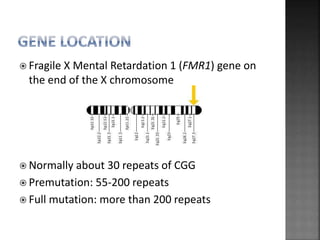
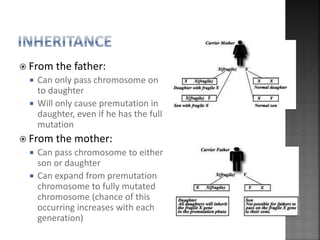
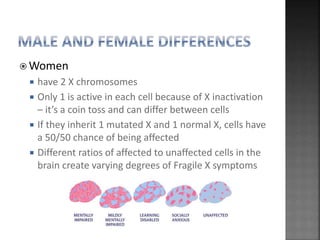
This document summarizes Fragile X syndrome. It is caused by a mutation on the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome, which normally produces a protein involved in brain development and function. Fragile X syndrome is characterized by intellectual disabilities and certain physical traits. While there is no cure, treatment aims to manage symptoms through educational and therapeutic interventions, as well as medication in some cases.