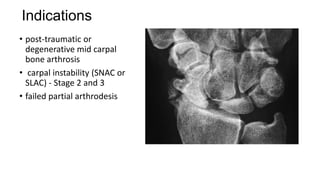
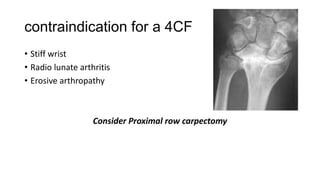
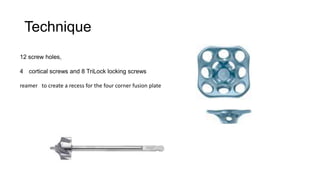
Four Corner Fusion is a surgical procedure used to treat carpal instability and arthritis. It involves fusing together the four small carpal bones (scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform) through bone preparation, temporary fixation with K-wires, and permanent fixation with a plate and screws. The procedure aims to reduce pain, maintain range of motion and grip strength, and allow activities of daily living. Contraindications include a stiff wrist, radiolunate arthritis, or erosive arthropathy, which may be better treated with proximal row carpectomy.