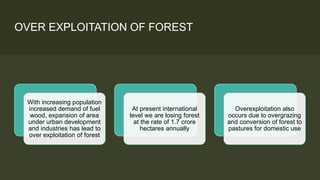
1. Forests provide many important resources but are facing overexploitation and deforestation due to increasing population and land usage.
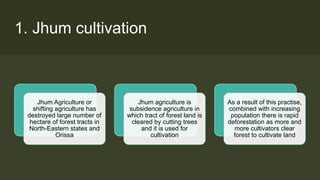
2. Case studies from Northeast India, the Chipko movement, and Western Himalayas show how shifting cultivation, commercial logging, and infrastructure development can degrade forests.
3. Sustainable forest management and conservation efforts are needed to protect these vital ecosystems and resources for the future.