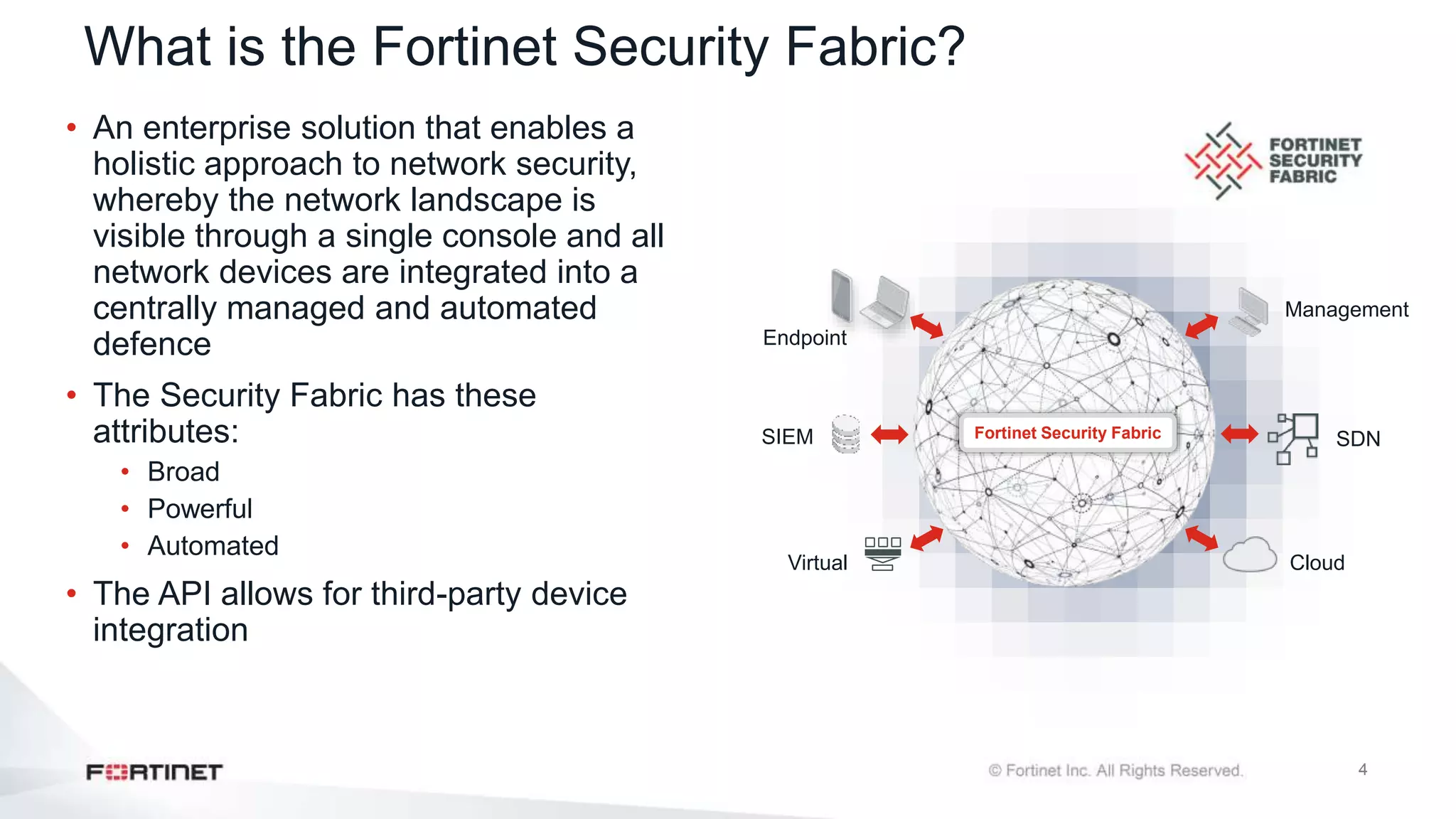
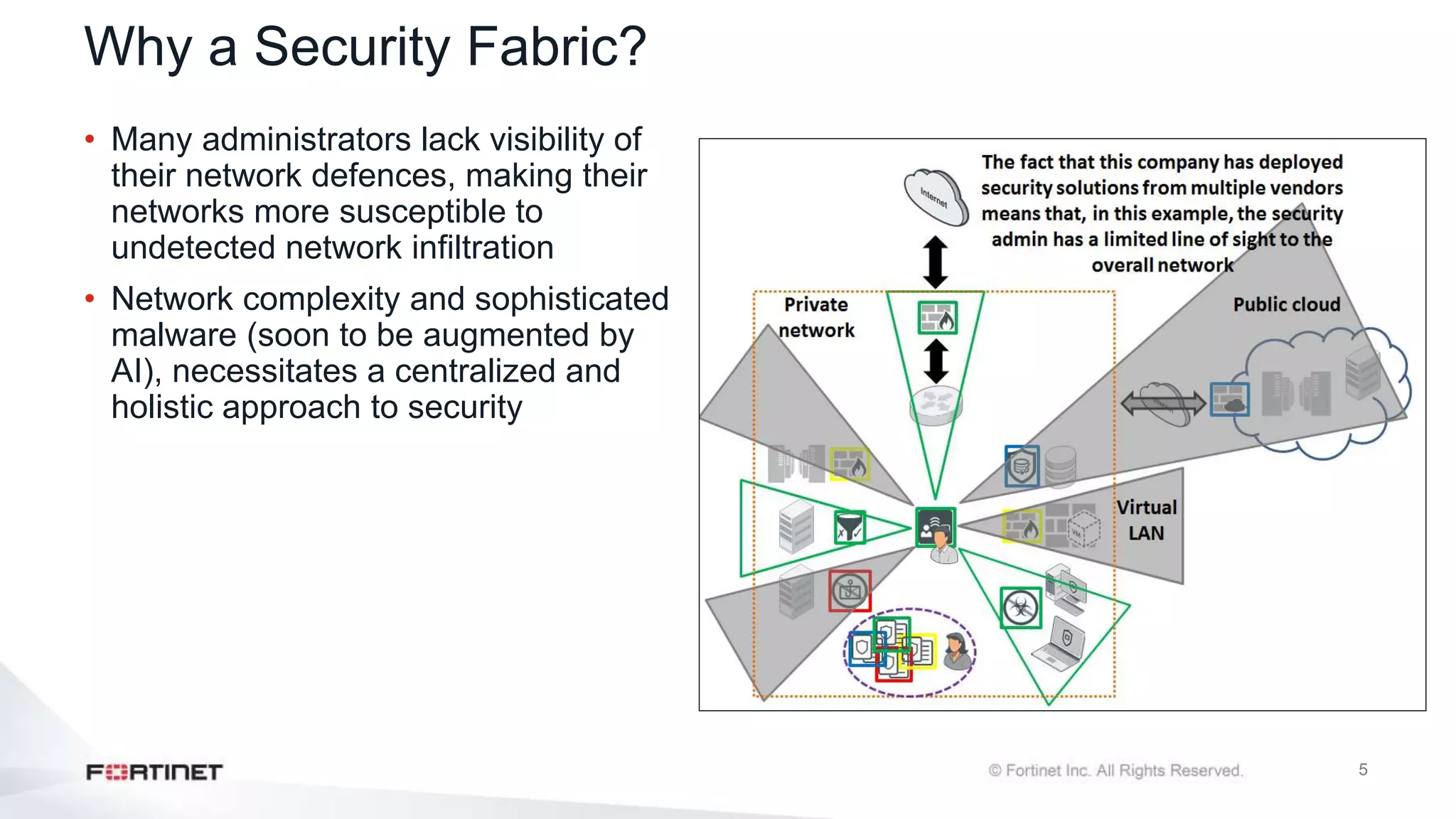
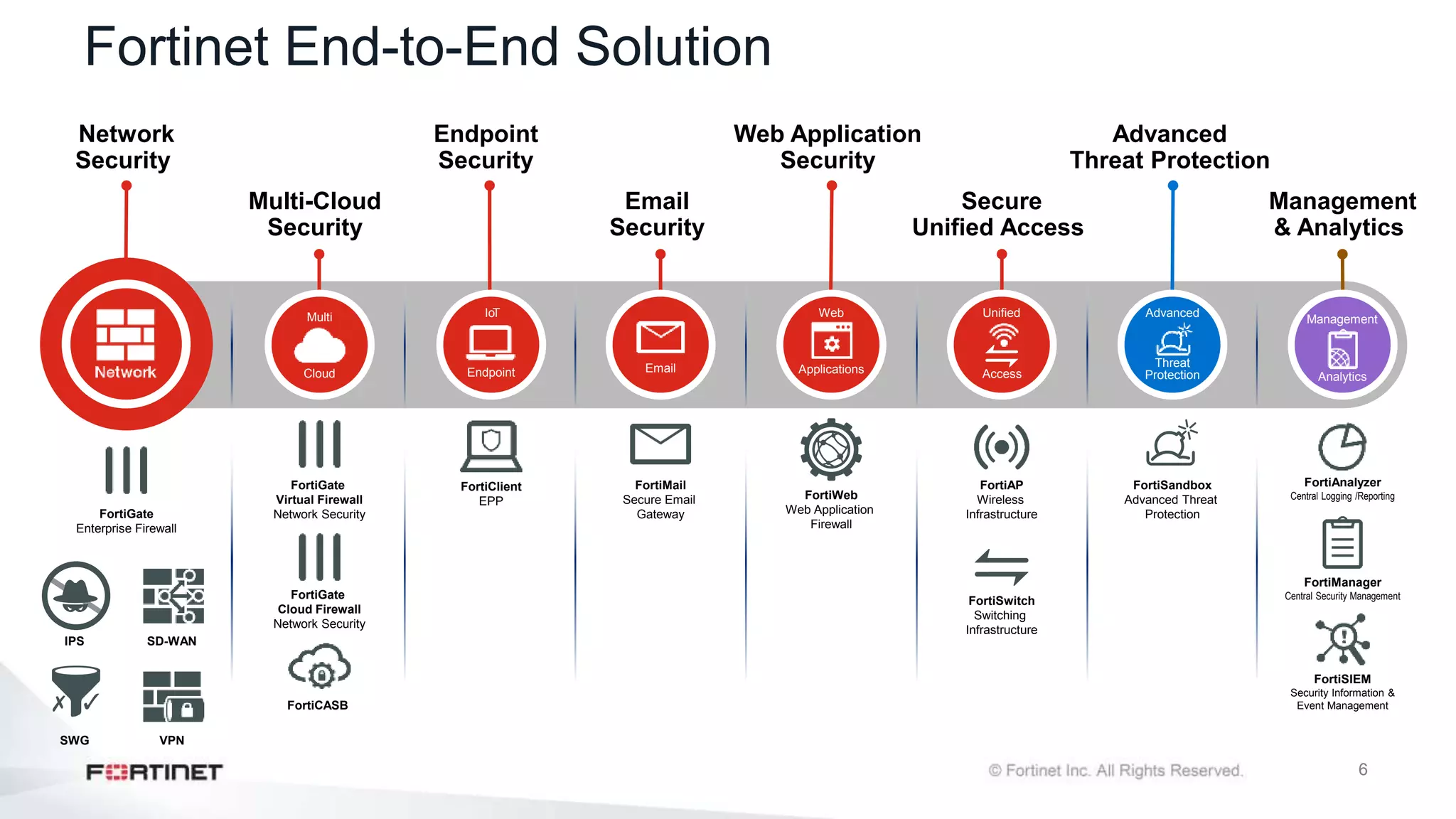
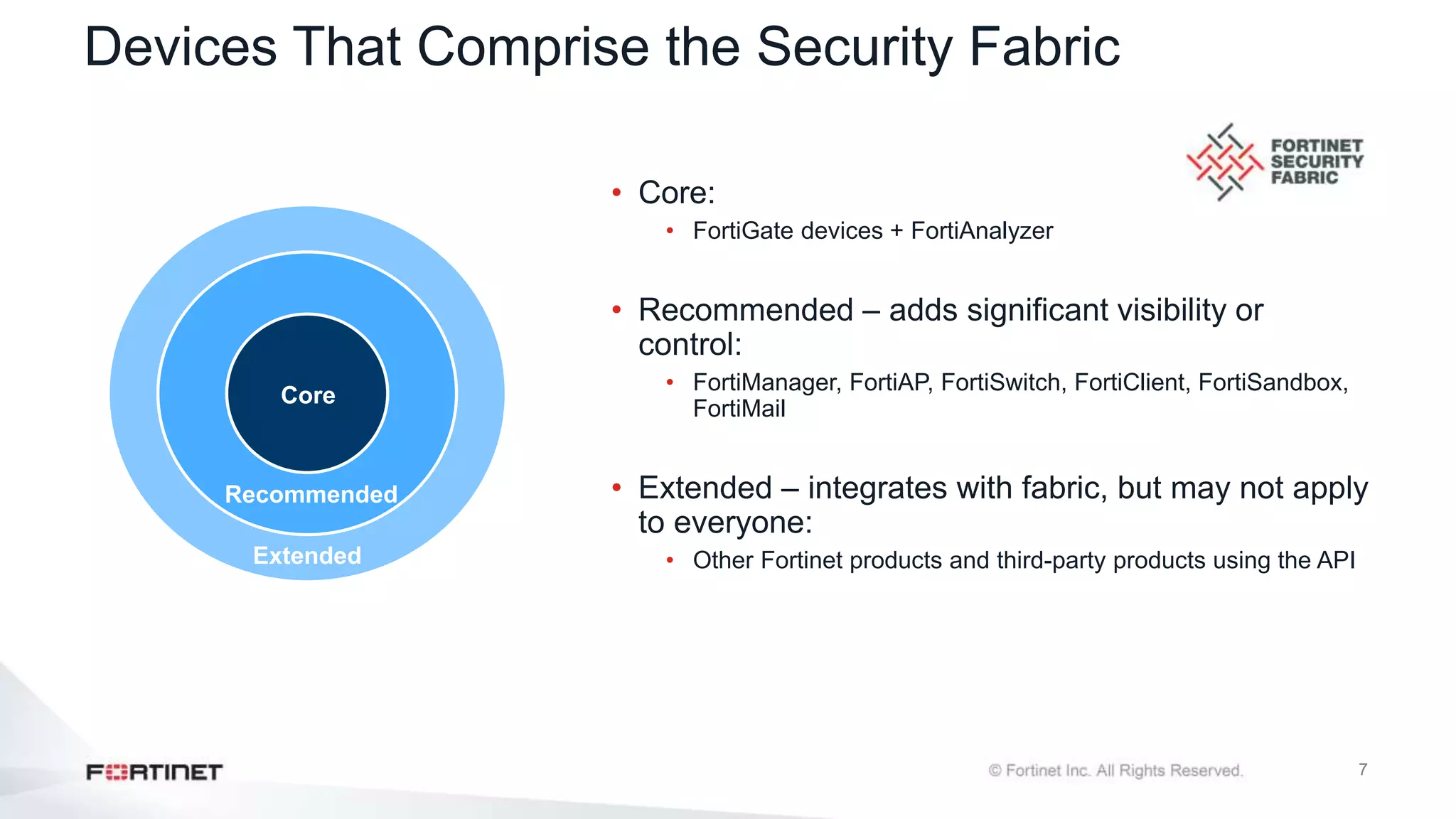
