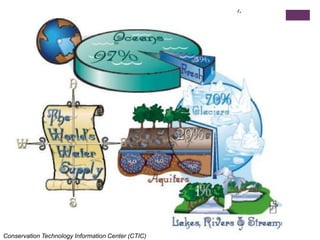
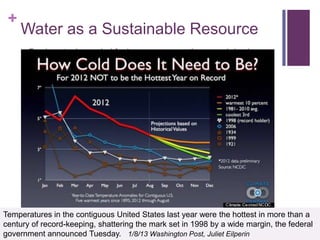
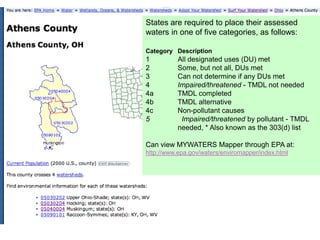
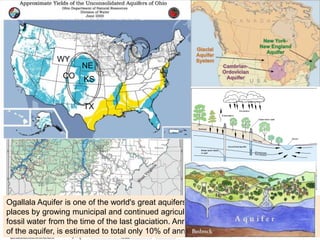
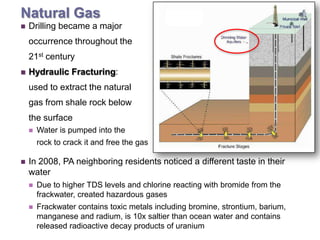
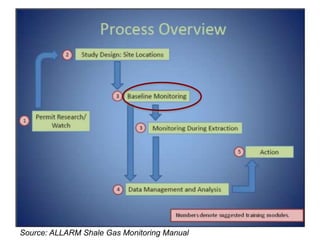
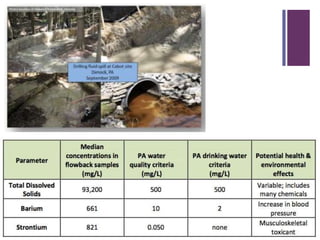
This document discusses the impacts of hydraulic fracturing or "fracking" on water quality and drought conditions. It provides background on fracking processes and chemicals used. It also summarizes recent drought conditions across the US and their effects. The document expresses concerns that fracking poses risks to water supplies by contaminating groundwater and exacerbating water scarcity issues. It notes various protests and studies that have linked fracking to water pollution and earthquakes.