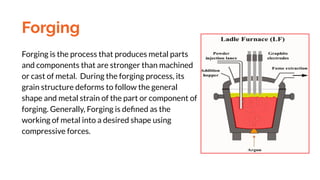
Forging is a metalworking process that creates stronger metal parts by using compressive forces to reshape heated ingots. The process involves several steps including heating, preforming, finish forging, cooling, and finishing, which helps optimize the metal's grain structure and strength. Additionally, surface treatments may be applied to enhance resistance to corrosion and improve aesthetics.