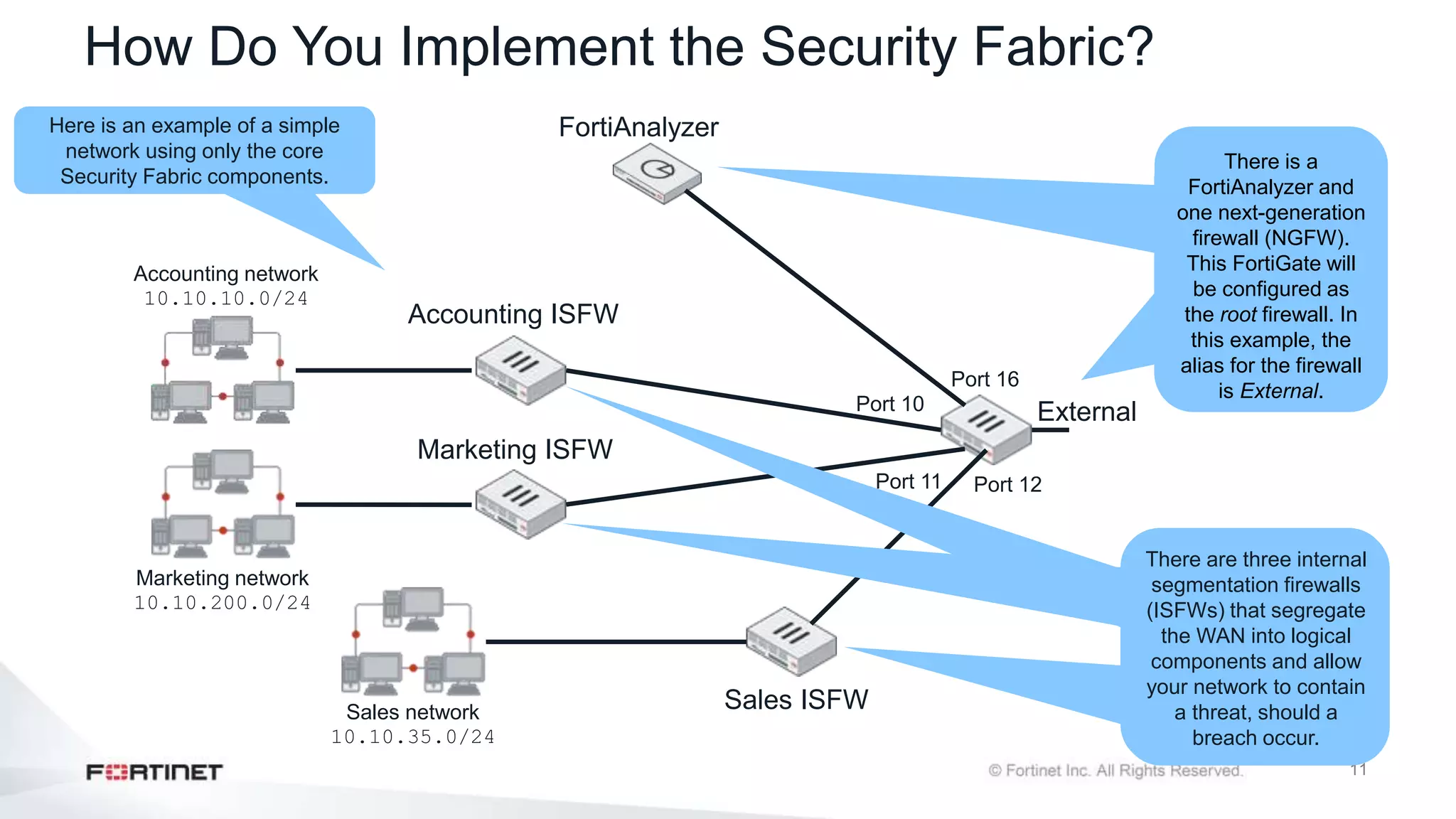
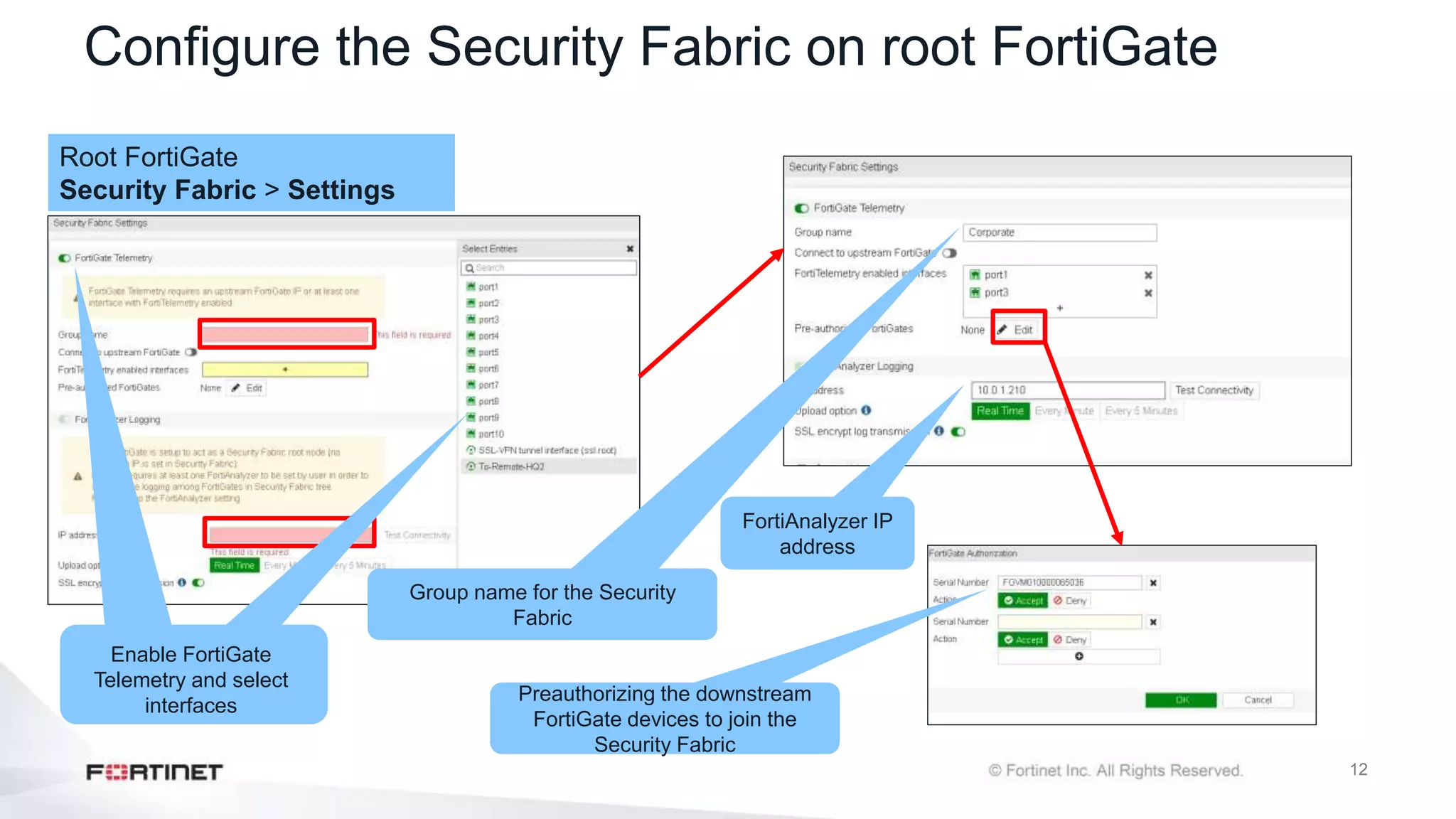
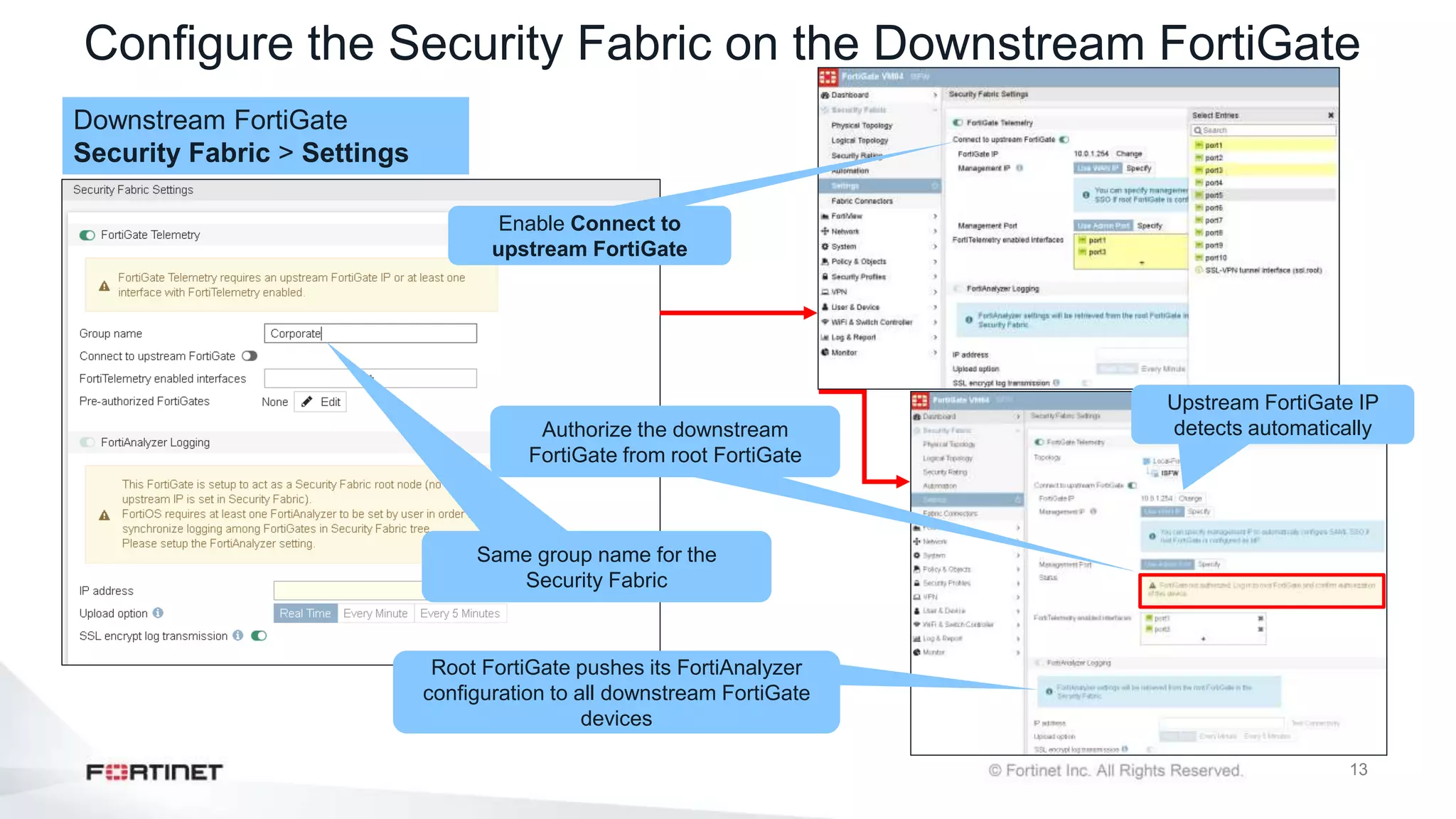
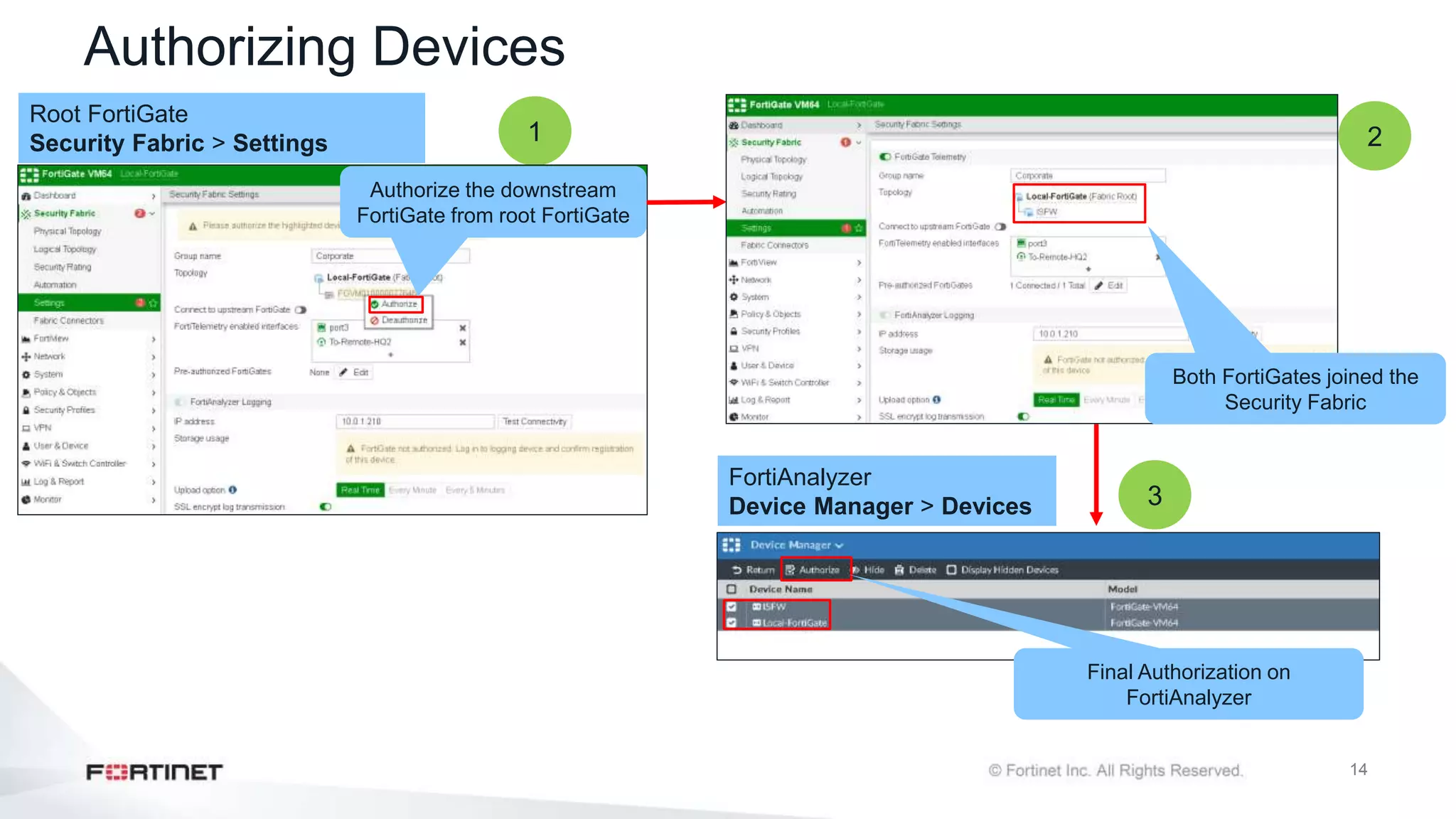
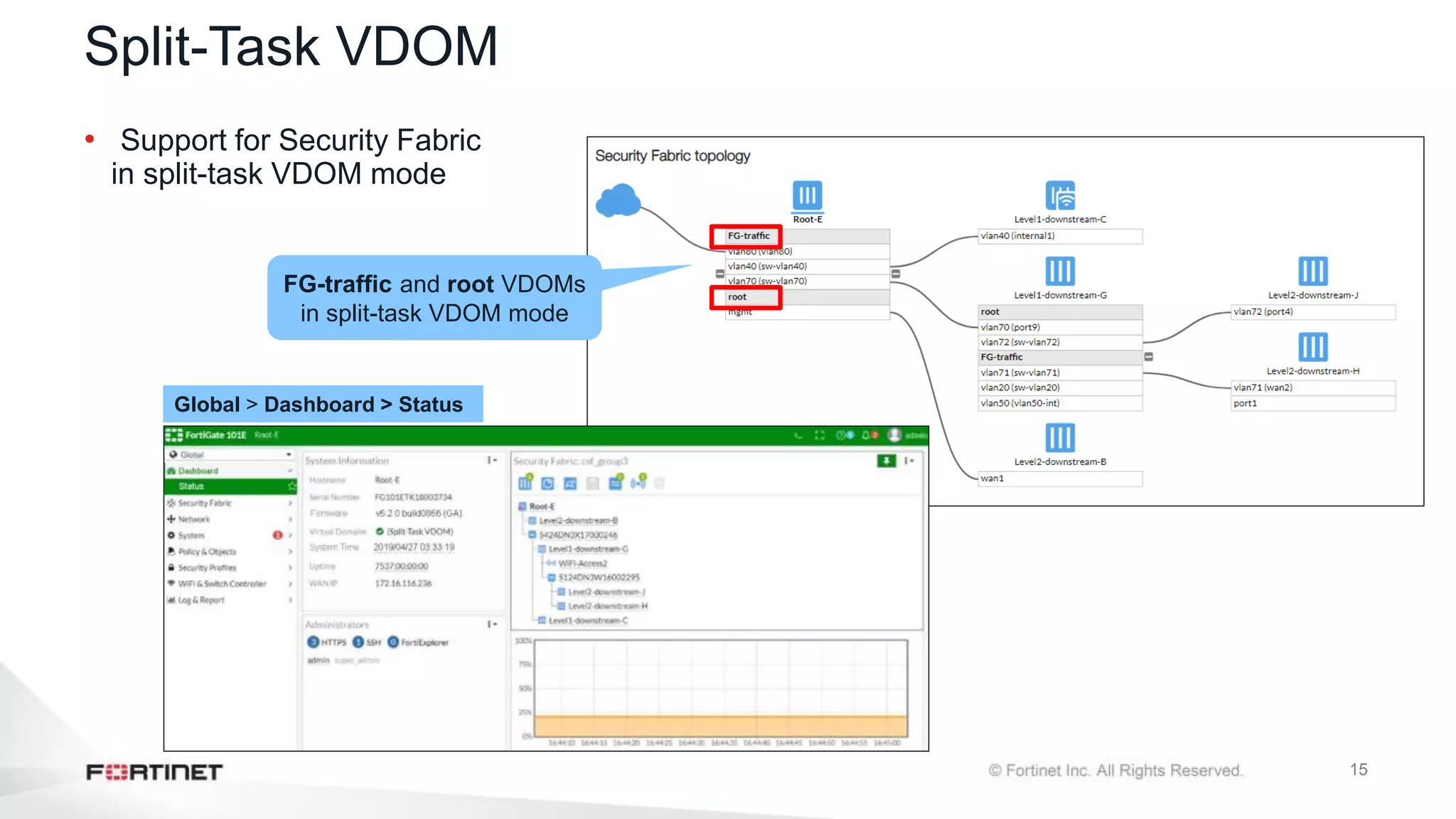
