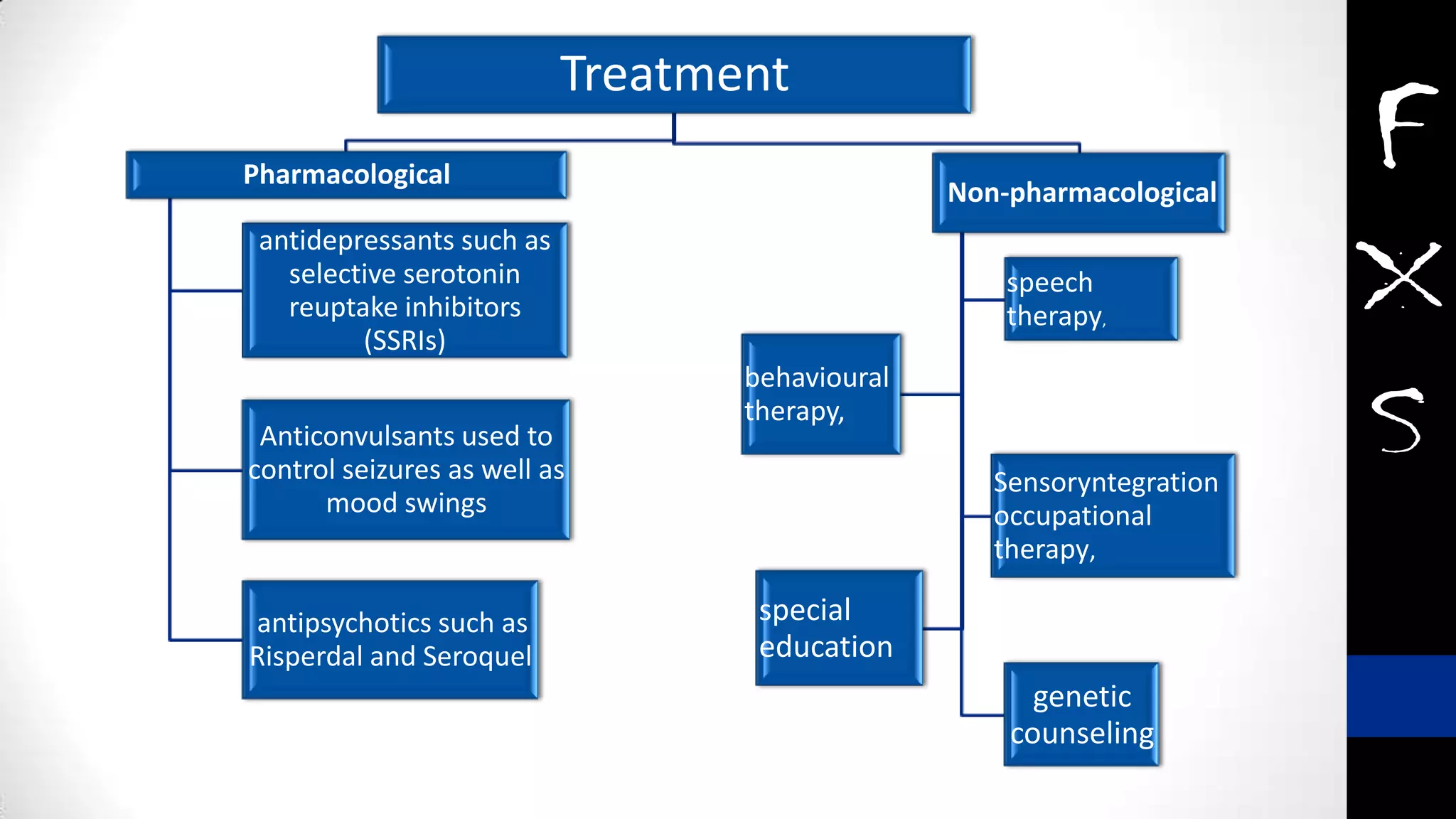
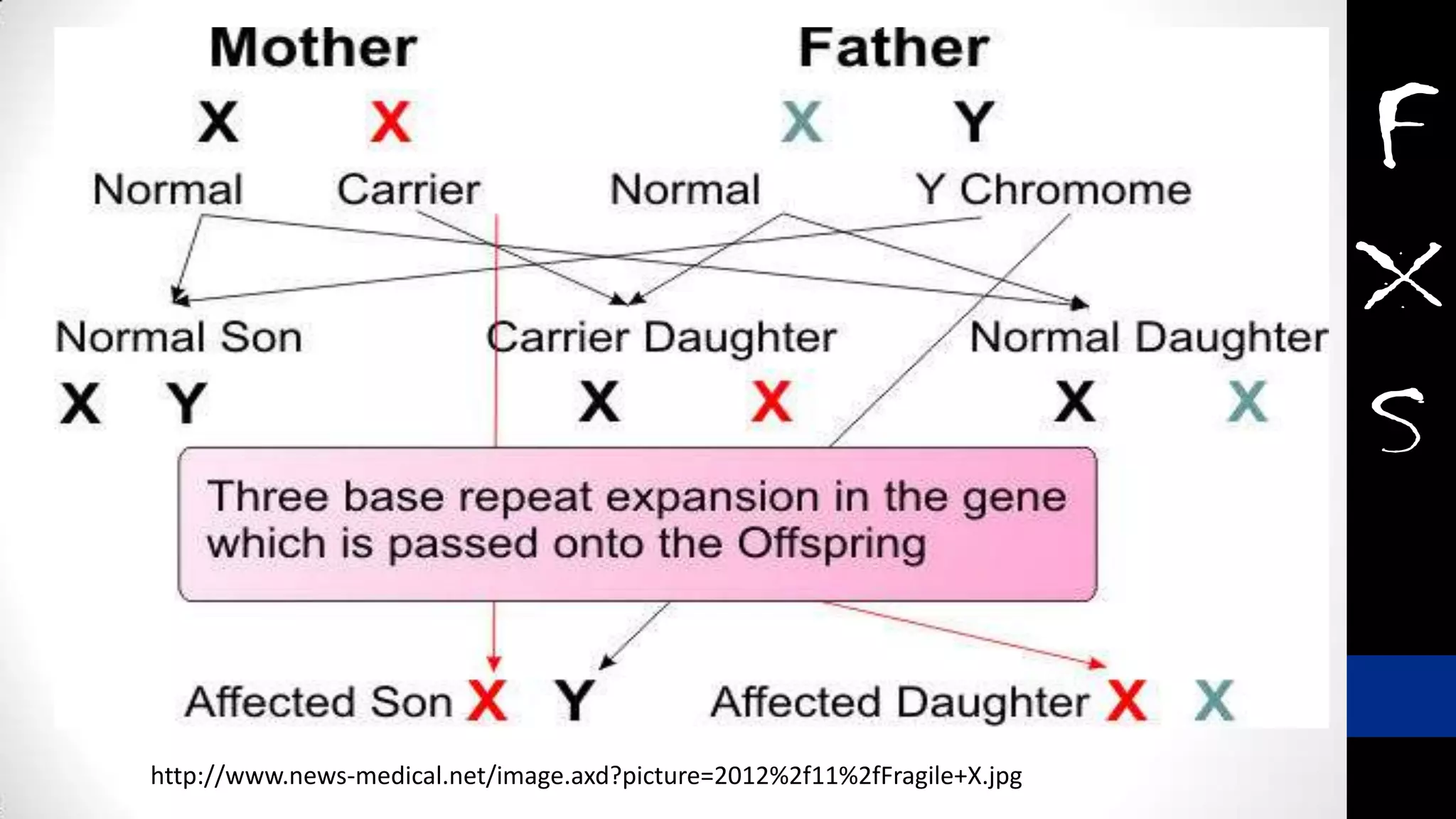
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition and the most common inherited cause of intellectual disability. It is caused by a mutation on the X chromosome that results in reduced production of the FMRP protein, important for neural development. Signs may include prominent ears, long face, joint flexibility, and cognitive impairment. Diagnosis is made through genetic testing. While there is no cure, treatment aims to manage symptoms through education, therapy and medication. Ongoing research studies new drugs that target underlying mechanisms.