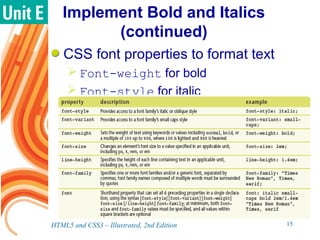
It is important to implement fonts consistently across different user agents using font stacks declared with the font-family property. The span element can be used to isolate text for formatting like bold or italics. Pseudo-elements allow styling of specific portions of an element. Colors can be specified by name, hex, rgb, or hsl values. Shadows are added using text-shadow and box-shadow properties. Media queries group rules by device using values like screen, print, and speech.