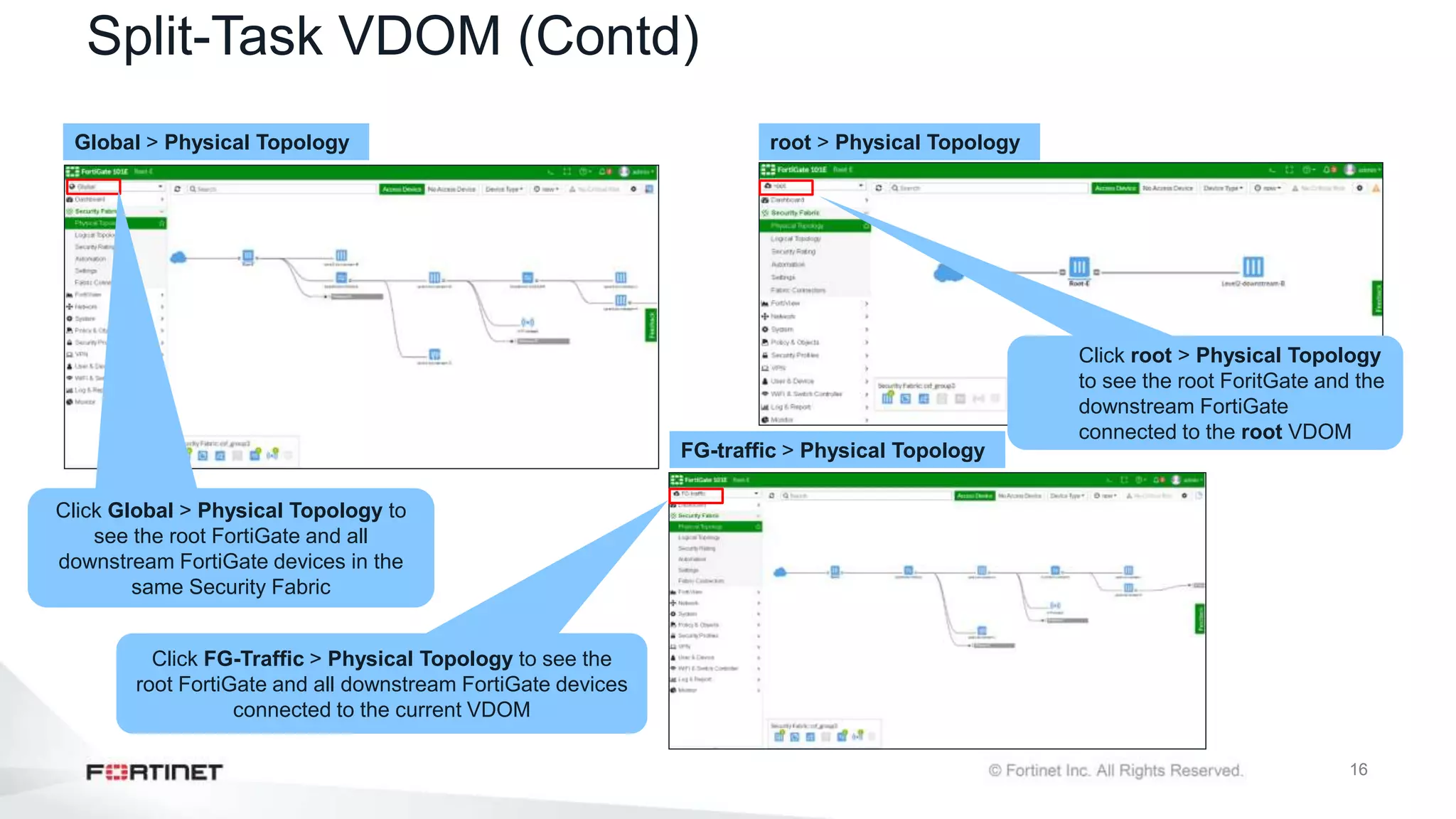
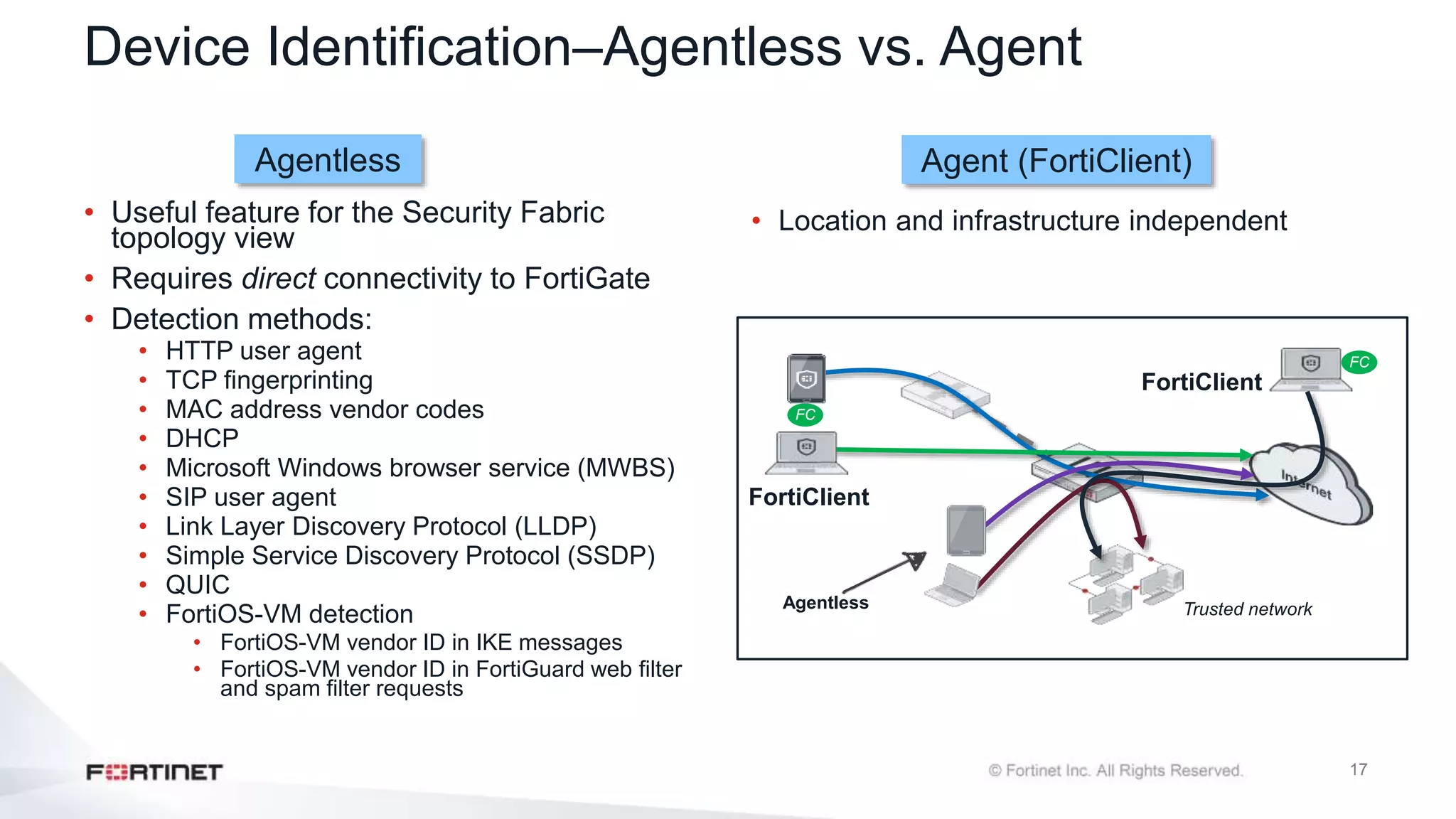
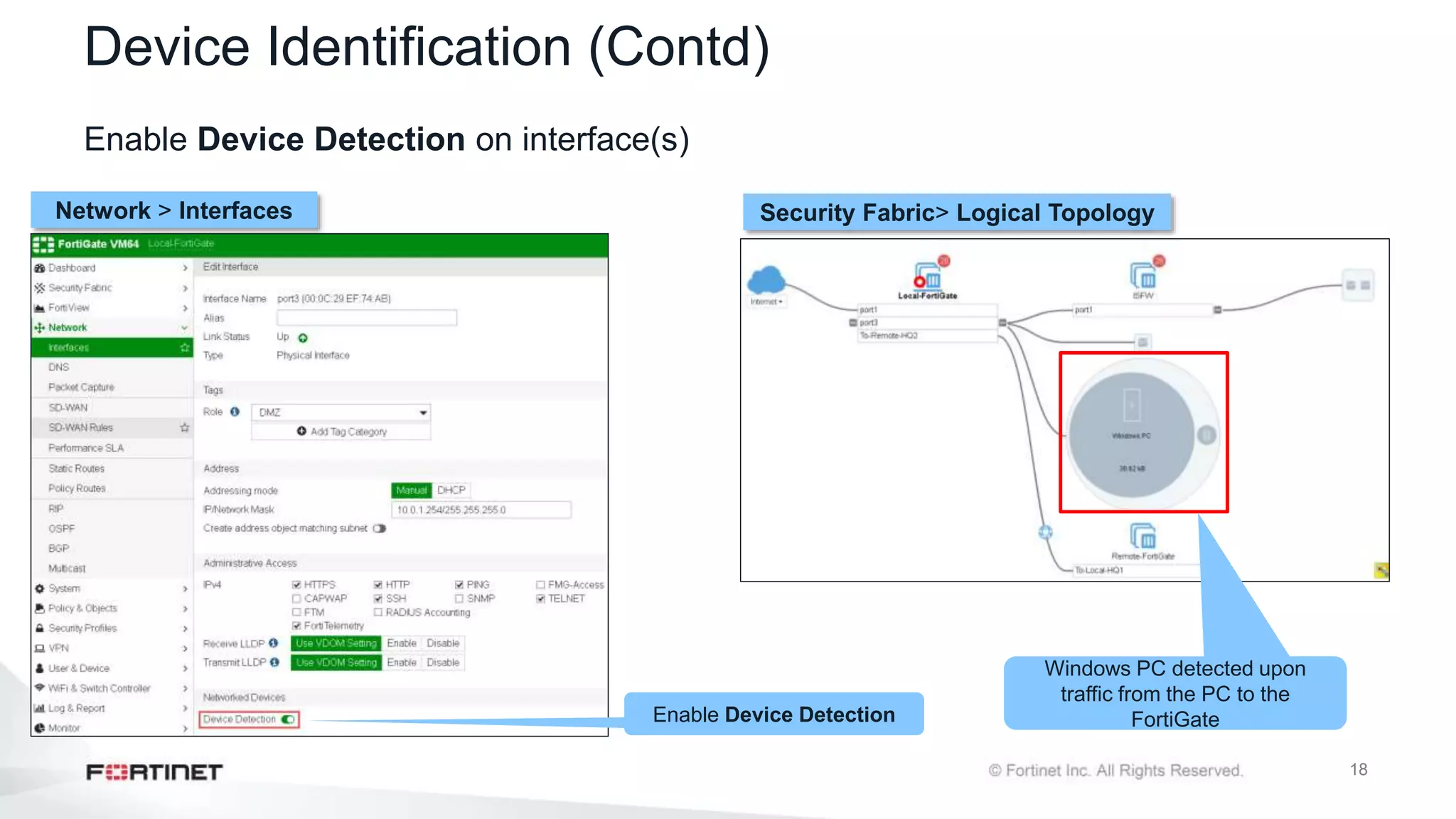
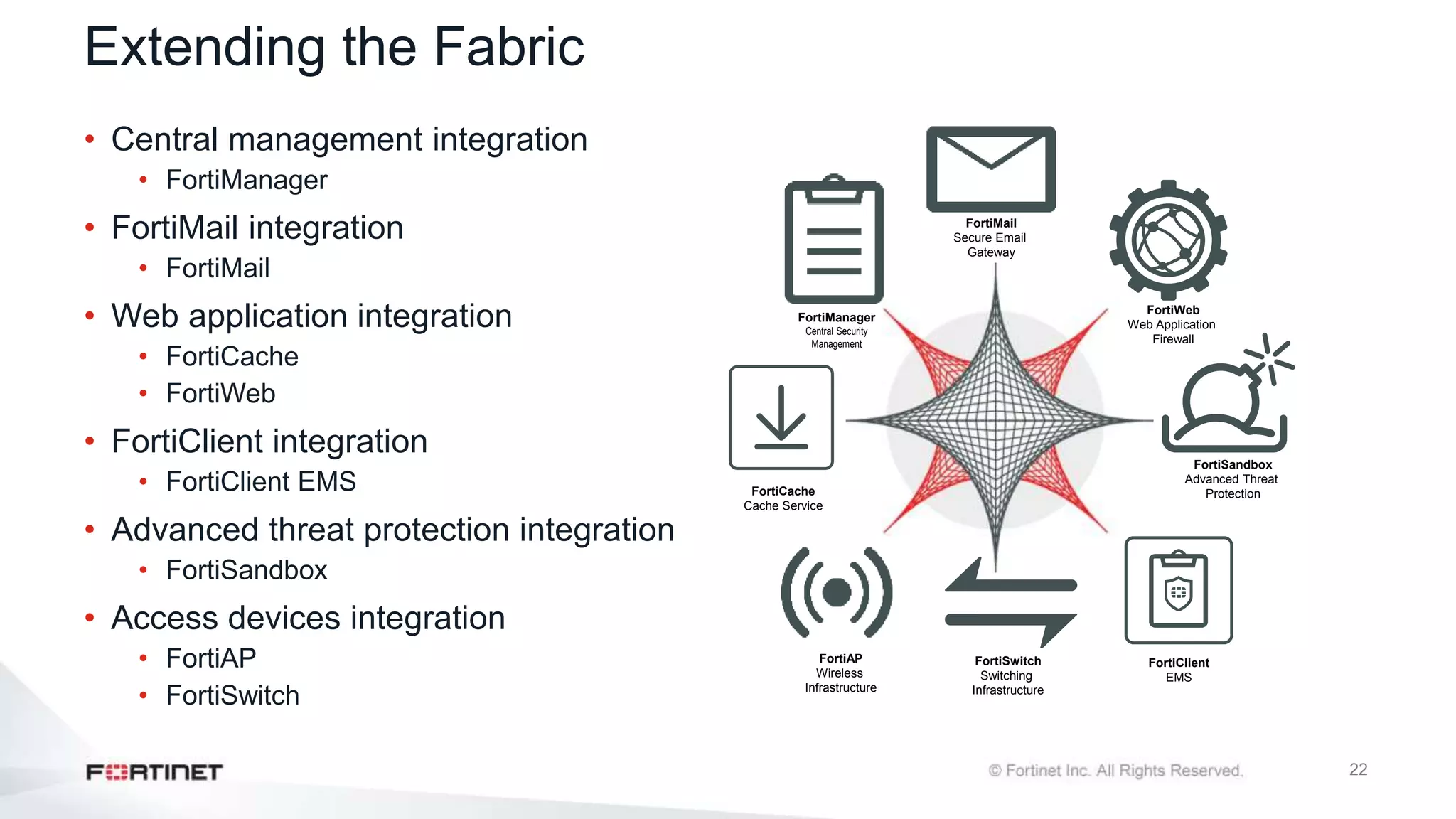
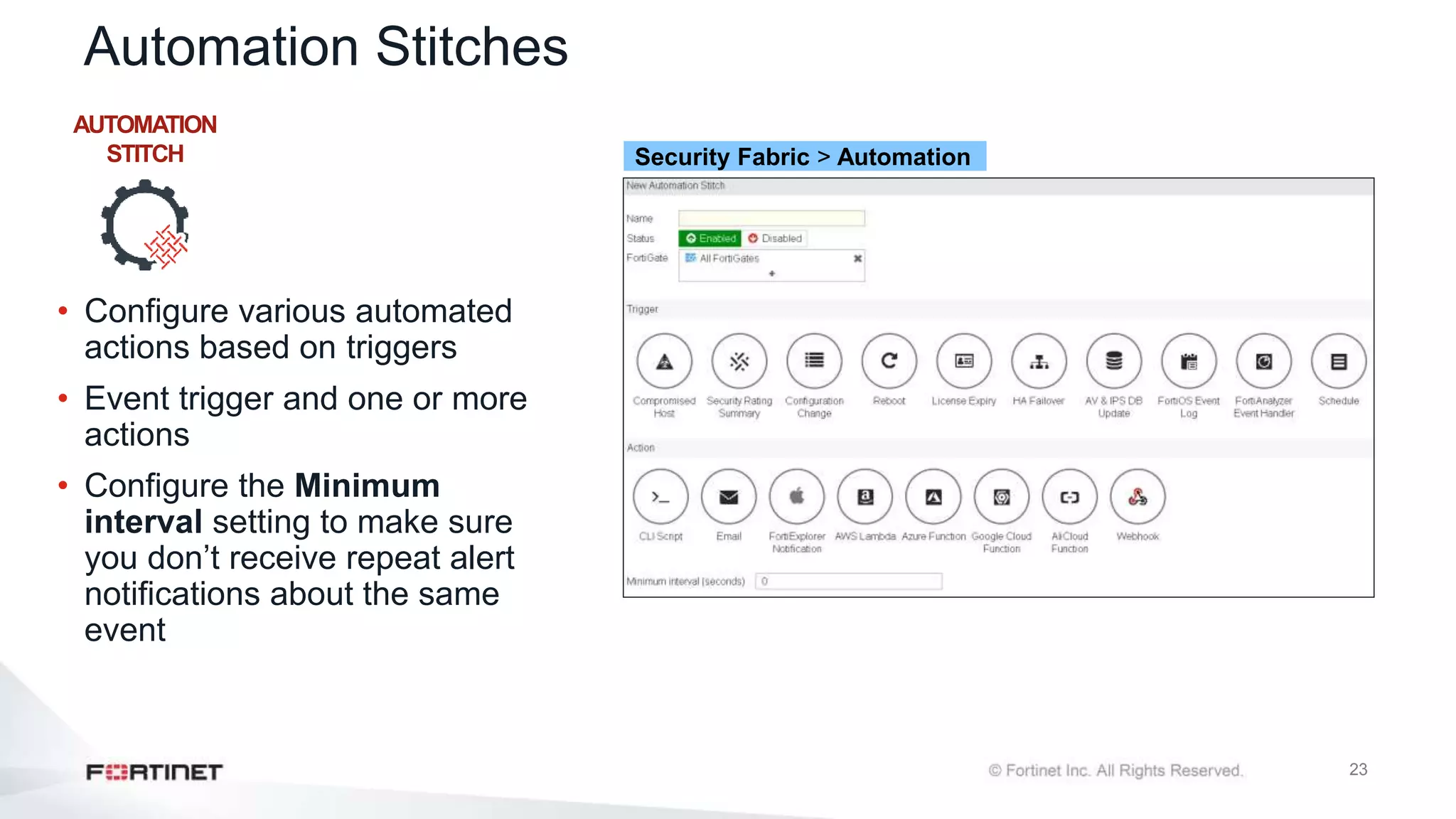
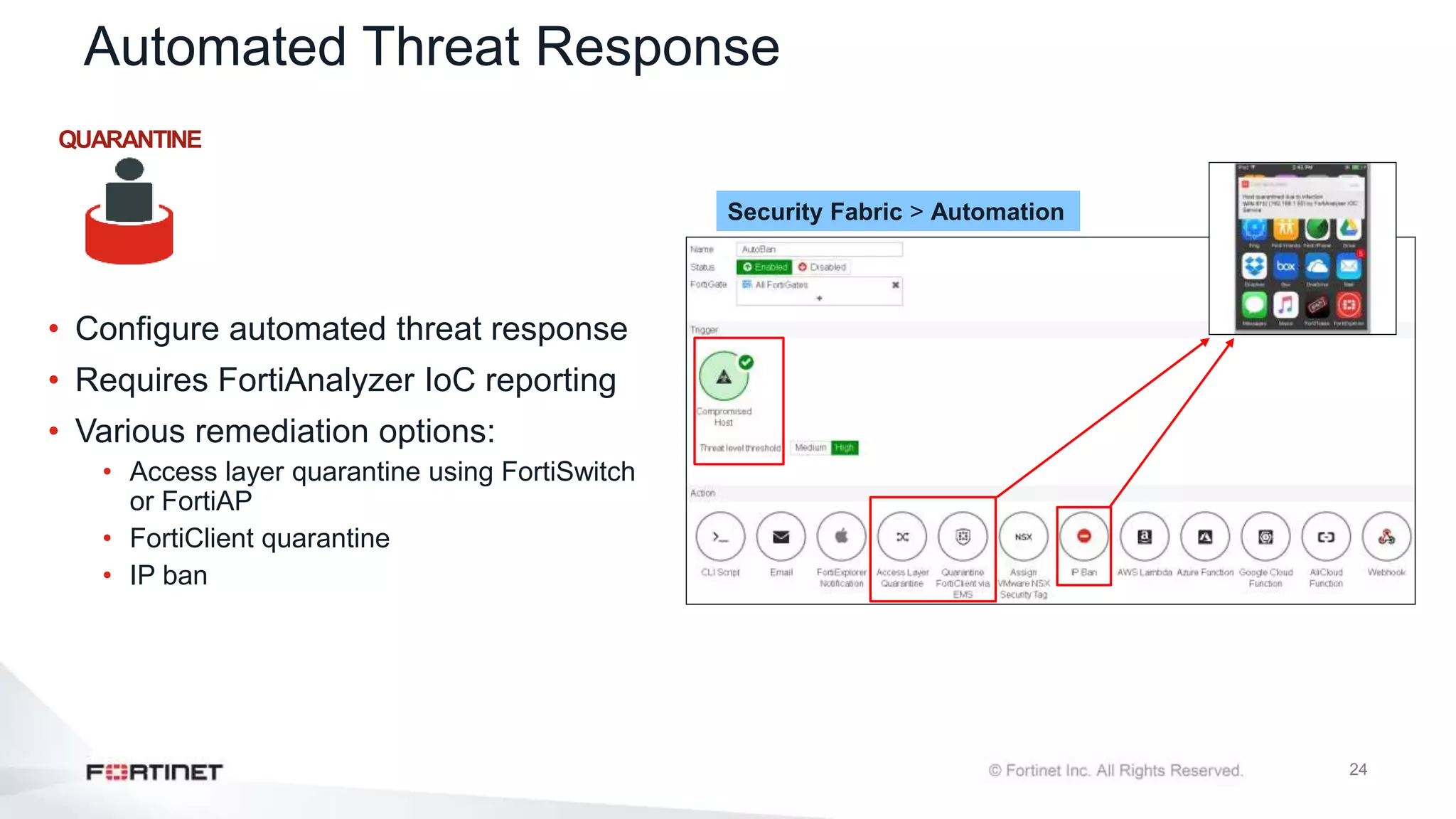
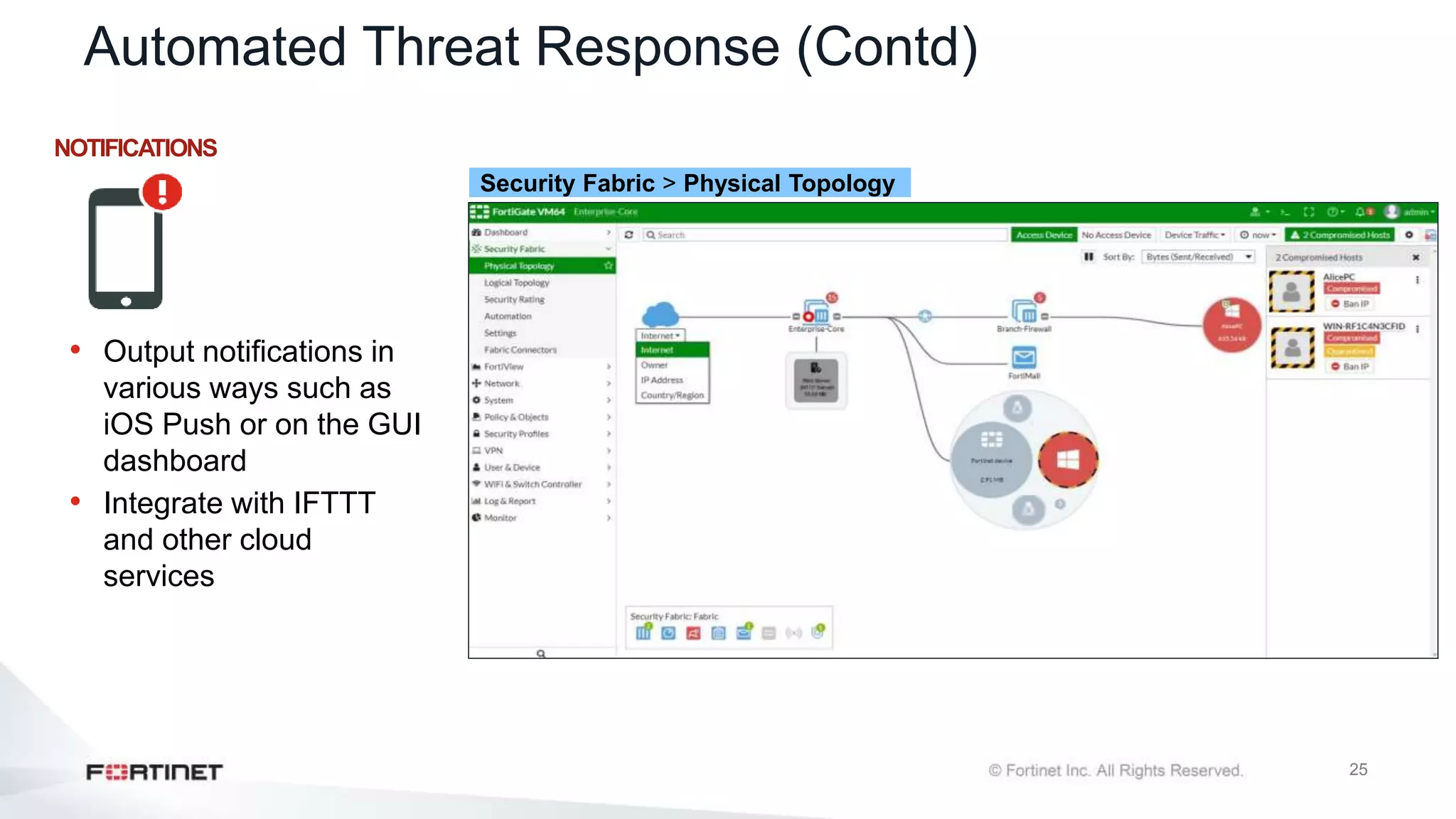
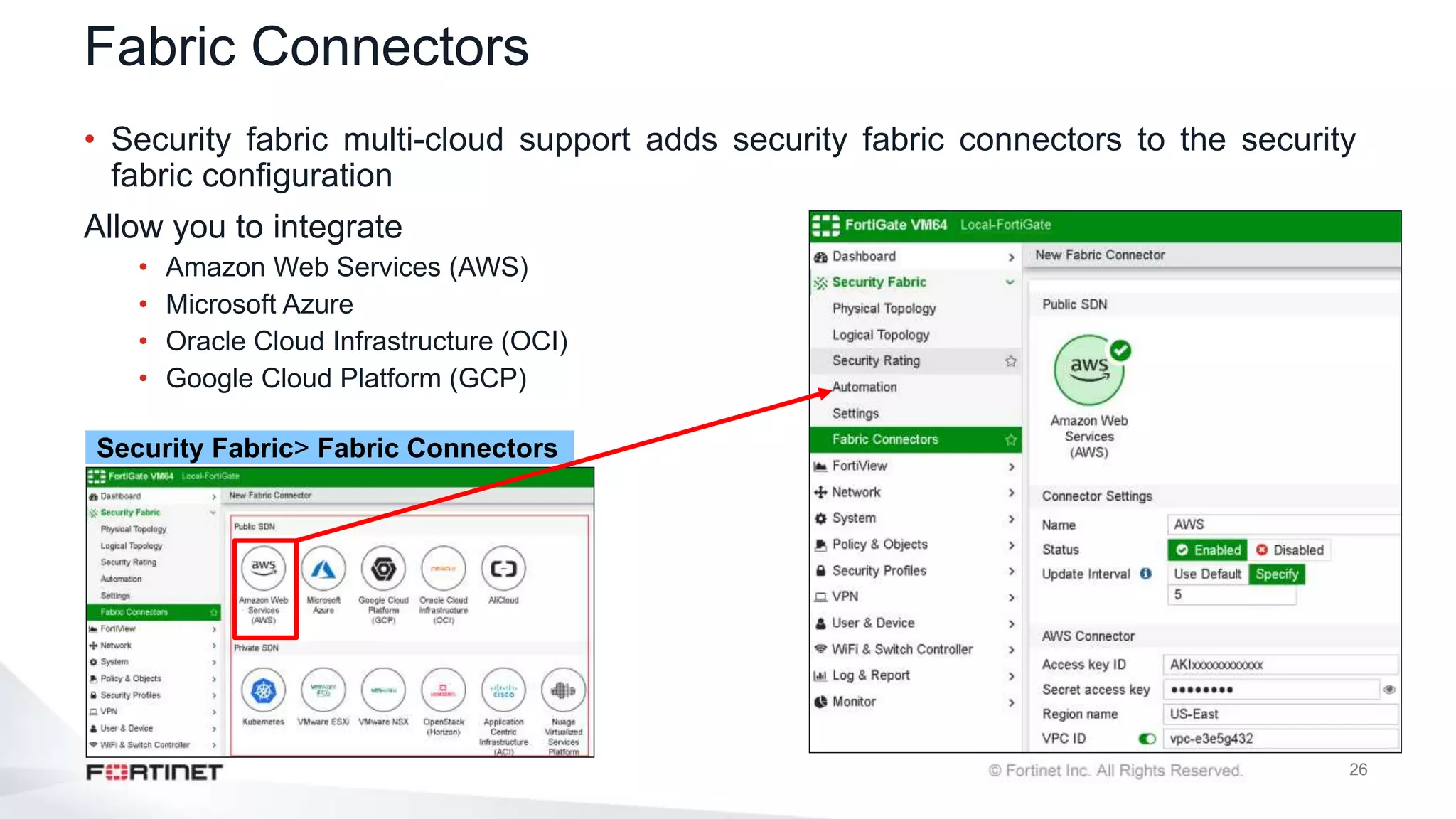
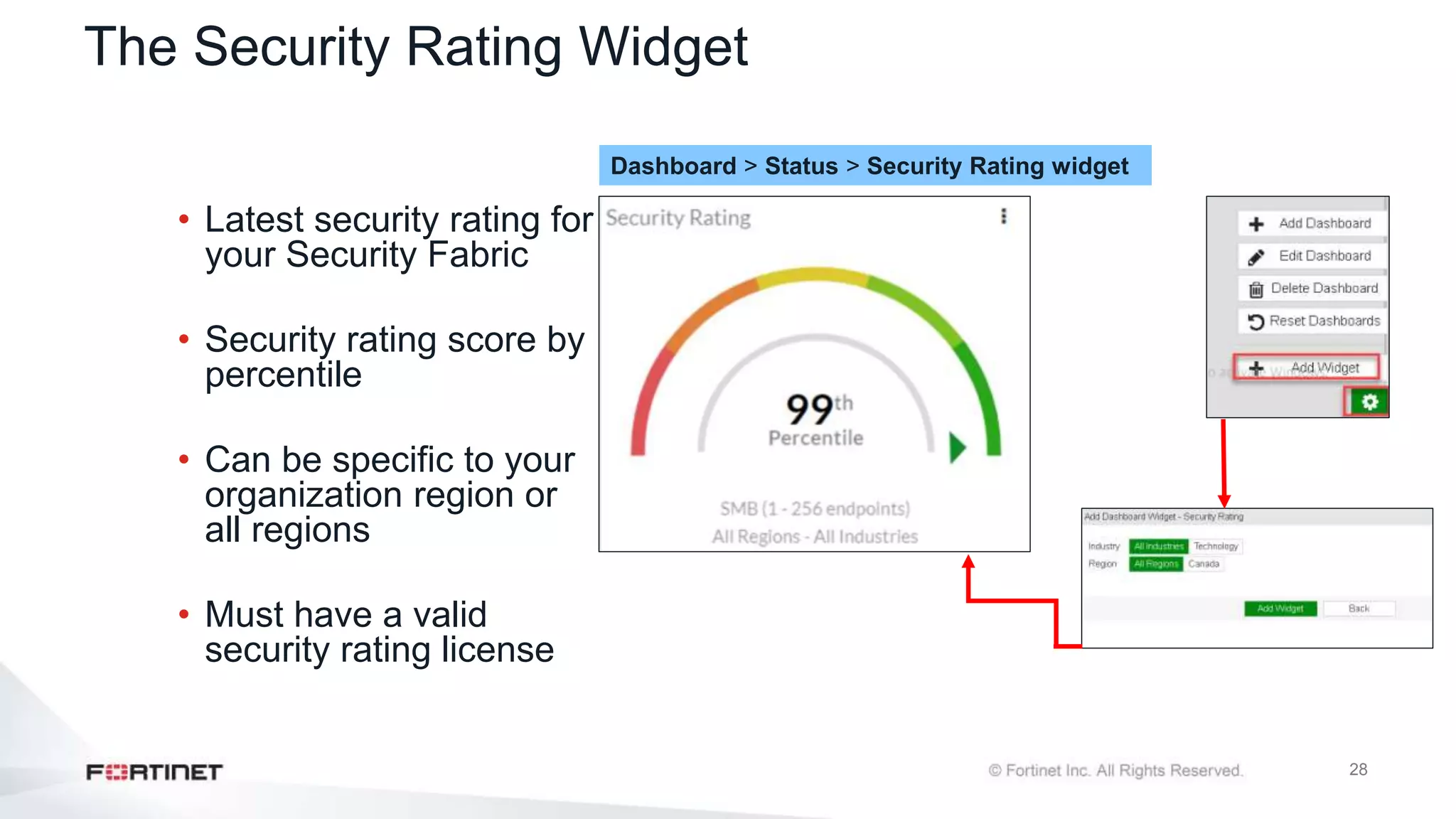
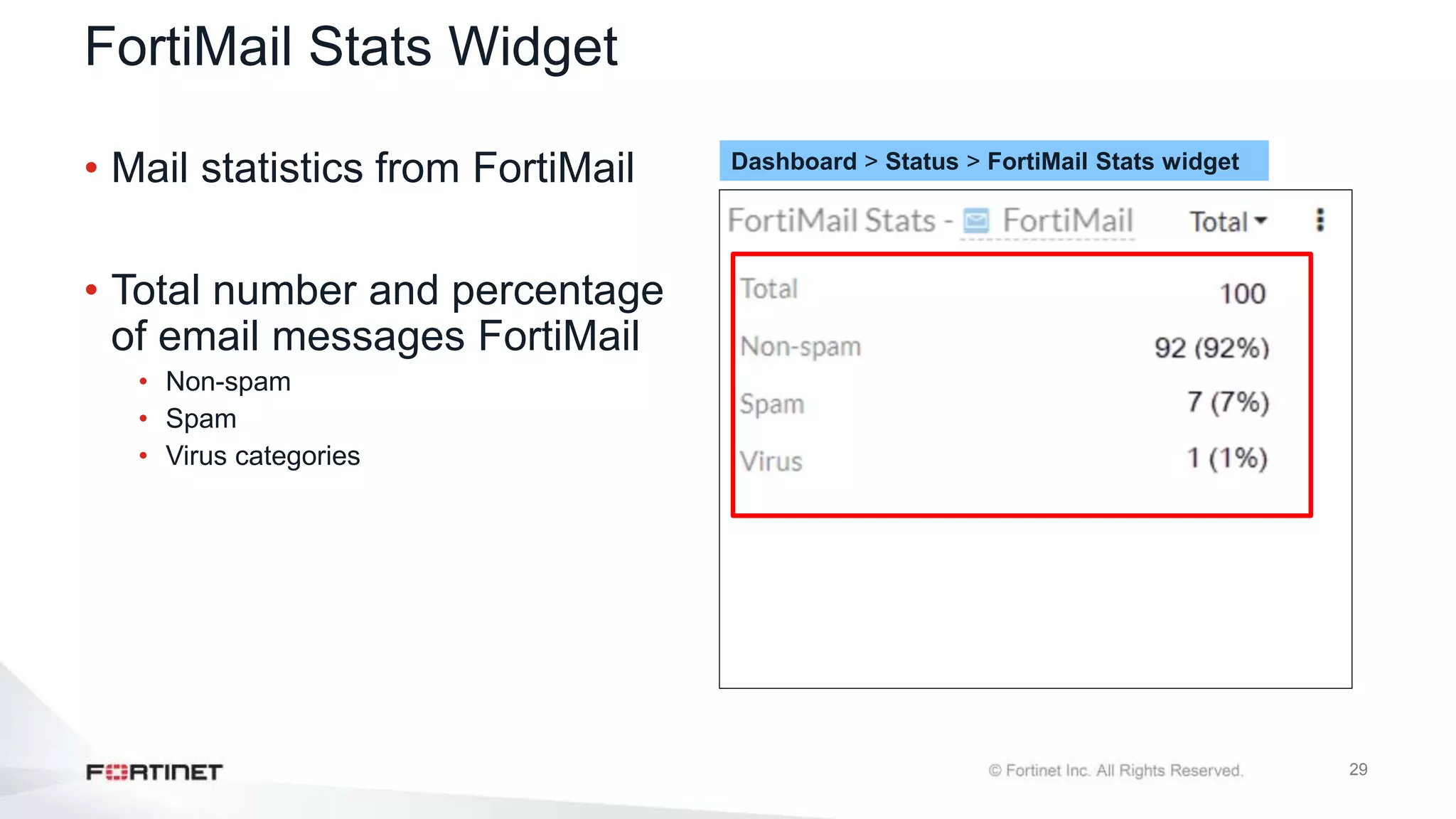
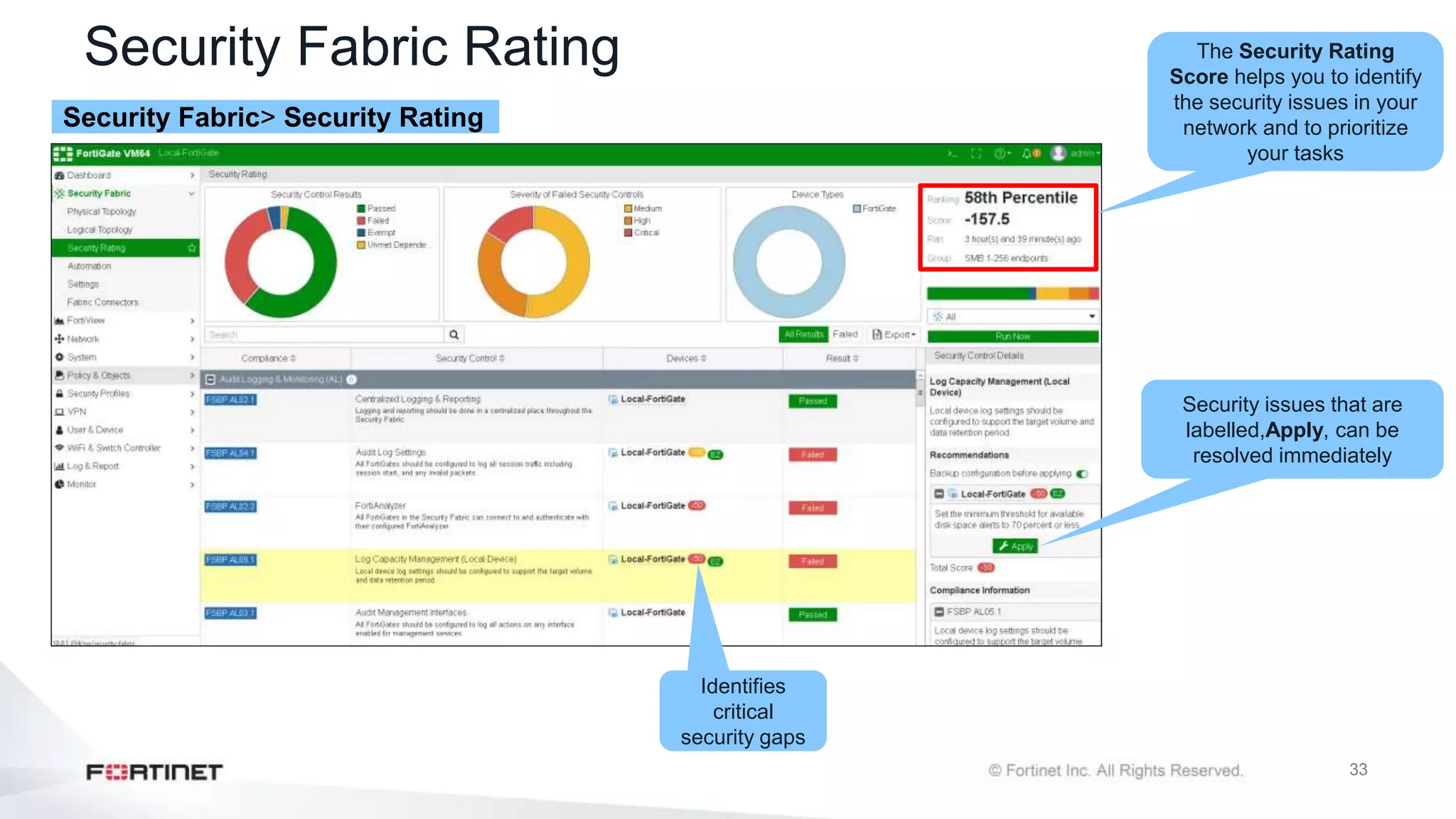
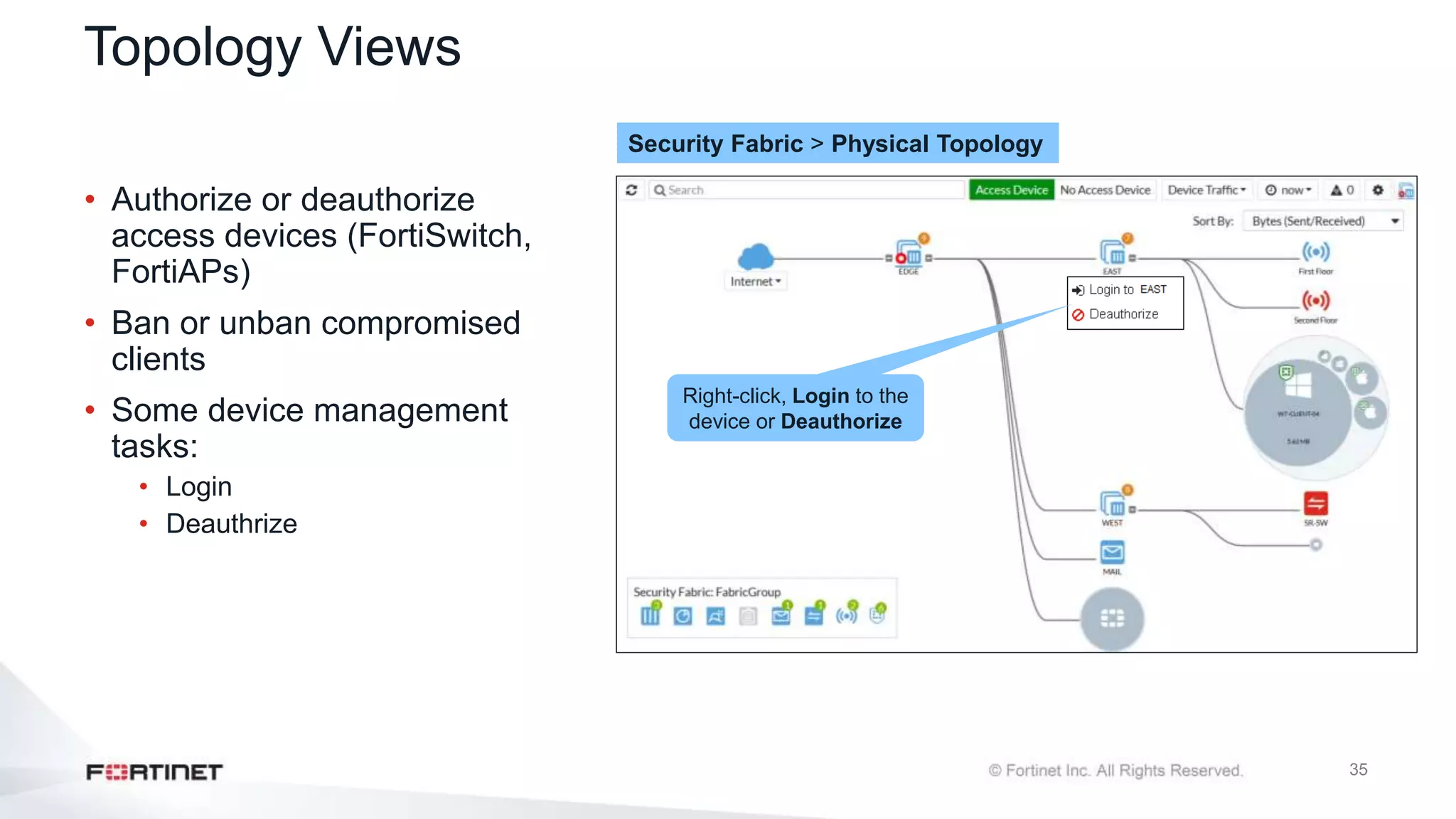
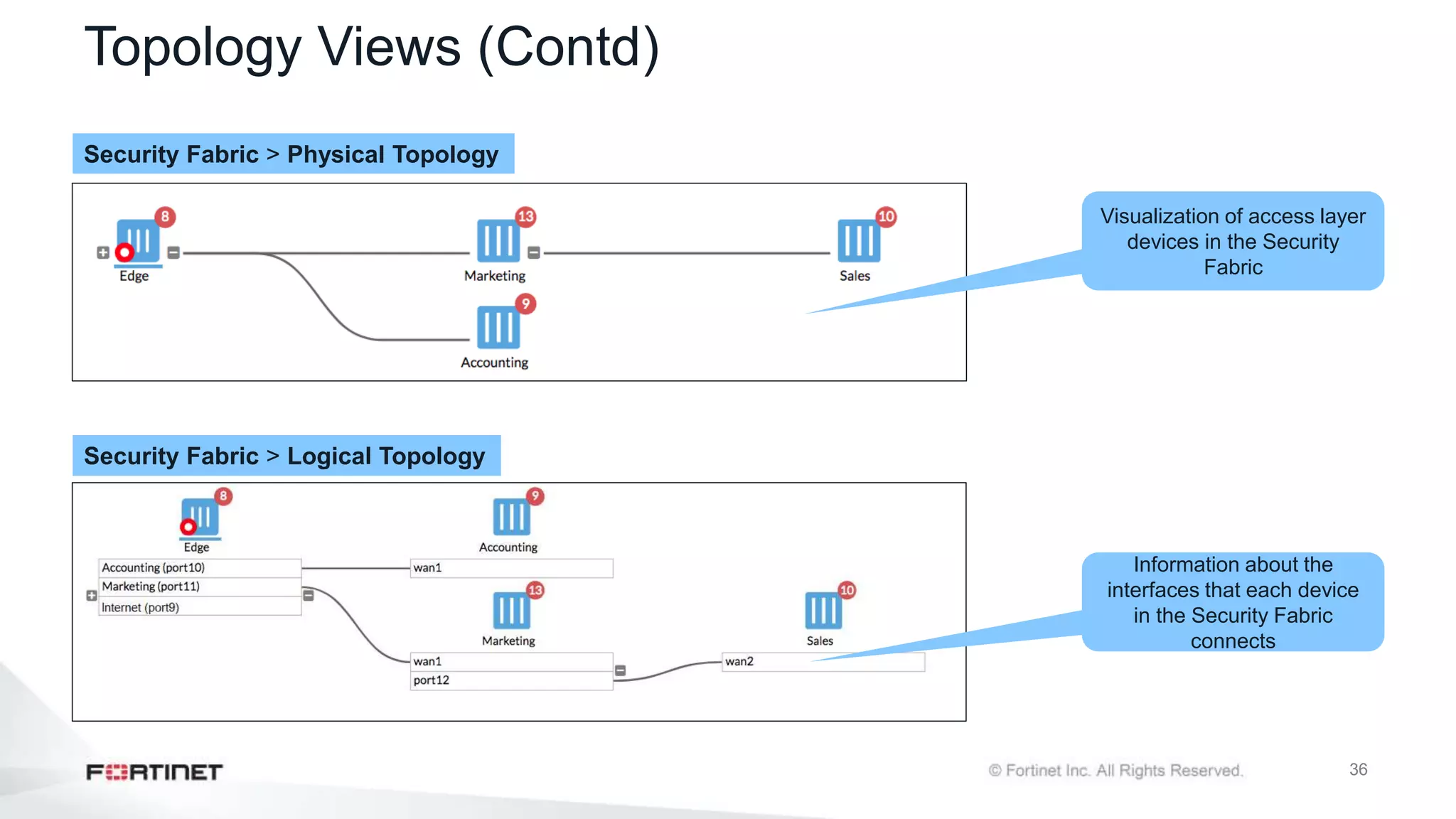
The document outlines the Fortinet Security Fabric, an enterprise solution for holistic network security management that enhances visibility and control across devices. It covers the components, implementation, and features of the security fabric, including device integration, automated threat response, and security rating services. Additionally, it provides guidance on configuring both root and downstream FortiGate devices along with extending the fabric to include various Fortinet and third-party products.